matrix_norm
Computes various norms of a rectangular matrix.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_matrix_norm (int m, int n, float a[], ..., 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_matrix_norm.
Required Arguments
int m (Input)
The number of rows in matrix A.
int n (Input)
The number of columns in matrix A.
float a[] (Input)
Matrix for which the norm will be computed.
Return Value
The requested norm of the input matrix. If the norm cannot be computed, NaN is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_matrix_norm (int m, int n, float a[],
IMSL_ONE_NORM,
IMSL_INF_NORM,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ONE_NORM,
Compute the 1-norm of matrix A,
IMSL_INF_NORM,
Compute the infinity norm of matrix A,
Description
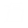
By default, imsl_f_matrix_norm computes the Frobenius norm
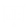
If the option IMSL_ONE_NORM is selected, the 1-norm
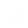
is returned. If the option IMSL_INF_NORM is selected, the infinity norm
is returned.
Example
Compute the Frobenius norm, infinity norm, and one norm of matrix A.
#include <imsl.h>
int main()
{
float a[] = {1.0, 2.0, -2.0, 3.0,
-2.0, 1.0, 3.0, 0.0,
0.0, 3.0, 1.0, -7.0,
5.0, -2.0, 7.0, 6.0,
4.0, 3.0, 4.0, 0.0};
int m = 5, n = 4;
float frobenius_norm, inf_norm, one_norm;
frobenius_norm = imsl_f_matrix_norm(m, n, a, 0);
inf_norm = imsl_f_matrix_norm(m, n, a, IMSL_INF_NORM, 0);
one_norm = imsl_f_matrix_norm(m, n, a, IMSL_ONE_NORM, 0);
printf("Frobenius norm = %f\n", frobenius_norm);
printf("Infinity norm = %f\n", inf_norm);
printf("One norm = %f\n", one_norm);
}
Output
Frobenius norm = 15.684387
Infinity norm = 20.000000
One norm = 17.000000