Evaluates a sequence of Bessel functions of the first kind with real order and complex arguments.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
f_complex *imsl_c_bessel_Jx (float xnu, f_complex z, int n, ¼, 0)
The type d_complex function is imsl_z_bessel_Jx.
Required Arguments
float xnu
(Input)
The lowest order desired. The argument xnu must be greater
than −1/2.
f_complex z
(Input)
Argument for which the sequence of Bessel functions is to be
evaluated.
int n
(Input)
Number of elements in the sequence.
Return Value
A pointer to the n values of the function through the series. Element i contains the value of the Bessel function of order xnu + i for i = 0, …, n − 1.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
f_complex
*imsl_c_bessel_Jx (float
xnu,
f_complex
z, int
n
IMSL_RETURN_USER, f_complex
bessel[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_RETURN_USER, f_complex bessel[]
(Output)
Store the sequence of Bessel functions in the user-provided array
bessel[].
Description
The Bessel function Jn(z) is defined to be

This function is based on the code BESSCC of Barnett (1981) and Thompson and Barnett (1987). This code computes Jn(z) from the modified Bessel function In(z), using the following relation, with ρ = eip/2:
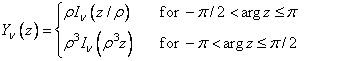
Example
In this example, J0.3+n-1 (1.2 + 0.5i), ν = 1, …, 4 is computed and printed.
#include
<imsl.h>
main()
{
int n = 4;
int i;
float xnu = 0.3;
static f_complex z = {1.2, 0.5};
f_complex *sequence;
sequence =
imsl_c_bessel_Jx(xnu, z, n, 0);
for (i = 0; i < n;
i++)
printf("I sub %4.2f ((%4.2f,%4.2f)) =
(%5.3f,%5.3f)\n",
xnu+i, z.re,
z.im, sequence[i].re, sequence[i].im);
}
Output
I sub 0.30 ((1.20,0.50)) = (0.774,-0.107)
I sub 1.30
((1.20,0.50)) = (0.400,0.159)
I sub 2.30 ((1.20,0.50)) = (0.087,0.092)
I
sub 3.30 ((1.20,0.50)) = (0.008,0.024)
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |