Evaluates Carlson’s elliptic integral of the third kind RJ (x, y, z, r)
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_elliptic_integral_RJ (float x, float y, float z, float rho)
The type double function is imsl_d_elliptic_integral_RJ.
Required Arguments
float x
(Input)
First variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. It must be
nonnegative.
float y
(Input)
Second variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. It must be
nonnegative.
float z
(Input)
Third variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. It must be
positive.
float rho
(Input)
Fourth variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. It must be
positive.
Return Value
The complete elliptic integral RJ (x, y, z, r)
Description
Carlson’s elliptic integral of the third kind is defined to be
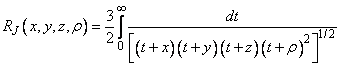
The arguments must be nonnegative. In addition, x + y, x + z, y + z and r must be greater than or equal to (5s)1/3 and less than or equal to 0.3(b/5)1/3, where s = imsl_f_machine(1) is the smallest representable floating-point number. Should any of these conditions fail, imsl_f_elliptic_integral_RJ is set to b = imsl_f_machine(2), the largest floating-point number.
The function imsl_f_elliptic_integral_RJ is based on the code by Carlson and Notis (1981) and the work of Carlson (1979).
Example
The integral RJ (2, 3, 4, 5) is computed.
#include <imsl.h>
main()
{
float x = 2.0;
float y = 3.0;
float z = 4.0;
float rho = 5.0;
float ans;
x =
imsl_f_elliptic_integral_RJ (x, y, z, rho);
printf ("RJ(2,
3, 4, 5) = %f\n", x);
}
Output
RJ(2, 3, 4, 5) = 0.142976
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |