Generates test matrices of class and E(n, c). Returns in band or band symmetric format.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_generate_test_band (int n, int c, ..., 0)
The function imsl_d_generate_test_band is the double precision analogue.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
Number of rows in the matrix.
int c
(Input)
Parameter used to alter structure, also the number of upper/lower
codiagonals.
Return Value
A pointer to a vector of type float. To release this space, use free. If no test was generated, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
void
*imsl_f_generate_sparse_test (int n, int c,
IMSL_SYMMETRIC_STORAGE,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_SYMMETRIC_STORAGE,
Return matrix stored in band
symmetric format.
Description
The same nomenclature as Østerby and Zlatev (1982) is used. Test matrices of class E(n, c), to which we will generally refer to as E-matrices, are symmetric, positive definite matrices of order n with 4 in the diagonal and -1 in the superdiagonal and subdiagonal. In addition there are two bands with -1 at a distance c from the diagonal. More precisely:
|
ai,i = 4 |
0 £ i < n |
|
ai,i+1 = -1 |
0 £ i < n - 1 |
|
ai+1,1 = -1 |
0 £ i < n - 1 |
|
ai,i+c = -1 |
0 £ i < n - c |
|
ai+c,I = -1 |
0 £ i < n - c |
for any n ³ 3 and 2 £ c £ n - 1.
E-matrices are similar to those obtained from the five-point formula in the discretization of elliptic partial differential equations.
By default, imsl_f_generate_test_band returns an E-matrix in band storage mode. Option IMSL_SYMMETRIC_STORAGE returns a matrix in band symmetric storage mode.
Example
This example generates the matrix
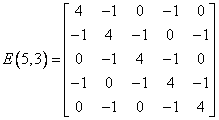
and prints the result.
#include <imsl.h>
main()
{
int n = 5;
int c = 3;
float *a;
a =
imsl_f_generate_test_band (n, c, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("E(5,3) in band storage", 2*c + 1, n,
a, 0);
}
Output
E(5,3) in band storage
1 2 3 4 5
1 0 0 0 -1 -1
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 -1 -1 -1 -1
4 4 4 4 4 4
5 -1 -1 -1 -1 0
6 0 0 0 0 0
7 -1 -1 0 0 0
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |