.p>.CMCH4.DOC!INT_FCN_HYPER_RECT;int_fcn_hyper_rect
Integrate a function on a hyper-rectangle,
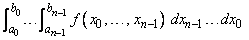
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float
imsl_f_int_fcn_hyper_rect (float
fcn(),
int
ndim,
float
a[],
float
b[], ¼, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_int_fcn_hyper_rect.
Required Arguments
float fcn (int ndim, float x[])
(Input)
User-supplied function to be integrated.
int ndim
(Input)
The dimension of the hyper-rectangle.
float a[]
(Input)
Lower limits of integration.
float b[]
(Input)
Upper limits of integration.
Return Value
The value of
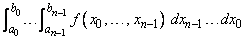
is returned. If no value can be computed, then NaN is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
imsl_f_int_fcn_hyper_rect (float
fcn(),
int
ndim,
float
a[],
float
b[],
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float
err_abs,
IMSL_ERR_REL, float
err_rel,
IMSL_ERR_EST, float
*err_est,
IMSL_MAX_EVALS, int
max_evals,
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float
fcn(),
void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float err_abs
(Input)
Absolute accuracy desired.
Default: 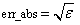
where ɛ is the machine precision
IMSL_ERR_REL, float err_rel
(Input)
Relative accuracy desired.
Default: 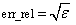
where ɛ is the machine precision
IMSL_ERR_EST, float *err_est
(Output)
Address to store an estimate of the absolute value of the error.
IMSL_MAX_EVALS, int max_evals
(Input)
Number of evaluations allowed.
Default: max_evals = 32n.
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float fcn
(int
ndim,
float
x[],
void
*data),
void
*data (Input)
User supplied function to be integrated, which also
accepts a pointer to data that is supplied by the user. data is a pointer
to the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the Introduction, Passing Data to
User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of this manual for more
details.
Description
The function imsl_f_int_fcn_hyper_rect approximates the n-dimensional iterated integral
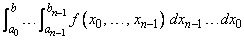
An estimate of the error is returned in the optional argument err_est. The approximation is achieved by iterated applications of product Gauss formulas. The integral is first estimated by a two-point tensor product formula in each direction. Then for i = 1, ¼, n, the function calculates a new estimate by doubling the number of points in the i-th direction, then halving the number immediately afterwards if the new estimate does not change appreciably. This process is repeated until either one complete sweep results in no increase in the number of sample points in any dimension; the number of Gauss points in one direction exceeds 256; or the number of function evaluations needed to complete a sweep exceeds max_evals.
Example
In this example, we compute the integral of

on an expanding cube. The values of the error estimates are machine dependent. The exact integral over R3 is π3/2.
#include <math.h>
#include
<imsl.h>
float
fcn(int n, float x[]);
main()
{
int i, j, ndim =
3;
float q, limit,
a[3], b[3];
printf("
integral limit \n");
limit = pow(imsl_f_constant("pi",0),
1.5);
/* Evaluate the integral */
for (i = 0; i <
6; i++) {
for (j = 0; j <
3; j++)
{
a[j] =
-(i+1)/2.;
b[j] = (i+1)/2.;
}
q = imsl_f_int_fcn_hyper_rect
(fcn, ndim, a, b,
0);
/* Print the result and the
*/
/* limiting answer */
printf(" %10.3f %10.3f\n",
q, limit);
}
}
float fcn(int n, float
x[])
{
float
s;
s = x[0]*x[0] + x[1]*x[1] +
x[2]*x[2];
return exp(-s);
}
Output
integral limit
0.785
5.568
3.332
5.568
5.021
5.568
5.491
5.568
5.561
5.568
5.568 5.568
Warning Errors
IMSL_MAX_EVALS_TOO_LARGE The argument max_evals was set greater than 28n.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_NOT_CONVERGENT The maximum number of function evaluations has been reached, and convergence has not been attained.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |