Solves a complex general system of linear equations Ax = b. Using optional arguments, any of several related computations can be performed. These extra tasks include computing the LU factorization of A using partial pivoting, computing the inverse matrix A-1, solving AHx = b, or computing the solution of Ax = b given the LU factorization of A.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
f_complex *imsl_c_lin_sol_gen (int n, f_complex a[], f_complex b[], …, 0)
The type d_complex procedure is imsl_z_lin_sol_gen.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
Number of rows and columns in the matrix.
f_complex a[]
(Input)
Array of size n × n containing the
matrix.
f_complex b[]
(Input)
Array of length n containing the right-hand side.
Return Value
A pointer to the solution x of the linear system Ax = b. To release this space, use free. If no solution was computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
f_complex
*imsl_c_lin_sol_gen (int
n, f_complex
a[],
f_complex b[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int
a_col_dim,
IMSL_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, f_complex
x[],
IMSL_FACTOR, int
**p_pvt,
f_complex
**p_factor,
IMSL_FACTOR_USER, int
pvt[],
f_complex
factor[],
IMSL_FAC_COL_DIM, int
fac_col_dim,
IMSL_INVERSE, f_complex
**p_inva,
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, f_complex
inva[],
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
inva_col_dim,
IMSL_CONDITION, float
*cond,
IMSL_FACTOR_ONLY,
IMSL_SOLVE_ONLY,
IMSL_INVERSE_ONLY,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array a.
Default: a_col_dim = n
IMSL_TRANSPOSE
Solve
AHx = b
Default:
Solve Ax = b
IMSL_RETURN_USER, f_complex x[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of length n containing the solution
x.
IMSL_FACTOR, int **p_pvt, f_complex **p_factor (Output)
p_pvt: The address of a pointer to an array of length n containing the pivot sequence for the factorization. On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_c_lin_sol_gen. Typically, int *p_pvt is declared, and &p_pvt is used as an argument.
p_factor: The address of a pointer to an array of size n × n containing the LU factorization of A with column pivoting. On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_c_lin_sol_gen. The lower-triangular part of this array contains information necessary to construct L, and the upper-triangular part contains U. Typically, f_complex *p_factor is declared, and &p_factor is used as an argument.
IMSL_FACTOR_USER, int pvt[], f_complex factor[] (Input/Output)
pvt[]: A user-allocated array of size n containing the pivot sequence for the factorization.
factor[]: A user-allocated array of size n × n containing the LU factorization of A. The lower-triangular part of this array contains information necessary to construct L, and the upper-triangular part contains U.
These parameters are input if IMSL_SOLVE is specified. They are output otherwise. If A is not needed, factor and a can share the same storage.
IMSL_FAC_COL_DIM, int
fac_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of the array
containing the LU factorization of A.
Default: fac_col_dim = n
IMSL_INVERSE, f_complex **p_inva
(Output)
The address of a pointer to an array of size
n × n containing the inverse of the matrix A. On
return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_c_lin_sol_gen.
Typically, f_complex *p_inva is declared,
and &p_inva
is used as an argument.
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, f_complex inva[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size n × n
containing the inverse of A.
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
inva_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of the array
containing the inverse of A.
Default: inva_col_dim = n
IMSL_CONDITION, float *cond
(Output)
A pointer to a scalar containing an estimate of the L1 norm condition
number of the matrix A. Do not use this option with IMSL_SOLVE_ONLY.
IMSL_FACTOR_ONLY
Compute
the LU factorization of A with partial pivoting. If IMSL_FACTOR_ONLY is
used, either IMSL_FACTOR or IMSL_FACTOR_USER
is required. The argument b is then ignored, and
the returned value of imsl_c_lin_sol_gen is
NULL.
IMSL_SOLVE_ONLY
Solve
Ax = b given the LU factorization previously
computed by imsl_c_lin_sol_gen. By
default, the solution to Ax = b is pointed to by imsl_c_lin_sol_gen. If
IMSL_SOLVE_ONLY
is used, argument IMSL_FACTOR_USER is
required and argument a is ignored.
IMSL_INVERSE_ONLY
Compute
the inverse of the matrix A. If IMSL_INVERSE_ONLY is
used, either IMSL_INVERSE or IMSL_INVERSE_USER is
required. Argument b is then ignored, and
the returned value of imsl_c_lin_sol_gen is
NULL.
Description
The function imsl_c_lin_sol_gen solves a system of linear algebraic equations with a complex coefficient matrix A. It first computes the LU factorization of A with partial pivoting such that L-1A = U. The matrix U is upper-triangular, while L-1A ≡ PnLn-1Pn-1 …L1P1A ≡ U. The factors Pi and Li are defined by the partial pivoting. Each Pi is an interchange of row i with row j ³ i. Thus, Pi is defined by that value of j. Every
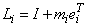
is an elementary elimination matrix. The vector mi is zero in entries 1, …, i. This vector is stored in the strictly lower-triangular part of column i of the working array containing the decomposition information.
The solution of the linear system is then found by solving two simpler systems, y = L-1b and x = U -1y. When the solution to the linear system or the inverse of the matrix is computed, an estimate of the L1 condition number of A is computed using the algorithm as in Dongarra et al. (1979). If the estimated condition number is greater than 1∕ɛ (where ɛ is the machine precision), a warning message is issued. This indicates that very small changes in A may produce large changes in the solution x. The function imsl_c_lin_sol_gen fails if U, the upper-triangular part of the factorization, has a zero diagonal element.
Examples
Example 1
This example solves a system of three linear equations. The equations are:
(1 + i) x1 + (2 + 3i) x2 + (3 − 3i) x3 = 3 + 5i
(2 + i) x1 + (5 + 3i) x2 + (7 − 5i) x3 = 22 + 10i
(−2 + i) x1 + (−4 + 4i) x2 + (5 + 3i) x3 = −10 + 4i
#include
<imsl.h>
f_complex a[] = {{1.0, 1.0}, {2.0,
3.0}, {3.0,
-3.0},
{2.0, 1.0}, {5.0, 3.0}, {7.0,
-5.0},
{-2.0, 1.0}, {-4.0, 4.0}, {5.0, 3.0}};
f_complex b[] =
{{3.0, 5.0}, {22.0, 10.0}, {-10.0,
4.0}};
main()
{
int n =
3;
f_complex
*x;
/* Solve Ax = b for x */
x =
imsl_c_lin_sol_gen (n, a, b,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Solution, x, of Ax =
b", 1, n, x, 0);
}
Output
Solution, x, of Ax =
b
1
2
3
(
1, -1)
(
2, 4)
(
3, -0)
Example 2
This example solves the conjugate transpose problem AHx = b and returns the LU factorization of A using partial pivoting. This example differs from the first example in that the solution array is allocated in the main program.
#include
<imsl.h>
f_complex a[] = {{1.0, 1.0},
{2.0, 3.0}, {3.0,
-3.0},
{2.0, 1.0}, {5.0, 3.0}, {7.0,
-5.0},
{-2.0, 1.0}, {-4.0, 4.0}, {5.0,
3.0}};
f_complex b[] = {{3.0, 5.0}, {22.0,
10.0}, {-10.0, 4.0}};
main()
{
int n = 3,
pvt[3];
f_complex
factor[9];
f_complex
x[3];
/* Solve ctrans(A)*x = b for x */
imsl_c_lin_sol_gen (n, a,
b,
IMSL_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_RETURN_USER,
x,
IMSL_FACTOR_USER, pvt,
factor,
0);
/* Print x */
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Solution, x, of
ctrans(A)x = b", 1, n, x,
0);
/* Print factors and pivot sequence */
imsl_c_write_matrix ("LU factors of A", n, n, factor, 0);
imsl_i_write_matrix ("Pivot sequence", 1, n, pvt, 0);
}
Output
Solution, x, of ctrans(A)x =
b
1
2
3
( -9.79, 11.23)
( 2.96, -3.13)
( 1.85,
2.47)
LU factors of
A
1
2
3
1 ( -2.000, 1.000)
( -4.000, 4.000)
( 5.000, 3.000)
2
( 0.600, 0.800)
( -1.200, 1.400)
( 2.200, 0.600)
3
( 0.200, 0.600)
( -1.118, 0.529)
( 4.824, 1.294)
Pivot
sequence
1 2 3
3 3 3
Example 3
This example computes the inverse of the 3 × 3 matrix A in the first example and also solves the linear system. The product matrix C = A-1A is computed as a check. The approximate result is C = I.
#include
<imsl.h>
f_complex a[] = {{1.0, 1.0},
{2.0, 3.0}, {3.0,
-3.0},
{2.0, 1.0}, {5.0, 3.0}, {7.0,
-5.0},
{-2.0, 1.0}, {-4.0, 4.0}, {5.0, 3.0}};
f_complex
b[] = {{3.0, 5.0}, {22.0, 10.0}, {-10.0,
4.0}};
main()
{
int n =
3;
f_complex
*x;
f_complex
*p_inva;
f_complex
*C;
/* Solve Ax = b for x */
x =
imsl_c_lin_sol_gen (n, a,
b,
IMSL_INVERSE,
&p_inva,
0);
/*
Print solution */
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Solution, x, of Ax
= b", 1, n, x,
0);
/* Print input and inverse matrices */
imsl_c_write_matrix
("Input A", n, n, a, 0);
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Inverse of
A", n, n, p_inva,
0);
/* Check and print result */
C = imsl_c_mat_mul_rect
("A*B",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, n,n,
p_inva,
IMSL_B_MATRIX, n,n,
a,
0);
imsl_c_write_matrix ("Product, inv(A)*A", n, n, C,
0);
}
Output
Solution, x, of Ax =
b
1
2
3
(
1, -1)
(
2, 4)
(
3,
-0)
Input
A
1
2
3
1 (
1, 1)
(
2, 3)
(
3, -3)
2
(
2, 1)
(
5, 3)
( 7,
-5)
3 (
-2, 1)
(
-4, 4)
(
5,
3)
Inverse of
A
1
2
3
1 ( 1.330, 0.594)
( -0.151, 0.028)
( -0.604, 0.613)
2
( -0.632, -0.538)
( 0.160, 0.189)
( 0.142, -0.245)
3
( -0.189, 0.160)
( 0.193, -0.052)
( 0.024,
0.042)
Product,
inv(A)*A
1
2
3
1 (
1, -0)
(
-0, -0)
(
-0, 0)
2
(
0, 0)
(
1, 0)
(
0, -0)
3
(
-0, -0)
(
-0, 0) (
1,
0)
Warning Errors
IMSL_ILL_CONDITIONED The input matrix is too ill-conditioned. An estimate of the reciprocal of the L1 condition number is “rcond” = #. The solution might not be accurate.
Fatal Errors
IMSL_SINGULAR_MATRIX The input matrix is singular.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |