Computes the SVD, A = USVT, of a real rectangular matrix A. An approximate generalized inverse and rank of A also can be computed.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (int m, int n, float a[], …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_lin_svd_gen.
Required Arguments
int m
(Input)
Number of rows in the matrix.
int n
(Input)
Number of columns in the matrix.
float a[]
(Input)
Array of size m × n containing the
matrix.
Return Value
If no optional arguments are used, imsl_f_lin_svd_gen returns a pointer to an array of size min (m, n) containing the ordered singular values of the matrix. To release this space, use free. If no value can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (int
m, int n, float
a[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int
a_col_dim,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
s[],
IMSL_RANK, float
tol,
int
*rank,
IMSL_U, float
**p_u,
IMSL_U_USER, float
u[],
IMSL_U_COL_DIM, int
u_col_dim,
IMSL_V, float
**p_v,
IMSL_V_USER, float
v[],
IMSL_V_COL_DIM, int
v_col_dim,
IMSL_INVERSE, float
**p_gen_inva,
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, float
gen_inva[],
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
gen_inva_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array a.
Default: a_col_dim = n
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float s[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size min (m+1, n) containing
the singular values of A in its first min (m, n) positions
in nonincreasing order. If IMSL_RETURN_USER is
used, the return value of imsl_f_lin_svd_gen is
s.
IMSL_RANK, float tol, int *rank (Input/Output)
tol: Scalar containing
the tolerance used to determine when a singular value is negligible and replaced
by the value zero. If tol > 0,
then a singular value si i is considered
negligible if i.i ≤ tol. If tol < 0,
then a singular value
si.i is considered
negligible if si.i ≤ |tol|*||A||∝. In this case, |tol| should be
an
estimate of relative error or uncertainty in the data.
*rank: Integer containing an estimate of the rank of A.
IMSL_U, float **p_u
(Output)
**p_u: The address of
a pointer to an array of size m × min (m, n)
containing the min (m, n) left-singular vectors of A.
On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_u is declared, and
&p_u is used
as an argument.
IMSL_U_USER, float u[]
(Output)
u[]:
The address of a pointer to an array of size
m × min (m, n) containing the
min (m, n) left-singular vectors of A. If
m ³ n, the
left-singular vectors can be returned using the storage locations of the array
a.
IMSL_U_COL_DIM, int u_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array containing the left-singular
vectors.
Default: u_col_dim = min
(m, n)
IMSL_V, float **p_v
(Output)
**p_v: The address of
a pointer to an array of size n × n containing the right
singular vectors of A. On return, the necessary space is allocated by
imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_v is declared, and
&p_v is used
as an argument.
IMSL_V_USER, float v[]
(Output)
v[]:
The address of a pointer to an array of size n × n
containing the right singular vectors of A. The right-singular vectors
can be returned using the storage locations of the array a. Note that the
return of the left- and right-singular vectors cannot use the storage locations
of a
simultaneously.
IMSL_V_COL_DIM, int v_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array containing the right-singular
vectors.
Default: v_col_dim =
n
IMSL_INVERSE, float
**p_gen_inva (Output)
The address of a pointer to an array
of size n × m containing the generalized inverse of the
matrix A. On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_gen_inva is
declared, and &p_gen_inva is
used as an argument.
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, float
gen_inva[] (Output)
A user-allocated array of size
n × m containing the general inverse of the matrix
A.
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
gen_inva_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of the array
containing the general inverse of the matrix A.
Default: gen_inva_col_dim = m
Description
The function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen
computes the singular value decomposition of a real matrix A. It first
reduces the matrix A to a bidiagonal matrix B by pre- and
post-multiplying Householder transformations. Then, the singular value
decomposition of
B is computed using the implicit-shifted QR
algorithm. An estimate of the rank of the matrix A is obtained by finding
the smallest integer k such that sk,k ≤ tol
or sk,k ≤ |tol|*||A||∝. Since si+1,i+1
≤ si,i, it follows that all
the si,i satisfy the
same inequality for i = k, …, min (m,
n) − 1.
The rank is set to the value k − 1. If
A = USVT, its generalized
inverse is A+ = VS+ UT. Here,
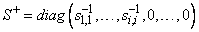
Only singular values that are not negligible are reciprocated. If IMSL_INVERSE or IMSL_INVERSE_USER is specified, the function first computes the singular value decomposition of the matrix A. The generalized inverse is then computed. The function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen fails if the QR algorithm does not converge after 30 iterations isolating an individual singular value.
Examples
Example 1
This example computes the singular values of a real 6 × 4 matrix.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] =
{1.0, 2.0, 1.0,
4.0,
3.0, 2.0, 1.0,
3.0,
4.0, 3.0, 1.0,
4.0,
2.0, 1.0, 3.0,
1.0,
1.0, 5.0, 2.0,
2.0,
1.0, 2.0, 2.0, 3.0};
main()
{
int m = 6, n =
4;
float
*s;
/* Compute singular values */
s = imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m,
n, a,
0);
/* Print singular values */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Singular
values", 1, n, s, 0);
}
Output
Singular values
1
2
3
4
11.49
3.27
2.65 2.09
Example 2
This example computes the singular value decomposition of the 6 × 4 real matrix A. The singular values are returned in the user-provided array. The matrices U and V are returned in the space provided by the function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] =
{1.0, 2.0, 1.0,
4.0,
3.0, 2.0, 1.0,
3.0,
4.0, 3.0, 1.0,
4.0,
2.0, 1.0, 3.0,
1.0,
1.0, 5.0, 2.0,
2.0,
1.0, 2.0, 2.0, 3.0};
main()
{
int m = 6, n =
4;
float s[4],
*p_u,
*p_v;
/* Compute SVD */
imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m, n,
a,
IMSL_RETURN_USER,
s,
IMSL_U,
&p_u,
IMSL_V,
&p_v,
0);
/* Print decomposition*/
imsl_f_write_matrix
("Singular values, S", 1, n, s, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix
("Left singular vectors, U", m, n, p_u, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Right singular vectors, V", n, n, p_v, 0);
}
Output
Singular values, S
1
2
3
4
11.49
3.27
2.65
2.09
Left singular vectors,
U
1
2
3
4
1 -0.3805
0.1197 0.4391
-0.5654
2 -0.4038
0.3451 -0.0566
0.2148
3 -0.5451
0.4293 0.0514
0.4321
4 -0.2648
-0.0683 -0.8839
-0.2153
5 -0.4463
-0.8168 0.1419
0.3213
6 -0.3546
-0.1021 -0.0043
-0.5458
Right singular vectors,
V
1
2
3 4
1
-0.4443
0.5555 -0.4354
0.5518
2 -0.5581
-0.6543 0.2775
0.4283
3 -0.3244
-0.3514 -0.7321
-0.4851
4 -0.6212
0.3739 0.4444 -0.5261
Example 3
This example computes the rank and generalized inverse of a 3 × 2 matrix A. The rank and the 2 × 3 generalized inverse matrix A+ are printed.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] =
{1.0,
0.0,
1.0,
1.0,
100.0, -50.0};
main()
{
int m = 3, n =
2;
float
tol;
float
gen_inva[6];
float *s;
int
*rank;
/* Compute generalized inverse */
tol =
1.e-4;
s = imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m, n, a,
IMSL_RANK, tol, &rank,
IMSL_INVERSE_USER,
gen_inva,
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM,
m,
0);
/* Print rank, singular values and
*/
/* generalized inverse. */
printf ("Rank of matrix = %2d",
rank);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Singular values", 1, n,
s, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Generalized inverse", n,
m, gen_inva,
IMSL_A_COL_DIM,
m,
0);
}
Output
Rank of matrix = 2
Singular
values
1
2
111.8
1.4
Generalized
inverse
1
2
3
1
0.100
0.300
0.006
2
0.200 0.600
-0.008
Warning Errors
IMSL_SLOWCONVERGENT_MATRIX Convergence cannot be reached after 30 iterations.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |