Adds two band matrices, both in band storage mode, C ¬ aA + bB.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_mat_add_band (int n, int nlca, int nuca, float alpha, float a[], int nlcb, int nucb, float beta, float b[], int *nlcc, int *nucc, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_mat_add_band.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
The order of the matrices A and B.
int nlca
(Input)
Number of lower codiagonals of A.
int nuca
(Input)
Number of upper codiagonals of A.
float alpha
(Input)
Scalar multiplier for A.
float a[]
(Input)
An n by n band matrix with nlca lower
codiagonals and nuca upper codiagonals stored in band mode with dimension
(nlca + nuca + 1) by n.
int nlcb
(Input)
Number of lower codiagonals of B.
int nucb
(Input)
Number of upper codiagonals of B.
float beta
(Input)
Scalar multiplier for B.
float b[]
(Input)
An n by n band matrix with nlcb lower
codiagonals and nucb upper codiagonals stored in band mode with dimension
(nlcb + nucb + 1) by n.
int *nlcc
(Output)
Number of lower codiagonals of C.
int *nucc
(Output)
Number of upper codiagonals of C.
Return Value
A pointer to an array of type float containing the computed sum. NULL is returned in the event of an error or if the return matrix has no nonzero elements.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_mat_add_band (int n, int nlca, int nuca,
float alpha, float a[], int nlcb, int nucb,
float beta, float b[], int *nlcc, int *nucc,
IMSL_A_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_B_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_SYMMETRIC,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_TRANSPOSE,
Replace A with AT in the expression aA + bB.
IMSL_B_TRANSPOSE,
Replace B with BT in the expression aA + bB.
IMSL_SYMMETRIC,
A,
B and C are stored in band symmetric storage mode.
Description
The function imsl_f_mat_add_band forms the sum aA + bB, given the scalars a and b, and, the matrices A and B in band format. The transpose of A and/or B may be used during the computation if optional arguments are specified. Symmetric storage mode may be used if the optional argument is specified.
If IMSL_SYMMETRIC is specified, the return value for the number of lower codiagonals, nlcc, will be equal to 0.
If the return matrix equals NULL, the return value for the number of lower codiagonals, nlcc, will be equal to -1 and the number of upper codiagonals, nucc, will be equal to 0.
Examples
Example 1
Add two real matrices of order 4 stored in band mode. Matrix A has one upper codiagonal and one lower codiagonal. Matrix B has no upper codiagonals and two lower codiagonals.
#include <imsl.h>
void main()
{
float a[] = {0.0, 2.0, 3.0, -1.0,
1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0,
0.0, 3.0, 4.0, 0.0};
float b[] = {3.0, 3.0, 3.0, 3.0,
1.0, -2.0, 1.0, 0.0,
-1.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0};
int nucb = 0, nlcb = 2;
int nuca = 1, nlca = 1;
int nucc, nlcc;
int n = 4, m;
float alpha = 1.0, beta = 1.0;
float *c;
c =
imsl_f_mat_add_band(n, nlca, nuca, alpha, a,
nlcb, nucb, beta, b,
&nlcc, &nucc, 0);
m = nlcc + nucc
+ 1;
imsl_f_write_matrix("C = A + B", m, n, c, 0);
free(c);
}
C = A + B
1 2 3 4
1 0 2 3 -1
2 4 4 4 4
3 1 1 5 0
4 -1 2 0 0
Example 2
Compute 4*A + 2*B, where
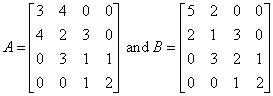
#include <imsl.h>
void main()
{
float a[] = {0.0, 4.0, 3.0, 1.0,
3.0, 2.0, 1.0, 2.0};
float b[] = {0.0, 2.0, 3.0, 1.0,
5.0, 1.0, 2.0, 2.0};
int nuca = 1, nlca = 1;
int nucb = 1, nlcb = 1;
int n = 4, m, nlcc, nucc;
float alpha = 4.0, beta = 2.0;
float *c;
c =
imsl_f_mat_add_band(n, nlca, nuca, alpha, a,
nlcb, nucb, beta, b,
&nlcc, &nucc,
IMSL_SYMMETRIC, 0);
m = nucc + nlcc
+ 1;
imsl_f_write_matrix("C = 4*A + 2*B\n", m, n, c, 0);
free(c);
}
Output
C = 4*A + 2*B
1
2
3 4
1 0 20 18 6
2 22 10 8 12
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |