Performs element-wise addition on two real matrices stored
in coordinate format,
C ¬
aA + bB.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_sparse_elem *imsl_f_mat_add_coordinate (int n, int nz_a, float alpha, Imsl_f_sparse_elem a[], int nz_b, float beta, Imsl_f_sparse_elem b[], int *nz_c, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_mat_add_coordinate.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
The order of the matrices A and B.
int nz_a
(Input)
Number of nonzeros in the matrix A.
float alpha
(Input)
Scalar multiplier for A.
Imsl_f_sparse_elem a[]
(Input)
Vector of length nz_a containing the
location and value of each nonzero entry in the matrix A.
int nz_b
(Input)
Number of nonzeros in the matrix B.
float beta
(Input)
Scalar multiplier for B.
Imsl_f_sparse_elem b[]
(Input)
Vector of length nz_b containing the
location and value of each nonzero entry in the matrix B.
int *nz_c
(Output)
The number of nonzeros in the sum aA + bB.
Return Value
A pointer to an array of type Imsl_f_sparse_elem containing the computed sum. In the event of an error or if the return matrix has no nonzero elements, NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
Imsl_f_sparse_elem *imsl_f_mat_add_coordinate
(int
n,
int
nz_a,
float
alpha,
Imsl_f_sparse_elem a[], int nz_b, float beta,
Imsl_f_sparse_elem b[], int *nz_c,
IMSL_A_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_B_TRANSPOSE,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_TRANSPOSE,
Replace A with AT in the expression aA + bB.
IMSL_B_TRANSPOSE,
Replace B with BT in the expression aA + bB.
Description
The function imsl_f_mat_add_coordinate forms the sum aA + bB, given the scalars a and b, and the matrices A and B in coordinate format. The transpose of A and/or B may be used during the computation if optional arguments are specified. The method starts by storing A in a linked list data structure, and performs the multiply by a. Next the data in matrix B is traversed and if the coordinates of a nonzero element correspond to those of a nonzero element in A, that entry in the linked list is updated. Otherwise, a new node in the linked list is created. The multiply by b occurs at this time. Lastly, the linked list representation of C is converted to coordinate representation, omitting any elements that may have become zero through cancellation.
Examples
Example 1
Add two real matrices of order 4 stored in coordinate format. Matrix A has five nonzero elements. Matrix B has seven nonzero elements.
#include <imsl.h>
void main ()
{
Imsl_f_sparse_elem a[] = {0, 0, 3,
0, 3, -1,
1, 2, 5,
2, 0, 1,
3, 1, 3};
Imsl_f_sparse_elem b[] = {0, 1, -2,
0, 3, 1,
1, 0, 3,
2, 2, 5,
2, 3, 1,
3, 0, 4,
3, 1, 3};
int nz_a = 5, nz_b = 7, nz_c;
int n = 4, i;
float alpha = 1.0, beta = 1.0;
Imsl_f_sparse_elem *c;
c =
imsl_f_mat_add_coordinate(n, nz_a, alpha, a,
nz_b, beta, b, &nz_c, 0);
printf("
row column value\n");
for (i = 0; i < nz_c; i++)
printf("%3d %5d %8.2f\n", c[i].row, c[i].col, c[i].val);
free(c);
}
Output
row column value
0 0 3.00
0 1 -2.00
1 0 3.00
1 2 5.00
2 0 1.00
2 2 5.00
2 3 1.00
3 0 4.00
3 1 6.00
Example 2
Compute 2*AT + 2*BT, where
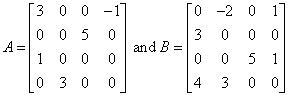
#include <imsl.h>
void main ()
{
Imsl_f_sparse_elem a[] = {0, 0, 3,
0, 3, -1,
1, 2, 5,
2, 0, 1,
3, 1, 3};
Imsl_f_sparse_elem b[] = {0, 1, -2,
0, 3, 1,
1, 0, 3,
2, 2, 5,
2, 3, 1,
3, 0, 4,
3, 1, 3};
int nz_a = 5, nz_b = 7, nz_c;
int n = 4, i;
float alpha = 2.0, beta = 2.0;
Imsl_f_sparse_elem *c;
c =
imsl_f_mat_add_coordinate(n, nz_a, alpha, a,
nz_b, beta, b, &nz_c,
IMSL_A_TRANSPOSE,
IMSL_B_TRANSPOSE, 0);
printf("
row column value\n");
for (i = 0; i < nz_c; i++)
printf("%3d %5d %8.2f\n", c[i].row, c[i].col, c[i].val);
free(c);
}
Output
row column value
0 0 6.00
0 1 6.00
0 2 2.00
0 3 8.00
1 0 -4.00
1 3 12.00
2 1 10.00
2 2 10.00
3 2 2.00
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |