Computes the transpose of a matrix, a matrix-vector product, or a matrix-matrix product, all matrices stored in band form.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band (char *string, ..., 0)
The equivalent double function is imsl_d_mat_mul_rect_band.
Required Arguments
char *string
(Input)
String indicating matrix multiplication to be performed.
Return Value
The result of the multiplication is returned. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
void
*imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band (char *string,
IMSL_A_MATRIX, int
nrowa, int ncola, int nlca, int nuca, float
*a,
IMSL_B_MATRIX, int nrowb, int ncolb, int nlcb,
int nucb, float *b,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, int nx, float
*x,
IMSL_RETURN_MATRIX_CODIAGONALS, int *nlc_result,
int *nuc_result,
IMSL_RETURN_USER_VECTOR, float
vector_user[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_MATRIX, int nrowa, int ncola, int nlca, int nuca, float *a
(Input)
The sparse matrix
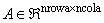
IMSL_B_MATRIX, int nrowb, int ncolb, int nlcb, int nucb, float *b
(Input)
The sparse matrix
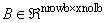
IMSL_X_VECTOR, int nx, float *x,
(Input)
The vector x of length nx.
IMSL_RETURN_MATRIX_CODIAGONALS, int *nlc_result, int *nuc_result,
(Output)
If the function imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band
returns data for a band matrix, use this option to retrieve the number of lower
and upper codiagonals of the return matrix.
IMSL_RETURN_USER_VECTOR, float
vector_user[], (Output)
If the result of the computation
in a vector, return the answer in the user supplied sparse vector_user.
Description
The function imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band
computes a matrix-matrix product or a matrix-vector product, where the
matrices are specified in band format. The operation performed is specified
by string. For example, if A*x
is given,
Ax is computed. In string,
the matrices A and B and the vector x can be used. Any of
these names can be used with trans,
indicating transpose. The vector x is treated as a dense n ΄ 1 matrix. If string
contains only one item, such as x
or trans(A), then a copy of the array, or its
transpose is returned.
The matrices and/or vector referred to in string must be given as optional arguments. Therefore, if string is A*x, then IMSL_A_MATRIX and IMSL_X_VECTOR must be given.
Examples
Example 1
Consider the matrix

After storing A in band format, multiply A by x = (1, 2, 3, 4)T and print the result.
#include <imsl.h>
main()
{
float a[] = {0.0, -1.0, -2.0, 2.0,
2.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0,
-3.0, 0.0, 2.0, 0.0};
float x[] =
{1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
int n = 4;
int nuca = 1;
int nlca = 1;
float *b;
/* Set b = A*x */
b =
imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band ("A*x",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, n, n, nlca, nuca, a,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, n, x,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Product, Ax", 1, n, b, 0);
}
Output
Product, Ax
1 2 3 4
0 -7 5 10
Example 2
This example uses the power method to determine the
dominant eigenvector of
E(100, 10). The same computation is performed
by using imsl_f_eig_sym, See Chapter 2,
Eigensystem
Analysis. The iteration stops when the component-wise
absolute difference between the dominant eigenvector found by imsl_f_eig_sym
and the eigenvector at the current iteration is less than the square root of
machine unit roundoff.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <math.h>
void main()
{
int i;
int j;
int k;
int n;
int c;
int nz;
int index;
int start;
int stop;
float *a;
float *z;
float *q;
float *dense_a;
float *dense_evec;
float *dense_eval;
float norm;
float *evec;
float error;
float tolerance;
n = 100;
c = 10;
tolerance = sqrt(imsl_f_machine(4));
error = 1.0;
evec = (float*) malloc (n*sizeof(*evec));
z = (float*) malloc (n*sizeof(*z));
q = (float*) malloc (n*sizeof(*q));
dense_a = (float*) calloc (n*n, sizeof(*dense_a));
a = imsl_f_generate_test_band (n, c, 0);
/* Convert to dense format,
starting with upper triangle */
start = c;
for (i=0; i<c; i++, start--)
for (k=0, j=start; j<n; j++, k++)
dense_a[k*n + j] = a[i*n + j];
/*
Convert diagonal */
for (j=0;
j<n; j++)
dense_a[j*n + j] = a[c*n + j];
/* Convert lower triangle */
stop = n-1;
for (i=c+1; i<2*c+1; i++, stop--)
for (k=i-c, j=0; j<stop; j++, k++)
dense_a[k*n + j] = a[i*n + j];
/* Determine dominant eigenvector by a dense method */
dense_eval =
imsl_f_eig_sym (n, dense_a,
IMSL_VECTORS, &dense_evec,
0);
for (i=0; i<n; i++) evec[i] = dense_evec[n*i];
/* Normalize */
norm =
imsl_f_vector_norm (n, evec, 0);
for (i=0; i<n; i++) evec[i] /= norm;
for (i=0;
i<n; i++) q[i] = 1.0/sqrt((float) n);
/* Do power method */
while (error
> tolerance) {
imsl_f_mat_mul_rect_band ("A*x",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, n, n, c, c, a,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, n, q,
IMSL_RETURN_USER_VECTOR, z,
0);
/* Normalize */
norm = imsl_f_vector_norm (n, z, 0);
for (i=0; i<n; i++) q[i] = z[i]/norm;
/* Compute maximum absolute error between any
two elements */
error = imsl_f_vector_norm (n, q,
IMSL_SECOND_VECTOR, evec,
IMSL_INF_NORM, &index,
0);
}
printf ("Maximum absolute error = %e\n", error);
}
Output
Maximum absolute error = 3.367960e-04
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |