.p>.CMCH10.DOC!RANDOM_GAMMA;random_gamma
Generates pseudorandom numbers from a standard gamma distribution.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_random_gamma (int n_random, float a, ¼, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_random_gamma.
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float a
(Input)
The shape parameter of the gamma distribution. This parameter must be
positive.
Return Value
If no optional arguments are used, imsl_f_random_gamma returns a pointer to a vector of length n_random containing the random standard gamma deviates. To release this space, use free.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_random_gamma (int
n_random,
float a,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
r[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_USER_RETURN, float r[]
(Output)
If specified, the vector of length n_random containing
the random standard gamma deviates is returned in the user-provided array r.
Description
The function imsl_f_random_gamma generates pseudorandom numbers from a gamma distribution with shape parameter a and unit scale parameter. The probability density function is
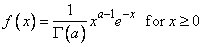
Various computational algorithms are used depending on the value of the shape parameter a. For the special case of a = 0.5, squared and halved normal deviates are used; and for the special case of a = 1.0, exponential deviates are generated. Otherwise, if a is less than 1.0, an acceptance-rejection method due to Ahrens, described in Ahrens and Dieter (1974), is used. If a is greater than 1.0, a ten-region rejection procedure developed by Schmeiser and Lal (1980) is used.
Deviates from the two-parameter gamma distribution with shape parameter a and scale parameter b can be generated by using imsl_f_random_gamma and then multiplying each entry in r by b. The following statements (in single precision) would yield random deviates from a gamma (a, b) distribution.
float *r;
r =
imsl_f_random_gamma(n_random, a, 0);
for (i=0; i<n_random; i++) *(r+i) *=
b;
The Erlang distribution is a standard gamma distribution with the shape parameter having a value equal to a positive integer; hence, imsl_f_random_gamma generates pseudorandom deviates from an Erlang distribution with no modifications required.
The function imsl_random_seed_set can be used to initialize the seed of the random number generator. The function imsl_random_option can be used to select the form of the generator.
Example
In this example, imsl_f_random_gamma is used to generate five pseudorandom deviates from a gamma (Erlang) distribution with shape parameter equal to 3.0.
#include <imsl.h>
void
main()
{
int seed =
123457;
int n_random =
5;
float a =
3.0;
float
*r;
imsl_random_seed_set(seed);
r = imsl_f_random_gamma(n_random, a, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("Gamma(3) random deviates", 1, n_random, r, 0);
}
Output
Gamma(3) random deviates
1
2
3
4
5
6.843
3.445
1.853
3.999 0.779
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |