Computes various norms of a vector or the difference of two vectors.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_vector_norm (int n, float *x, ¼., 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_vector_norm.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
The length of the input vector(s).
float *x
(Input)
Input vector for which the norm is to be computed
Return Value
The requested norm of the input vector. If the norm cannot be computed, NaN is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
imsl_f_vector_norm (int n, float
*x,
IMSL_ONE_NORM,
IMSL_INF_NORM,
IMSL_SECOND_VECTOR, float
*y,
0)
Description
By default, imsl_f_vector_norm computes the Euclidean norm
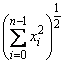
If the option IMSL_ONE_NORM is selected, the 1-norm
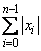
is returned. If the option IMSL_INF_NORM is selected, the infinity norm
max |xi|
is returned. In the case of the infinity norm, the program also returns the index of the element with maximum modulus. If IMSL_SECOND_VECTOR is selected, then the norm of x −y is computed.
Examples
Example 1
In this example, the Euclidean norm of an input vector is computed.
#include <stdio.h>
#include
"imsl.h"
main()
{
float x[] = {1.0, 3.0, -2.0,
4.0};
float norm;
int n;
n =
sizeof(x)/sizeof(*x);
norm = imsl_f_vector_norm (n, x,
0);
printf("Euclidean norm of x = %f\n",
norm);
}
Output
Euclidean norm of x = 5.477226
Example 2
This example computes max |xi − yi| and prints the norm and index.
#include <stdio.h>
#include
"imsl.h"
main()
{
float x[] = {1.0, 3.0, -2.0,
4.0};
float y[] = {4.0, 2.0, -1.0,
-5.0};
float norm;
int
index;
int n;
n =
sizeof(x)/sizeof(*x);
norm = imsl_f_vector_norm (n, x,
IMSL_SECOND_VECTOR,
y,
IMSL_INF_NORM, &index, 0);
printf("Infinity norm
of x-y = %f ", norm);
printf("at location %d\n",
index);
}
Output
Infinity norm of x-y = 9.000000 at location 3
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |