Appendix A: References
Abe
Abe, S. (2001) Pattern Classification: Neuro-Fuzzy Methods and their Comparison, Springer-Verlag.
Abramowitz and Stegun
Abramowitz, Milton and Irene A. Stegun (editors) (1964), Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, National Bureau of Standards, Washington.
Afifi and Azen
Afifi, A.A. and S.P. Azen (1979), Statistical Analysis: A Computer Oriented Approach, 2d ed., Academic Press, New York.
Agresti, Wackerly, and Boyette
Agresti, Alan, Dennis Wackerly, and James M. Boyette (1979), Exact conditional tests for cross-classifications: Approximation of attained significance levels, Psychometrika, 44, 75-83.
Ahrens and Dieter
Ahrens, J.H. and U. Dieter (1974), Computer methods for sampling from gamma, beta, Poisson, and binomial distributions, Computing, 12, 223-246.
Ahrens, J.H., and U. Dieter (1985), Sequential random sampling, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 11, 157−169.
Akaike
Akaike, H., (1978), Covariance Matrix Computation of the State Variable of a Stationary Gaussian Process, Ann. Inst. Statist. Math. 30 , Part B, 499-504.
Akaike et al
Akaike, H. , Kitagawa, G., Arahata, E., Tada, F., (1979), Computer Science Monographs No. 13, The Institute of Statistical Mathematics, Tokyo.
Anderberg
Anderberg, Michael R. (1973), Cluster Analysis for Applications, Academic Press, New York.
Anderson
Anderson, T.W. (1971), The Statistical Analysis of Time Series, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Anderson, T. W. (1994) The Statistical Analysis of Time Series, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Anderson and Bancroft
Anderson, R.L. and T.A. Bancroft (1952), Statistical Theory in Research, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York.
Atkinson
Atkinson, A.C. (1979), A family of switching algorithms for the computer generation of beta random variates, Biometrika, 66, 141-145.
Atkinson, A.C. (1985), Plots, Transformations, and Regression, Claredon Press, Oxford.
Barrodale and Roberts
Barrodale, I., and F.D.K. Roberts (1973), An improved algorithm for discrete L1 approximation, SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 10, 839−848.
Barrodale, I., and F.D.K. Roberts (1974), Solution of an overdetermined system of equations in the l1 norm, Communications of the ACM, 17, 319−320.
Barrodale, I., and C. Phillips (1975), Algorithm 495. Solution of an overdetermined system of linear equations in the Chebyshev norm, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1, 264−270.
Bartlett, M. S.
Bartlett, M.S. (1935), Contingency table interactions, Journal of the Royal Statistics Society Supplement, 2, 248-252.
Bartlett, M. S. (1937) Some examples of statistical methods of research in agriculture and applied biology, Supplement to the Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 4, 137-183.
Bartlett, M. (1937), The statistical conception of mental factors, British Journal of Psychology, 28, 97–104.
Bartlett, M.S. (1946), On the theoretical specification and sampling properties of autocorrelated time series, Supplement to the Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 8, 27–41.
Bartlett, M.S. (1978), Stochastic Processes, 3rd. ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Bays and Durham
Bays, Carter and S.D. Durham (1976), Improving a poor random number generator, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2, 59-64.
Bendel and Mickey
Bendel, Robert B., and M. Ray Mickey (1978), Population correlation matrices for sampling experiments, Communications in Statistics, B7, 163−182.
Berry
Berry, M. J. A. and Linoff, G. (1997) Data Mining Techniques, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Best and Fisher
Best, D.J., and N.I. Fisher (1979), Efficient simulation of the von Mises distribution, Applied Statistics, 28, 152−157.
Bishop
Bishop, C. M. (1995) Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition, Oxford University Press.
Bishop et al
Bishop, Yvonne M.M., Stephen E. Feinberg, and Paul W. Holland (1975), Discrete Multivariate Analysis: Theory and Practice, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass.
Bjorck and Golub
Bjorck, Ake, and Gene H. Golub (1973), Numerical Methods for Computing Angles Between Subspaces, Mathematics of Computation, 27, 579-594.
Blom
Blom, Gunnar (1958), Statistical Estimates and Transformed Beta-Variables, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Bosten and Battiste
Bosten, Nancy E. and E.L. Battiste (1974), Incomplete beta ratio, Communications of the ACM, 17, 156s-157.
Box and Jenkins
Box, George E.P. and Gwilym M. Jenkins (1970) Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, Holden-Day, Inc.
Box, George E.P. and Gwilym M. Jenkins (1976), Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, revised ed., Holden-Day, Oakland.
Box and Pierce
Box, G.E.P., and David A. Pierce (1970), Distribution of residual autocorrelations in autoregressive-integrated moving average time series models, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 65, 1509–1526.
Box and Tidwell
Box, G.E.P. and P.W. Tidwell (1962), Transformation of the Independent Variables, Technometrics, 4, 531-550.
Box et al.
Box, George E.P., Jenkins,Gwilym M. and Reinsel G.C., (1994) Time Series Analysis, Third edition, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Boyette
Boyette, James M. (1979), Random RC tables with given row and column totals, Applied Statistics, 28, 329−332.
Bradley
Bradley, J.V. (1968), Distribution-Free Statistical Tests, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.
Breiman
Breiman, L., Friedman, J. H., Olshen, R. A. and Stone, C. J. (1984) Classification and Regression Trees, Chapman & Hall. For the latest information on CART visit http://www.salford-systems.com/cart.php.
Breslow
Breslow, N.E. (1974), Covariance analysis of censored survival data, Biometrics, 30, 89-99.
Bridel
Bridle, J. S. (1990) Probabilistic Interpretation of Feedforward Classification Network Outputs, with relationships to statistical pattern recognition, in F. Fogelman Soulie and J. Herault (Eds.), Neuralcomputing: Algorithms, Architectures and Applications, Springer-Verlag, 227-236.
Brown
Brown, Morton E. (1983), MCDP4F, two-way and multiway frequency tables-measures of association and the log-linear model (complete and incomplete tables), in BMDP Statistical Software, 1983 Printing with Additions, (edited by W.J. Dixon), University of California Press, Berkeley.
Brown and Benedetti
Brown, Morton B. and Jacqualine K. Benedetti (1977), Sampling behavior and tests for correlation in two-way contingency tables, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 42, 309-315.
Calvo
Calvo, R. A. (2001) Classifying Financial News with Neural Networks, Proceedings of the 6th Australasian Document Computing Symposium.
Chen and Liu
Chen, C. and Liu, L., Joint Estimation of Model Parameters and Outlier Effects in Time Series, Journal of the American Statistical Association, Vol. 88, No.421, March 1993.
Cheng
Cheng, R.C.H. (1978), Generating beta variates with nonintegral shape parameters, Communications of the ACM, 21, 317-322.
Chiang
Chiang, Chin Long (1968), Introduction to Stochastic Processes in Statistics, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Clarkson and Jenrich
Clarkson, Douglas B. and Robert B Jenrich (1991), Computing extended maximum likelihood estimates for linear parameter models, submitted to Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 53, 417-426.
Conover
Conover, W.J. (1980), Practical Nonparametric Statistics, 2d ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Conover and Iman
Conover, W.J. and Ronald L. Iman (1983), Introduction to Modern Business Statistics, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Conover, W. J., Johnson, M. E., and Johnson, M. M
Conover, W. J., Johnson, M. E., and Johnson, M. M. (1981) A comparative study of tests for homogeneity of variances, with applications to the outer continental shelf bidding data, Technometrics, 23, 351-361.
Cook and Weisberg
Cook, R. Dennis and Sanford Weisberg (1982), Residuals and Influence in Regression, Chapman and Hall, New York.
Cooper
Cooper, B.E. (1968), Algorithm AS4, An auxiliary function for distribution integrals, Applied Statistics, 17, 190-192.
Cox
Cox, David R. (1970), The Analysis of Binary Data, Methuen, London.
Cox, D.R. (1972), Regression models and life tables (with discussion), Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, Methodology, 34, 187–220.
Cox and Lewis
Cox, D.R., and P.A.W. Lewis (1966), The Statistical Analysis of Series of Events, Methuen, London.
Cox and Oakes
Cox, D.R., and D. Oakes (1984), Analysis of Survival Data, Chapman and Hall, London.
Cox and Stuart
Cox, D.R., and A. Stuart (1955), Some quick sign tests for trend in location and dispersion, Biometrika, 42, 80-95.
D'Agostino and Stevens
D'Agostino, Ralph B. and Michael A. Stevens (1986), Goodness-of-Fit Techniques, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Dallal and Wilkinson
Dallal, Gerald E. and Leland Wilkinson (1986), An analytic approximation to the distribution of Lilliefor's test statistic for normality, The American Statistician, 40, 294-296.
Dennis and Schnabel
Dennis, J.E., Jr. and Robert B. Schnabel (1983), Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Devore
Devore, Jay L (1982), Probability and Statistics for Engineering and Sciences, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company, Monterey, Calif.
Draper and Smith
Draper, N.R. and H. Smith (1981), Applied Regression Analysis, 2d ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Durbin
Durbin, J. (1960), The fitting of time series models, Revue Institute Internationale de Statistics, 28, 233–243.
Efroymson
Efroymson, M.A. (1960), Multiple regression analysis, Mathematical Methods for Digital Computers, Volume 1, (edited by A. Ralston and H. Wilf), John Wiley & Sons, New York, 191-203.
Ekblom
Ekblom, Hakan (1973), Calculation of linear best Lp-approximations, BIT, 13, 292−300.
Ekblom, Hakan (1987), The L1-estimate as limiting case of an Lp or Huber-estimate, in Statistical Data Analysis Based on the L1-Norm and Related Methods (edited by Yadolah Dodge), North-Holland, Amsterdam, 109−116.
Elandt-Johnson and Johnson
Elandt-Johnson, Regina C., and Norman L. Johnson (1980), Survival Models and Data Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 172-173.
Elman
Elman, J. L. (1990) Finding Structure in Time, Cognitive Science, 14, 179-211.
Emmett
Emmett, W.G. (1949), Factor analysis by Lawless method of maximum likelihood, British Journal of Psychology, Statistical Section, 2, 90-97.
Engle
Engle, C. (1982), Autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity with estimates of the variance of U.K. inflation, Econometrica , 50, 987-1008.
Fisher
Fisher, R.A. (1936), The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems, The Annals of Eugenics, 7, 179-188.
Fishman
Fishman, George S. (1978), Principles of Discrete Event Simulation, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Fishman and Moore
Fishman, George S. and Louis R. Moore (1982), A statistical evaluation of multiplicative congruential random number generators with modulus , Journal of the American Statistical Association, 77, 129-136.
Forsythe
Forsythe, G.E. (1957), Generation and use of orthogonal polynomials for fitting data with a digital computer, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 5, 74-88.
Fuller
Fuller, Wayne A. (1976), Introduction to Statistical Time Series, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Furnival and Wilson
Furnival, G.M. and R.W. Wilson, Jr. (1974), Regressions by leaps and bounds, Technometrics, 16, 499-511.
Fushimi
Fushimi, Masanori (1990), Random number generation with the
recursion
Xt = Xt−3p ÅXt−3q, Journal of
Computational and Applied Mathematics, 31, 105−118.
Gentleman
Gentleman, W. Morven (1974), Basic procedures for large, sparse or weighted linear least squares problems, Applied Statistics, 23, 448-454.
Gibbons
Gibbons, J.D. (1971), Nonparametric Statistical Inference, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Girschick
Girschick, M.A. (1939), On the sampling theory of roots of determinantal equations, Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 10, 203-224.
Golub and Van Loan
Golub, Gene H. and Charles F. Van Loan (1983), Matrix Computations, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Md.
Gonin and Money
Gonin, Rene, and Arthur H. Money (1989), Nonlinear Lp-Norm Estimation, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Goodnight
Goodnight, James H. (1979), A tutorial on the SWEEP operator, The American Statistician, 33, 149-158.
Graybill
Graybill, Franklin A. (1976), Theory and Application of the Linear Model, Duxbury Press, North Scituate, Mass.
Griffin and Redish
Griffin, R. and K.A. Redish (1970), Remark on Algorithm 347:
An efficient algorithm for sorting with minimal storage, Communications of
the ACM,
13, 54.
Gross and Clark
Gross, Alan J., and Virginia A. Clark (1975), Survival Distributions: Reliability Applications in the Biomedical Sciences, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Gruenberger and Mark
Gruenberger, F., and A.M. Mark (1951), The d2 test of random digits, Mathematical Tables and Other Aids in Computation, 5, 109-110.
Guerra et al.
Guerra, Victor O., Richard A. Tapia, and James R. Thompson (1976), A random number generator for continuous random variables based on an interpolation procedure of Akima, in Proceedings of the Ninth Interface Symposium on Computer Science and Statistics, (edited by David C. Hoaglin and Roy E. Welsch), Prindle, Weber & Schmidt, Boston, 228−230.
Giudici
Giudici, P. (2003) Applied Data Mining: Statistical Methods for Business and Industry, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Haldane
Haldane, J.B.S. (1939), The mean and variance of when used as a test of homogeneity, when expectations are small, Biometrika, 31, 346.
Hamilton
Hamilton, James D., Time Series Analysis, Princeton University Press, Princeton (NewJersey), 1994.
Harman
Harman, Harry H. (1976), Modern Factor Analysis, 3d ed. revised, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Hart et al
Hart, John F., E.W. Cheney, Charles L. Lawson, Hans J. Maehly, Charles K. Mesztenyi, John R. Rice, Henry G. Thacher, Jr., and Christoph Witzgall (1968), Computer Approximations, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Hartigan
Hartigan, John A. (1975), Clustering Algorithms, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Hartigan and Wong
Hartigan, J.A. and M.A. Wong (1979), Algorithm AS 136: A K-means clustering algorithm, Applied Statistics, 28, 100-108.
Hayter
Hayter, Anthony J. (1984), A proof of the conjecture that the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons procedure is conservative, Annals of Statistics, 12, 61-75.
Hebb
Hebb, D. O. (1949) The Organization of Behaviour: A Neuropsychological Theory, John Wiley.
Heiberger
Heiberger, Richard M. (1978), Generation of random orthogonal matrices, Applied Statistics, 27, 199−206.
Hemmerle.
Hemmerle, William J. (1967), Statistical Computations on a Digital Computer, Blaisdell Publishing Company, Waltham, Mass.
Herraman
Herraman, C. (1968), Sums of squares and products matrix, Applied Statistics, 17, 289-292.
Hill
Hill, G.W. (1970), Student's t-distribution,
Communications of the ACM, 13,
617-619.
Hill, G.W. (1970), Student's t-quantiles,
Communications of the ACM, 13,
619-620.
Hinkelmann, K and Kemthorne
Hinkelmann, K and Kemthorne, O (1994) Design and Analysis of Experiments – Vol 1, John Wiley.
Hinkley
Hinkley, David (1977), On quick choice of power transformation, Applied Statistics, 26, 67-69.
Hoaglin and Welsch
Hoaglin, David C. and Roy E. Welsch (1978), The hat matrix in regression and ANOVA, The American Statistician, 32, 17-22.
Hocking
Hocking, R.R. (1972), Criteria for selection of a subset regression: Which one should be used?, Technometrics, 14, 967-970.
Hocking, R.R. (1973), A discussion of the two-way mixed model, The American Statistician, 27, 148−152.
Hocking, R.R. (1985), The Analysis of Linear Models, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company, Monterey, California.
Hopfield
Hopfield, J. J. (1987) Learning Algorithms and Probability Distributions in Feed-Forward and Feed-Back Networks, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 84, 8429-8433.
Huber
Huber, Peter J. (1981), Robust Statistics, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Hutchinson
Hutchinson, J. M. (1994) A Radial Basis Function Approach to Financial Timer Series Analysis, Ph.D. dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Hughes and Saw
Hughes, David T., and John G. Saw (1972), Approximating the
percentage points of Hotelling’s generalized 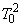 statistic, Biometrika,
59, 224−226.
statistic, Biometrika,
59, 224−226.
Hwang
Hwang, J. T. G. and Ding, A. A. (1997) Prediction Intervals for Artificial Neural Networks, Journal of the American Statistical Society, 92(438) 748-757.
Iman and Davenport
Iman, R.L., and J.M. Davenport (1980), Approximations of the
critical region of the Friedman statistic, Communications in Statistics,
A9(6),
571-595.
Jacobs
Jacobs, R. A., Jorday, M. I., Nowlan, S. J., and Hinton, G. E. (1991) Adaptive Mixtures of Local Experts, Neural Computation, 3(1), 79-87.
Jennrich and Robinson
Jennrich, R.I. and S.M. Robinson (1969), A Newton-Raphson algorithm for maximum likelihood factor analysis, Psychometrika, 34, 111-123.
Jennrich and Sampson
Jennrich, R.I. and P.F. Sampson (1966), Rotation for simple loadings, Psychometrika, 31, 313–323.
John
John, Peter W.M. (1971), Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments, Macmillan Company, New York.
Jöhnk
Jöhnk, M.D. (1964), Erzeugung von Betaverteilten und Gammaverteilten Zufallszahlen, Metrika, 8, 5-15.
Johnson and Kotz
Johnson, Norman L., and Samuel Kotz (1969), Discrete Distributions, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston.
Johnson, Norman L., and Samuel Kotz (1970a), Continuous Univariate Distributions-1, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Johnson, Norman L., and Samuel Kotz (1970b), Continuous Univariate Distributions-2, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Johnson and Welch
Johnson, D.G., and W.J. Welch (1980), The generation of
pseudo-random correlation matrices, Journal of Statistical Computation and
Simulation, 11,
55−69.
Jonckheere
Jonckheere, A.R. (1954), A distribution-free k-sample test against ordered alternatives, Biometrika, 41, 133-143.
Jöreskog
Jöreskog, K.G. (1977), Factor analysis by least squares and
maximum-likelihood methods, Statistical Methods for Digital Computers,
(edited by Kurt Enslein, Anthony Ralston, and Herbert S. Wilf), John Wiley &
Sons, New York,
125-153.
Kachitvichyanukul
Kachitvichyanukul, Voratas (1982), Computer generation of Poisson, binomial, and hypergeometric random variates, Ph.D. dissertation, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana.
Kaiser
Kaiser, H.F. (1963), Image analysis, Problems in Measuring Change, (edited by C. Harris), University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, Wis.
Kaiser and Caffrey
Kaiser, H.F. and J. Caffrey (1965), Alpha factor analysis,
Psychometrika, 30,
1-14.
Kalbfleisch and Prentice
Kalbfleisch, John D., and Ross L. Prentice (1980), The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Kemp
Kemp, A.W., (1981), Efficient generation of logarithmically distributed pseudo-random variables, Applied Statistics, 30, 249-253.
Kendall and Stuart
Kendall, Maurice G. and Alan Stuart (1973), The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 2: Inference and Relationship, 3d ed., Charles Griffin & Company, London.
Kendall, Maurice G. and Alan Stuart (1979), The Advanced
Theory of Statistics,
Volume 2: Inference and Relationship, 4th
ed., Oxford University Press, New York.
Kendall et al.
Kendall, Maurice G., Alan Stuart, and J. Keith Ord (1983), The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 3: Design and Analysis, and Time Series, 4th. ed., Oxford University Press, New York.
Kennedy and Gentle
Kennedy, William J., Jr. and James E. Gentle (1980), Statistical Computing, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Kohonen
Kohonen, T. (1995), Self-Organizing Maps, Third Edition. Springer Series in Information Sciences., New York.
Kuehl, R. O.
Kuehl, R. O. (2000) Design of Experiments: Statistical Principles of Research Design and Analysis, 2nd edition, Duxbury Press.
Kim and Jennrich
Kim, P.J., and R.I. Jennrich (1973), Tables of the exact sampling distribution of the two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion Dmn (m < n), in Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics, Volume 1, (edited by H. L. Harter and D.B. Owen), American Mathematical Society, Providence, Rhode Island.
Kinderman and Ramage
Kinderman, A.J., and J.G. Ramage (1976), Computer generation of normal random variables, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 71, 893−896.
Kinderman et al.
Kinderman, A.J., J.F. Monahan, and J.G. Ramage (1977),
Computer methods for sampling from Student’s t distribution,
Mathematics of Computation 31,
1009−1018.
Kinnucan and Kuki
Kinnucan, P. and H. Kuki (1968), A Single Precision INVERSE Error Function Subroutine, Computation Center, University of Chicago.
Kirk
Kirk, Roger E. (1982), Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences, 2d ed., Brooks/Cole Publishing Company, Monterey, Calif.
Kitagawa and Akaike
Kitagawa, G. and Akaike, H., A Procedure for the modeling of non-stationary time series, Ann. Inst. Statist. Math. 30 (1978), Part B, 351-363.
Knuth
Knuth, Donald E. (1981), The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 2: Seminumerical Algorithms, 2d ed., Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass.
Kshirsagar
Kshirsagar, Anant M. (1972), Multivariate Analysis, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Lachenbruch
Lachenbruch, Peter A. (1975), Discriminant Analysis, Hafner Press, London.
Lai
Lai, D. (1998a), Local asymptotic normality for location-scale type processes. Far East Journal of Theorectical Statistics, (in press).
Lai, D. (1998b), Asymptotic distributions of the correlation integral based statistics. Journal of Nonparametric Statistics, (in press).
Lai, D. (1998c), Asymptotic distributions of the estimated
BDS statistic and residual analysis of AR Models on the Canadian lynx data.
Journal
of Biological Systems, (in press).
Laird and Oliver
Laird, N.M., and D. Fisher (1981), Covariance analysis of censored survival data using log-linear analysis techniques, JASA 76, 1231−1240.
Lawless
Lawless, J.F. (1982), Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Lawley and Maxwell
Lawley, D.N. and A.E. Maxwell (1971), Factor Analysis as a Statistical Method, 2d ed., Butterworth, London.
Lawrence et al
Lawrence, S., Giles, C. L, Tsoi, A. C., Back, A. D. (1997) Face Recognition: A Convolutional Neural Network Approach, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, Special Issue on Neural Networks and Pattern Recognition, 8(1), 98-113.
Learmonth and Lewis
Learmonth, G.P. and P.A.W. Lewis (1973), Naval Postgraduate School Random Number Generator Package LLRANDOM, NPS55LW73061A, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif.
Lee
Lee, Elisa T. (1980), Statistical Methods for Survival Data Analysis, Lifetime Learning Publications, Belmont, Calif.
Lehmann
Lehmann, E.L. (1975), Nonparametrics: Statistical Methods Based on Ranks, Holden-Day, San Francisco.
Levenberg
Levenberg, K. (1944), A method for the solution of certain problems in least squares, Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 2, 164-168.
Levene, H.
Levene, H. (1960) In Contributions to Probability and Statistics: Essays in Honor of Harold Hotelling, I. Olkin et al. editors, Stanford University Press, 278-292.
Lewis et al.
Lewis, P.A.W., A.S. Goodman, and J.M. Miller (1969), A pseudorandom number generator for the System/360, IBM Systems Journal, 8, 136-146.
Li
Li, L. K. (1992) Approximation Theory and Recurrent Networks, Proc. Int. Joint Conf. On Neural Networks, vol. II, 266-271.
Liffiefors
Lilliefors, H.W. (1967), On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 62, 534-544.
Lippmann
Lippmann, R. P. (1989) Review of Neural Networks for Speech Recognition, Neural Computation, I, 1-38.
Ljung and Box
Ljung, G.M., and G.E.P. Box (1978), On a measure of lack of fit in time series models, Biometrika, 65, 297–303.
Loh
Loh, W.-Y. and Shih, Y.-S. (1997) Split Selection Methods for Classification Trees, Statistica Sinica, 7, 815-840. For information on the latest version of QUEST see http://www.stat.wisc.edu/~loh/quest.html.
Longley
Longley, James W. (1967), An appraisal of least-squares programs for the electronic computer from the point of view of the user, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 62, 819-841.
Matsumoto and Nishimure
Makoto Matsumoto and Takuji Nishimura, ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation, Vol. 8, No. 1, January 1998, Pages 3–30.
Mandic
Mandic, D. P. and Chambers, J. A. (2001) Recurrent Neural Networks for Prediction, John Wiley & Sons, LTD.
Manning
Manning, C. D. and Schütze, H. (1999) Foundations of Statistical Natural Language Processing, MIT Press.
Marsaglia
Marsaglia, George (1964), Generating a variable from the tail of a normal distribution, Technometrics, 6, 101−102.
Marsaglia, G. (1968), Random numbers fall mainly in the planes, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 61, 25−28.
Marsaglia, G. (1972), The structure of linear congruential sequences, in Applications of Number Theory to Numerical Analysis, (edited by S. K. Zaremba), Academic Press, New York, 249−286.
Marsaglia, George (1972), Choosing a point from the surface
of a sphere,
The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 43,
645−646.
McCulloch
McCulloch, W. S. and Pitts, W. (1943) A Logical Calculus for Ideas Imminent in Nervous Activity, Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 5, 115-133.
McKean and Schrader
McKean, Joseph W., and Ronald M. Schrader (1987), Least
absolute errors analysis of variance, in Statistical Data Analysis Based on
the L1-Norm and Related
Methods (edited by Yadolah Dodge), North-Holland, Amsterdam,
297−305.
McKeon
McKeon, James J. (1974), F approximations to the
distribution of Hotelling’s 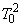 ,
Biometrika, 61, 381−383.
,
Biometrika, 61, 381−383.
McCullagh and Nelder
McCullagh, P., and J.A. Nelder, (1983), Generalized Linear Models, Chapman and Hall, London.
Maindonald
Maindonald, J.H. (1984), Statistical Computation, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Marazzi
Marazzi, Alfio (1985), Robust affine invariant covariances in ROBETH, ROBETH-85 document No. 6, Division de Statistique et Informatique, Institut Universitaire de Medecine Sociale et Preventive, Laussanne.
Mardia et al.
Mardia, K.V. (1970), Measures of multivariate skewness and kurtosis with applications, Biometrics, 57, 519−530.
Mardia, K.V., J.T. Kent, J.M. Bibby (1979), Multivariate Analysis, Academic Press, New York.
Mardia and Foster
Mardia, K.V. and K. Foster (1983), Omnibus tests of multinormality based on skewness and kurtosis, Communications in Statistics A, Theory and Methods, 12, 207−221.
Marquardt
Marquardt, D. (1963), An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters, SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 11, 431-441.
Marsaglia
Marsaglia, George (1964), Generating a variable from the tail of a normal distribution, Technometrics, 6, 101−102.
Marsaglia and Bray
Marsaglia, G. and T.A. Bray (1964), A convenient method for generating normal variables, SIAM Review, 6, 260−264.
Marsaglia et al.
Marsaglia, G., M.D. MacLaren, and T.A. Bray (1964), A fast procedure for generating normal random variables, Communications of the ACM, 7, 4−10.
Merle and Spath
Merle, G., and H. Spath (1974), Computational experiences with discrete Lp approximation, Computing, 12, 315−321.
Miller
Miller, Rupert G., Jr. (1980), Simultaneous Statistical Inference, 2d ed., Springer-Verlag, New York.
Milliken and Johnson
Milliken, George A. and Dallas E. Johnson (1984), Analysis of Messy Data, Volume 1: Designed Experiments, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York.
Moran
Moran, P.A.P. (1947), Some theorems on time series I,
Biometrika, 34,
281-291.
Moré et al.
Moré, Jorge, Burton Garbow, and Kenneth Hillstrom (1980), User Guide for [4] MINPACK-1, Argonne National Laboratory Report ANL-80_74, Argonne, Ill.
Morrison
Morrison, Donald F. (1976), Multivariate Statistical Methods, 2nd. ed. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York.
Muller
Muller, M.E. (1959), A note on a method for generating
points uniformly on
N-dimensional spheres, Communications of the ACM,
2, 19−20.
Nelson
Nelson, D. B. (1991), Conditional heteroskedasticity in asset returns: A new approach. Econometrica, , 59, 347-370.
Nelson
Nelson, Peter (1989), Multiple Comparisons of Means Using Simultaneous Confidence Intervals, Journal of Quality Technology, 21, 232-241.
Neter
Neter, John (1983), Applied Linear Regression Models, Richard D. Irwin, Homewood, Ill.
Neter and Wasserman
Noether
Noether, G.E. (1956), Two sequential tests against trend, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 51, 440-450.
Owen
Owen, D.B. (1962), Handbook of Statistical Tables, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, Mass.
Owen, D.B. (1965), A special case of the bivariate non-central t distribution, Biometrika, 52, 437-446.
Ozaki and Oda
Ozaki, T and Oda H (1978) Nonlinear time series model identification by Akaike's information criterion. Information and Systems, Dubuisson eds, Pergamon Press. 83-91.
Pao
Pao, Y. (1989) Adaptive Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks, Addison-Wesley Publishing.
Palm
Palm, F. C. (1996), GARCH models of volatility. In
Handbook of Statistics,
Vol. 14, 209-240. Eds: Maddala and Rao.
Elsevier,New York.
Parker
Parker, D. B., (1985), Learning Logic. Technical Report TR-47, Cambridge, MA: MIT Center for Research in computational Economics and Management Science.
Patefield
Patefield, W.M. (1981), An efficient method of generating R ´ C tables with given row and column totals, Applied Statistics, 30, 91−97.
Patefield and Tandy
Patefield, W.M. (1981), and Tandy D. (2000) Fast and Accurate Calculation of Owen’s T-Function, J. Statistical Software, 5, Issue 5.
Peixoto
Peixoto, Julio L. (1986), Testable hypotheses in singular
fixed linear models, Communications in Statistics: Theory and Methods,
15,
1957-1973.
Petro
Petro, R. (1970), Remark on Algorithm 347: An efficient algorithm for sorting with minimal storage, Communications of the ACM, 13, 624.
Pillai
Pillai, K.C.S. (1985), Pillai’s trace, in Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, Volume 6, (edited by Samuel Kotz and Norman L. Johnson), John Wiley & Sons, New York, 725-729.
Poli
Poli, I. and Jones, R. D. (1994) A Neural Net Model for Prediction, Journal of the American Statistical Society, 89(425) 117-121.
Pregibon
Pregibon, Daryl (1981), Logistic regression diagnostics, The Annals of Statistics, 9, 705-724.
Prentice
Prentice, Ross L. (1976), A generalization of the probit and logit methods for dose response curves, Biometrics, 32, 761-768.
Priestley
Priestley, M.B. (1981), Spectral Analysis and Time Series, Volumes 1 and 2, Academic Press, New York.
Quinlan
Quinlan, J. R. (1993). C4.5 Programs for Machine Learning, Morgan Kaufmann. For the latest information on Quinlan’s algorithms see http://www.rulequest.com/.
Rao
Rao, C. Radhakrishna (1973), Linear Statistical Inference and Its Applications, 2d ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Reed
Reed, R. D. and Marks, R. J. II (1999) Neural Smithing: Supervised Learning in Feedforward Artificial Neural Networks, The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Ripley
Ripley, B. D. (1994) Neural Networks and Related Methods for Classification, Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 56(3), 409-456.
Ripley, B. D. (1996) Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks, Cambridge University Press.
Robinson
Robinson, Enders A. (1967), Multichannel Time Series Analysis with Digital Computer Programs, Holden-Day, San Francisco.
Rosenblatt
Rosenblatt, F. (1958) The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model for Information Storage and Organization in the Brain, Psychol. Rev., 65, 386-408.
Royston
Royston, J.P. (1982a), An extension of Shapiro and Wilk's W test for normality to large samples, Applied Statistics, 31, 115-124.
Royston, J.P. (1982b), The W test for normality, Applied Statistics, 31, 176-180.
Royston, J.P. (1982c), Expected normal order statistics (exact and approximate), Applied Statistics, 31, 161-165.
Rumelhart
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E. and Williams, R. J. (1986) Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors, Nature, 323, 533-536.
Rumelhart, D. E. and McClelland, J. L. eds. (1986) Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, 1, 318-362, MIT Press.
Sallas
Sallas, William M. (1990), An algorithm for an Lp norm fit of a multiple linear regression model, American Statistical Association 1990 Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section, 131−136.
Sallas and Lionti
Sallas, William M. and Abby M. Lionti (1988), Some useful computing formulas for the nonfull rank linear model with linear equality restrictions, IMSL Technical Report 8805, IMSL, Houston.
Savage
Savage, I. Richard (1956), Contributions to the theory of rank order statistics-the two-sample case, Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 27, 590-615.
Scheffe
Scheffe, Henry (1959), The Analysis of Variance, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Schmeiser
Schmeiser, Bruce (1983), Recent advances in generating observations from discrete random variates, Computer Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the Fifteenth Symposium on the Interface, (edited by James E. Gentle), North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 154-160.
Schmeiser and Babu
Schmeiser, Bruce W. and A.J.G. Babu (1980), Beta variate generation via exponential majorizing functions, Operations Research, 28, 917-926.
Schmeiser and Kachitvichyanukul
Schmeiser, Bruce and Voratas Kachitvichyanukul (1981), Poisson Random Variate Generation, Research Memorandum 81-4, School of Industrial Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Ind.
Schmeiser and Lal
Schmeiser, Bruce W. and Ram Lal (1980), Squeeze methods for generating gamma variates, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 75, 679-682.
Searle
Searle, S.R. (1971), Linear Models, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Seber
Seber, G.A.F. (1984), Multivariate Observations, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Snedecor and Cochran
Snedecor and Cochran (1967) Statistical Methods, 6th edition, Iowa State University Press.
Snedecor, George W. & Cochran, William G.
Snedecor, George W. and Cochran, William G. (1967) Statistical Methods, 6th edition, Iowa State University Press, 296-298.
Shampine
Shampine, L.F. (1975), Discrete least-squares polynomial fits, Communications of the ACM, 18, 179-180.
Siegal
Siegal, Sidney (1956), Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Singleton
Singleton, R.C. (1969), Algorithm 347: An efficient algorithm for sorting with minimal storage, Communications of the ACM, 12, 185-187.
Smirnov
Smirnov, N.V. (1939), Estimate of deviation between empirical distribution functions in two independent samples (in Russian), Bulletin of Moscow University, 2, 3-16.
Smith and Dubey
Smith, H., and S. D. Dubey (1964), "Some reliability problems in the chemical industry", Industrial Quality Control, 21 (2), 1964, 64-70.
Smith
Smith, M. (1993) Neural Networks for Statistical Modeling, New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Snedecor and Cochran
Snedecor, George W. and William G. Cochran (1967), Statistical Methods, 6th ed., Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa.
Sposito
Sposito, Vincent A. (1989), Some properties of Lp-estimators, in Robust Regression: Analysis and Applications (edited by Kenneth D. Lawrence and Jeffrey L. Arthur), Marcel Dekker, New York, 23−58.
Spurrier and Isham
Spurrier, John D. and Steven P. Isham (1985), Exact simultaneous confidence intervals for pairwise comparisons of three normal means, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 80, 438-442.
Stablein, Carter, and Novak
Stablein, D.M, W.H. Carter, and J.W. Novak (1981), Analysis of survival data with nonproportional hazard functions, Controlled Clinical Trials, 2, 149–159.
Stahel
Stahel, W. (1981), Robuste Schatzugen: Infinitesimale Opimalitat und Schatzugen von Kovarianzmatrizen, Dissertation no. 6881, ETH, Zurich.
Steel and Torrie
Steel and Torrie (1960) Principles and Procedures of Statistics, McGraw-Hill.
Stephens
Stephens, M.A. (1974), EDF statistics for goodness of fit and some comparisons, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 69, 730-737.
Stirling
Stirling, W.D. (1981), Least squares subject to linear constraints, Applied Statistics, 30, 204-212. (See correction, p. 357.)
Stoline
Stoline, Michael R. (1981), The status of multiple
comparisons: simultaneous estimation of all pairwise comparisons in one-way
ANOVA designs,
The American Statistician, 35, 134-141.
Strecok
Strecok, Anthony J. (1968), On the calculation of the inverse of the error function, Mathematics of Computation, 22, 144-158.
Studenmund
Studenmund, A. H. (1992) Using Economics: A Practical Guide, New York: Harper Collins.
Swingler
Swingler, K. (1996) Applying Neural Networks: A Practical Guide, Academic Press.
Tanner and Wong
Tanner, Martin A., and Wing H. Wong (1983), The estimation of the hazard function from randomly censored data by the kernel method, Annals of Statistics, 11, 989–993.
Tanner, Martin A., and Wing H. Wong (1984), Data-based nonparametric estimation of the hazard function with applications to model diagnostics and exploratory analysis, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 79, 123–456.
Taylor and Thompson
Taylor, Malcolm S., and James R. Thompson (1986), Data based random number generation for a multivariate distribution via stochastic simulation, Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 4, 93−101.
Tesauro
Tesauro, G. (1990) Neurogammon Wins Computer Olympiad, Neural Computation, 1, 321-323.
Tezuka
Tezuka, S. (1995), Uniform Random Numbers: Theory and Practice. Academic Publishers, Boston.
Thompson
Thompson, James R, (1989), Empirical Model Building, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Tucker and Lewis
Tucker, Ledyard and Charles Lewis (1973), A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis, Psychometrika, 38, 1-10.
Tukey
Tukey, John W. (1962), The future of data analysis, Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 33, 1-67.
Velleman and Hoaglin
Velleman, Paul F. and David C. Hoaglin (1981), Applications, Basics, and Computing of Exploratory Data Analysis, Duxbury Press, Boston.
Verdooren
Verdooren, L. R. (1963), Extended tables of critical values for Wilcoxon's test statistic, Biometrika, 50, 177-186.
Wallace
Wallace, D.L. (1959), Simplified Beta-approximations to the Kruskal-Wallis H-test, Journal of the American Statistical Association, 54, 225-230.
Warner
Warner, B. and Misra, M. (1996) Understanding Neural Networks as Statistical Tools, The American Statistician, 50(4) 284-293.
Weisberg
Weisberg, S. (1985), Applied Linear Regression, 2d ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Werbos
Werbos, P. (1974) Beyond Regression: New Tools for Prediction and Analysis in the Behavioral Science, PhD thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA.
Werbos, P. (1990) Backpropagation Through Time: What It Does and How to do It, Proc. IEEE, 78, 1550-1560.
Williams
Williams, R. J. and Zipser, D. (1989) A Learning Algorithm for Continuously Running Fully Recurrent Neural Networks, Neural Computation, 1, 270-280.
Witten
Witten, I. H. and Frank, E. (2000) Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques with Java Implementations, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Woodfield
Woodfield, Terry J. (1990), Some notes on the Ljung-Box portmanteau statistic, American Statistical Association 1990 Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section, 155–160.
Wu
Wu, S-I (1995) Mirroring Our Thought Processes, IEEE Potentials, 14, 36-41.
Yates, F.
Yates, F. (1936) A new method of arranging variety trials involving a large number of varieties. Journal of Agricultural Science, 26, 424-455.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |