.p>.CSCH11.DOC!POISSON_CDF;poisson_cdf
Evaluates the Poisson distribution function.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_poisson_cdf (int k, float theta)
The type double function is imsls_d_poisson_cdf.
Required Arguments
int k
(Input)
Argument for which the Poisson distribution function is to be
evaluated.
float theta
(Input)
Mean of the Poisson distribution. Argument theta must be
positive.
Return Value
The probability that a Poisson random variable takes a
value less than or equal
to k.
Description
Function imsls_f_poisson_cdf evaluates the distribution function of a Poisson random variable with parameter theta. The mean of the Poisson random variable, theta, must be positive. The probability function (with θ = theta) is as follows:
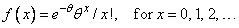
The individual terms are calculated from the tails of the distribution to the mode of the distribution and summed. Function imsls_f_poisson_cdf uses the recursive relationship
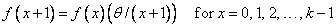
with f (0) = e−q.
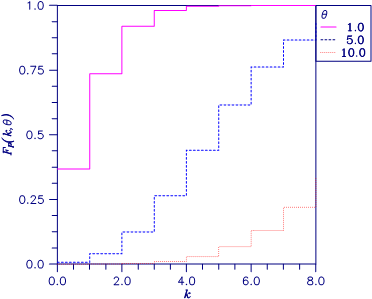
Figure 11-1 Plot of Fp (k, θ)
Example
Suppose X is a Poisson random variable with θ = 10. In this example, we evaluate the probability that X is less than or equal to 7.
#include <imsls.h>
void
main()
{
int k = 7;
float theta = 10.0;
float p;
p =
imsls_f_poisson_cdf(k, theta);
printf("Pr(x <= 7) =
%6.4f\n", p);
}
Output
Pr(x <= 7) = 0.2202
Informational Errors
IMSLS_LESS_THAN_ZERO Since “k” = # is less than zero, the distribution function is set to zero.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |