Computes the SVD, A = USVT, of a real rectangular matrix A. An approximate generalized inverse and rank of A also can be computed.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (int m, int n, float a[], …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_lin_svd_gen.
Required Arguments
int m
(Input)
Number of rows in the matrix.
int n
(Input)
Number of columns in the matrix.
float a[]
(Input)
Array of size m × n containing the
matrix.
Return Value
If no optional arguments are used, imsl_f_lin_svd_gen returns a pointer to an array of size min (m, n) containing the ordered singular values of the matrix. To release this space, use imsl_free. If no value can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (int
m, int n, float
a[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int
a_col_dim,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
s[],
IMSL_RANK, float
tol,
int
*rank,
IMSL_U, float
**p_u,
IMSL_U_USER, float
u[],
IMSL_U_COL_DIM, int
u_col_dim,
IMSL_V, float
**p_v,
IMSL_V_USER, float
v[],
IMSL_V_COL_DIM, int
v_col_dim,
IMSL_INVERSE, float
**p_gen_inva,
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, float
gen_inva[],
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
gen_inva_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array a.
Default: a_col_dim = n
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float s[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array of size min (m+1, n) containing
the singular values of A in its first min (m, n) positions
in nonincreasing order. If IMSL_RETURN_USER is
used, the return value of imsl_f_lin_svd_gen is
s.
IMSL_RANK, float tol, int *rank (Input/Output)
tol: Scalar containing
the tolerance used to determine when a singular value is negligible and replaced
by the value zero. If tol > 0,
then a singular value si i is considered
negligible if i.i ≤ tol. If tol < 0,
then a singular value
si.i is considered
negligible if si.i ≤ |tol|*||A||∝. In this case, |tol| should be
an
estimate of relative error or uncertainty in the data.
*rank: Integer containing an estimate of the rank of A.
IMSL_U, float **p_u
(Output)
**p_u: The address of
a pointer to an array of size m × min (m, n)
containing the min (m, n) left-singular vectors of A.
On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_u is declared, and
&p_u is used
as an argument.
IMSL_U_USER, float u[]
(Output)
u[]:
The address of a pointer to an array of size
m × min (m, n) containing the
min (m, n) left-singular vectors of A. If
m ³ n, the
left-singular vectors can be returned using the storage locations of the array
a.
IMSL_U_COL_DIM, int u_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array containing the left-singular
vectors.
Default: u_col_dim = min
(m, n)
IMSL_V, float **p_v
(Output)
**p_v: The address of
a pointer to an array of size n × n containing the right
singular vectors of A. On return, the necessary space is allocated by
imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_v is declared, and
&p_v is used
as an argument.
IMSL_V_USER, float v[]
(Output)
v[]:
The address of a pointer to an array of size n × n
containing the right singular vectors of A. The right-singular vectors
can be returned using the storage locations of the array a. Note that the
return of the left- and right-singular vectors cannot use the storage locations
of a
simultaneously.
IMSL_V_COL_DIM, int v_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the array containing the right-singular
vectors.
Default: v_col_dim =
n
IMSL_INVERSE, float
**p_gen_inva (Output)
The address of a pointer to an array
of size n × m containing the generalized inverse of the
matrix A. On return, the necessary space is allocated by imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
Typically, float *p_gen_inva is
declared, and &p_gen_inva is
used as an argument.
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, float
gen_inva[] (Output)
A user-allocated array of size
n × m containing the general inverse of the matrix
A.
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, int
gen_inva_col_dim (Input)
The column dimension of the array
containing the general inverse of the matrix A.
Default: gen_inva_col_dim = m
Description
The function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen
computes the singular value decomposition of a real matrix A. It first
reduces the matrix A to a bidiagonal matrix B by pre- and
post-multiplying Householder transformations. Then, the singular value
decomposition of
B is computed using the implicit-shifted QR
algorithm. An estimate of the rank of the matrix A is obtained by finding
the smallest integer k such that sk,k ≤ tol
or sk,k ≤ |tol|*||A||∝. Since si+1,i+1
≤ si,i, it follows that all
the si,i satisfy the
same inequality for i = k, …, min (m,
n) − 1.
The rank is set to the value k − 1. If
A = USVT, its generalized
inverse is A+ = VS+ UT. Here,
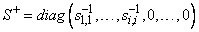
Only singular values that are not negligible are reciprocated. If IMSL_INVERSE or IMSL_INVERSE_USER is specified, the function first computes the singular value decomposition of the matrix A. The generalized inverse is then computed. The function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen fails if the QR algorithm does not converge after 30 iterations isolating an individual singular value.
Examples
Example 1
This example computes the singular values of a real 6 × 4 matrix.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] = {1.0, 2.0, 1.0, 4.0,
3.0, 2.0, 1.0, 3.0,
4.0, 3.0, 1.0, 4.0,
2.0, 1.0, 3.0, 1.0,
1.0, 5.0, 2.0, 2.0,
1.0, 2.0, 2.0, 3.0};
int main()
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
float *s;
/* Compute singular values */
s = imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m, n, a, 0);
/* Print singular values */
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Singular values", 1, n, s, 0);
}
Output
Singular values
1 2 3 4
11.49 3.27 2.65 2.09
Example 2
This example computes the singular value decomposition of the 6 × 4 real matrix A. The singular values are returned in the user-provided array. The matrices U and V are returned in the space provided by the function imsl_f_lin_svd_gen.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] = {1.0, 2.0, 1.0, 4.0,
3.0, 2.0, 1.0, 3.0,
4.0, 3.0, 1.0, 4.0,
2.0, 1.0, 3.0, 1.0,
1.0, 5.0, 2.0, 2.0,
1.0, 2.0, 2.0, 3.0};
int main()
{
int m = 6, n = 4;
float s[4], *p_u, *p_v;
/* Compute SVD */
imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m, n, a,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, s,
IMSL_U, &p_u,
IMSL_V, &p_v,
0);
/* Print decomposition*/
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Singular values, S", 1, n, s, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Left singular vectors, U", m, n, p_u, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Right singular vectors, V", n, n, p_v, 0);
}
Output
Singular values, S
1 2 3 4
11.49 3.27 2.65 2.09
Left singular vectors, U
1 2 3 4
1 -0.3805 0.1197 0.4391 -0.5654
2 -0.4038 0.3451 -0.0566 0.2148
3 -0.5451 0.4293 0.0514 0.4321
4 -0.2648 -0.0683 -0.8839 -0.2153
5 -0.4463 -0.8168 0.1419 0.3213
6 -0.3546 -0.1021 -0.0043 -0.5458
Right singular vectors, V
1 2 3 4
1 -0.4443 0.5555 -0.4354 0.5518
2 -0.5581 -0.6543 0.2775 0.4283
3 -0.3244 -0.3514 -0.7321 -0.4851
4 -0.6212 0.3739 0.4444 -0.5261
Example 3
This example computes the rank and generalized inverse of a 3 × 2 matrix A. The rank and the 2 × 3 generalized inverse matrix A+ are printed.
#include <imsl.h>
float a[] = {1.0, 0.0,
1.0, 1.0,
100.0, -50.0};
int main()
{
int m = 3, n = 2;
float tol;
float gen_inva[6];
float *s;
int *rank;
/* Compute generalized inverse */
tol = 1.e-4;
s = imsl_f_lin_svd_gen (m, n, a,
IMSL_RANK, tol, &rank,
IMSL_INVERSE_USER, gen_inva,
IMSL_INV_COL_DIM, m,
0);
/* Print rank, singular values and */
/* generalized inverse. */
printf ("Rank of matrix = %2d", rank);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Singular values", 1, n, s, 0);
imsl_f_write_matrix ("Generalized inverse", n, m, gen_inva,
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, m,
0);
}
Output
Rank of matrix = 2
Singular values
1 2
111.8 1.4
Generalized inverse
1 2 3
1 0.100 0.300 0.006
2 0.200 0.600 -0.008
Warning Errors
IMSL_SLOWCONVERGENT_MATRIX Convergence cannot be reached after 30 iterations.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |
