Computes the sample variance-covariance or correlation matrix.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_covariances (int n_rows, int n_variables, float x[], ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_covariances.
Required Arguments
int n_rows
(Input)
Number of rows in x.
int
n_variables (Input)
Number of variables.
float x[]
(Input)
Array of size n_rows × n_variables containing
the data.
Return Value
If no optional arguments are used, imsls_f_covariances returns a pointer to an n_variables × n_variables array containing the sample variance-covariance matrix of the observations. The rows and columns of this array correspond to the columns of x.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_covariances (int
n_rows,
int
n_variables, float x[],
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, int
x_col_dim,
IMSLS_MISSING_VALUE_METHOD, int
missing_value_method,
IMSLS_INCIDENCE_MATRIX, int
**incidence_matrix,
IMSLS_INCIDENCE_MATRIX_USER, int
incidence_matrix[],
IMSLS_N_OBSERVATIONS, int
*n_observations,
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX,
or
IMSLS_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX, or
IMSLS_CORRELATION_MATRIX, or
IMSLS_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX,
IMSLS_MEANS, float
**means,
IMSLS_MEANS_USER, float
means[],
IMSLS_COVARIANCE_COL_DIM, int
covariance_col_dim,
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES, float
frequencies[],
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float
weights[],
IMSLS_SUM_WEIGHTS, float
*sumwt,
IMSLS_N_ROWS_MISSING, int
*nrmiss,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
covariance[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, int x_col_dim
(Input)
Column dimension of array x.
Default:
x_col_dim = n_variables
IMSLS_MISSING_VALUE_METHOD, int
missing_value_method (Input)
Method used to exclude
missing values in x from the
computations, where NaN is interpreted as the missing value code. See function
imsls_f_machine/imsls_d_machine
(Chapter 15, “Utilities”). The methods are as follows:
|
Missing_value_method |
Action |
|
0 |
The exclusion is listwise. (The entire row of x is excluded if any of the values of the row is equal to the missing value code.) |
|
1 |
Raw crossproducts are computed from all valid pairs and means, and variances are computed from all valid data on the individual variables. Corrected crossproducts, covariances, and correlations are computed using these quantities. |
|
2 |
Raw crossproducts, means, and variances are computed as in the case of missing_value_method = 1. However, corrected crossproducts and covariances are computed only from the valid pairs of data. Correlations are computed using these covariances and the variances from all valid data. |
|
3 |
Raw crossproducts, means, variances, and covariances are computed as in the case of missing_value_method = 2. Correlations are computed using these covariances, but the variances used are computed from the valid pairs of data. |
IMSLS_INCIDENCE_MATRIX, int
**incidence_matrix (Output)
Address of a pointer to an
internally allocated array containing the incidence matrix. If missing_value_method
is 0, incidence_matrix is
1 × 1 and
contains the number of valid observations; otherwise, incidence_matrix is
n_variables × n_variables and
contains the number of pairs of valid observations used in calculating the
crossproducts for covariance.
IMSLS_INCIDENCE_MATRIX_USER, int
incidence_matrix[] (Output)
Storage for array incidence_matrix is
provided by the user. See IMSLS_INCIDENCE_MATRIX.
IMSLS_N_OBSERVATIONS, int
*n_observations (Output)
Sum of the frequencies. If missing_value_method
is 0, observations with missing values are not included in n_observations;
otherwise, all observations are included except for observations with missing
values for the weight or the frequency.
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX, or
IMSLS_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX, or
IMSLS_CORRELATION_MATRIX, or
IMSLS_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX
Exactly
one of these options can be used to specify the type of matrix to be
computed.
|
Keyword |
Type of Matrix |
|
IMSLS_VARIANCE_COVARIANCE_MATRIX |
variance-covariance matrix (default) |
|
IMSLS_CORRECTED_SSCP_MATRIX |
corrected sums of squares and crossproducts matrix |
|
IMSLS_CORRELATION_MATRIX |
correlation matrix |
|
IMSLS_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX |
correlation matrix except for the diagonal elements which are the standard deviations |
IMSLS_MEANS, float **means
(Output)
Address of a pointer to the internally allocated array containing
the means of the variables in x. The components of
the array correspond to the columns of x.
IMSLS_MEANS_USER, float means[]
(Output)
Storage for array means is provided by the user. See IMSLS_MEANS.
IMSLS_COVARIANCE_COL_DIM, int
covariance_col_dim (Input)
Column dimension of array
covariance if IMSLS_RETURN_USER is
specified; otherwise, the column dimension of the return
value.
Default: covariance_col_dim = n_variables
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES, float
frequencies[] (Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the frequency for each observation.
Default: frequencies [ ] = 1
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float weights[]
(Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the weight for each observation.
Default: weights [ ] = 1
IMSLS_SUM_WEIGHTS, float *sum_wt
(Output)
Sum of the weights of all observations. If missing_value_method
is equal to 0, observations with missing values are not included in sum_wt. Otherwise, all
observations are included except for observations with mssing values for
the weight or the frequency.
IMSLS_N_ROWS_MISSING, int *nrmiss
(Output)
Total number of observations that contain any missing values
(NaN).
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
covariance[] (Output)
If specified, the output is
stored in the array covariance of size n_variables × n_variables provided
by the user.
Description
Function imsls_f_covariances computes estimates of correlations, covariances, or sums of squares and crossproducts for a data matrix x. Weights and frequencies are allowed but not required.
The means, (corrected) sums of squares, and (corrected) sums of crossproducts are computed using the method of provisional means. Let xki denote the mean based on i observations for the k-th variable, fi denote the frequency of the i-th observation, wi denote the weight of the i-th observations, and cjki denote the sum of crossproducts (or sum of squares if j = k) based on i observations. Then the method of provisional means finds new means and sums of crossproducts as shown in the example below.
The means and crossproducts are initialized as follows:
xk0 = 0.0 for k = 1, …, p
cjk0 = 0.0 for j, k = 1, …, p
where p denotes the number of variables. Letting xk,i+1 denote the k-th variable of observation i + 1, each new observation leads to the following updates for xki and cjki using the update constant ri+1:
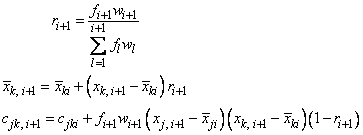
The default value for weights and frequencies is 1. Means and variances are computed based on the valid data for each variable or, if required, based on all the valid data for each pair of variables.
Usage Notes
Function imsls_f_covariances defines a sample mean by

where n is the number of observations.
The following formula defines the sample covariance, sjk, between variables j and k:
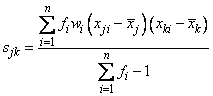
The sample correlation between variables j and k, rjk, is defined as follows:
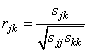
Examples
Example 1
This example illustrates the use of imsls_f_covariances for the first 50 observations in the Fisher iris data (Fisher 1936). Note that the first variable is constant over the first 50 observations.
#include <imsls.h>
#define N_VARIABLES 5
#define N_OBSERVATIONS 50
int main()
{
float *covariances, *means;
float x[] = {
1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.0, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.1, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.6, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.7, .4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.4, 1.4, .3, 1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 4.4, 2.9, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .1,
1.0, 5.4, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .1, 1.0, 4.3, 3.0, 1.1, .1,
1.0, 5.8, 4.0, 1.2, .2, 1.0, 5.7, 4.4, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.3, .4, 1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .3,
1.0, 5.7, 3.8, 1.7, .3, 1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.5, .3,
1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.7, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.7, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.6, 1.0, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.3, 1.7, .5,
1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.9, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.0, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.6, .4, 1.0, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.2, 3.4, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.1, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 5.2, 4.1, 1.5, .1, 1.0, 5.5, 4.2, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.2, 1.2, .2,
1.0, 5.5, 3.5, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.6, 1.4, .1,
1.0, 4.4, 3.0, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.4, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.3, .3, 1.0, 4.5, 2.3, 1.3, .3,
1.0, 4.4, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.6, .6,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.9, .4, 1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .3,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.2, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 5.3, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.3, 1.4, .2};
/* Perform analysis */
covariances = imsls_f_covariances (N_OBSERVATIONS,
N_VARIABLES, x, 0);
/* Print results */
imsls_f_write_matrix ("The default case: variances/covariances",
N_VARIABLES, N_VARIABLES, covariances,
IMSLS_PRINT_UPPER, 0);
}
Output
The default case: variances/covariances
1 2 3 4 5
1 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000
2 0.1242 0.0992 0.0164 0.0103
3 0.1437 0.0117 0.0093
4 0.0302 0.0061
5 0.0111
Example 2
This example, which uses the first 50 observations in the Fisher iris data, illustrates the use of optional arguments.
#include <imsls.h>
#define N_VARIABLES 5
#define N_OBSERVATIONS 50
int main()
{
char *title;
float *means, *correlations;
float x[] = {
1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.0, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.1, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.6, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.7, .4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.4, 1.4, .3, 1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 4.4, 2.9, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .1,
1.0, 5.4, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .1, 1.0, 4.3, 3.0, 1.1, .1,
1.0, 5.8, 4.0, 1.2, .2, 1.0, 5.7, 4.4, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 5.4, 3.9, 1.3, .4, 1.0, 5.1, 3.5, 1.4, .3,
1.0, 5.7, 3.8, 1.7, .3, 1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.5, .3,
1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.7, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.7, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 4.6, 3.6, 1.0, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.3, 1.7, .5,
1.0, 4.8, 3.4, 1.9, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.0, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.4, 1.6, .4, 1.0, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.2, 3.4, 1.4, .2, 1.0, 4.7, 3.2, 1.6, .2,
1.0, 4.8, 3.1, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 5.4, 3.4, 1.5, .4,
1.0, 5.2, 4.1, 1.5, .1, 1.0, 5.5, 4.2, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 4.9, 3.1, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.2, 1.2, .2,
1.0, 5.5, 3.5, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 4.9, 3.6, 1.4, .1,
1.0, 4.4, 3.0, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.1, 3.4, 1.5, .2,
1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.3, .3, 1.0, 4.5, 2.3, 1.3, .3,
1.0, 4.4, 3.2, 1.3, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.5, 1.6, .6,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.9, .4, 1.0, 4.8, 3.0, 1.4, .3,
1.0, 5.1, 3.8, 1.6, .2, 1.0, 4.6, 3.2, 1.4, .2,
1.0, 5.3, 3.7, 1.5, .2, 1.0, 5.0, 3.3, 1.4, .2};
/* Perform analysis */
correlations = imsls_f_covariances (N_OBSERVATIONS,
N_VARIABLES-1, x+1,
IMSLS_STDEV_CORRELATION_MATRIX,
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, N_VARIABLES,
IMSLS_MEANS, &means,
0);
/* Print results */
imsls_f_write_matrix ("Means\n", 1, N_VARIABLES-1, means, 0);
title = "Correlations with Standard Deviations on the Diagonal\n";
imsls_f_write_matrix (title, N_VARIABLES-1, N_VARIABLES-1,
correlations, IMSLS_PRINT_UPPER, 0);
}
Output
Means
1 2 3 4
5.006 3.428 1.462 0.246
Correlations with Standard Deviations on the Diagonal
1 2 3 4
1 0.3525 0.7425 0.2672 0.2781
2 0.3791 0.1777 0.2328
3 0.1737 0.3316
4 0.1054
Warning Errors
IMSLS_CONSTANT_VARIABLE Correlations are requested, but the observations on one or more variables are constant. The corresponding correlations are set to NaN.
IMSLS_INSUFFICIENT_DATA Variances and covariances are requested, but fewer than two valid observations are present for a variable. The pertinent statistics are set to NaN.
IMSLS_ZERO_SUM_OF_WEIGHTS_2 The sum of the weights is zero. The means, variances, and covariances are set to NaN.
IMSLS_ZERO_SUM_OF_WEIGHTS_3 The sum of the weights is zero. The means and correlations are set to NaN.
IMSLS_TOO_FEW_VALID_OBS_CORREL Correlations are requested, but fewer than two valid observations are present for a variable. The pertinent correlation coefficients are set to NaN.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |
