Evaluates the Poisson probability function.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_poisson_pdf (int k, float theta)
The type double function is imsls_d_poisson_pdf.
Required Arguments
int k
(Input)
Argument for which the Poisson distribution function is to be
evaluated.
float theta (Input)
Mean of the
Poisson distribution. theta must be
positive.
Return Value
Function value, the probability that a Poisson random variable takes a value equal to k.
Description
Function imsls_f_poisson_pdf evaluates the probability function of a Poisson random variable with parameter theta. theta, which is the mean of the Poisson random variable, must be positive. The probability function (with q = theta) is
f(x) = e−θ qk/k!, for k = 0, 1, 2,¼
imsls_f_poisson_pdf evaluates this function directly, taking logarithms and using the log gamma function.
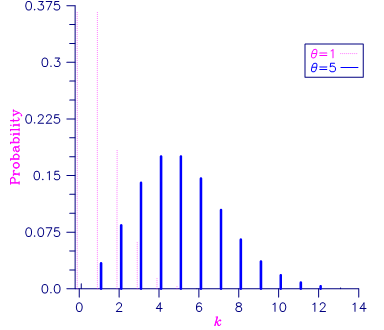
Figure 11- 2 Poisson Probability Function
Example
Suppose X is a Poisson random variable with q = 10. In this example, we evaluate the probability function at 7.
#include <imsls.h>
int main () {
int k = 7;
float theta = 10.0;
printf ("The probability that X is equal to 7 is %g.\n",
imsls_f_poisson_pdf (k, theta));
}
Output
The probability that X is equal to 7 is 0.0900792.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |