Computes the value of a Hermite quintic spline or the value of one of its derivatives. In particular, computes solutions to the Feynman-Kac PDE handled by function imsl_f_feynman_kac.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_feynman_kac_evaluate (int nw, int m, float breakpoints[], float w[], float coef[],…, 0)
The type double function is imsl_d_feynman_kac_evaluate.
Required Arguments
int nw
(Input)
Length of the array containing the evaluation points of the
spline.
int m
(Input)
Number of breakpoints for the Hermite quintic spline interpolation.
It is required that m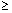 2. When applied to imsl_f_feynman_kac,
m is identical
to argument nxgrid.
2. When applied to imsl_f_feynman_kac,
m is identical
to argument nxgrid.
float breakpoints[]
(Input)
Array of length m containing the
breakpoints for the Hermite quintic spline interpolation. The breakpoints must
be in strictly increasing order. When applied to imsl_f_feynman_kac,
breakpoints[] is
identical to array xgrid[].
float w[]
(Input)
Vector of length nw containing the
evaluation points for the spline. It is required that breakpoints[0] 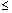 w[i]
w[i] 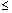 breakpoints[m-1]
breakpoints[m-1]
for
i=0,…,nw-1.
float coef[]
(Input)
Vector of length 3*m containing the
coefficients of the Hermite quintic spline.
When applied to imsl_f_feynman_kac,
this vector is one of the rows of output arrays y or y_prime related to the
spline coefficients at time points t=tgrid[j], j=1,…, ntgrid.
Return Value
A pointer to an array of length nw containing the values of the Hermite quintic spline or one of its derivatives at the evaluation points in array w[]. If no values can be computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_feynman_kac_evaluate(int nw, int m, float breakpoints[], float w[], float coef[],
IMSL_DERIV, int deriv,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float value[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_DERIV, int deriv
(Input)
Let 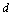 = deriv and let
= deriv and let  be the given Hermite quintic spline.
Then, this option produces the d-th derivative of
be the given Hermite quintic spline.
Then, this option produces the d-th derivative of  at
at 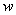 ,
, 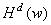 . It is required that deriv = 0,1,2
or 3.
. It is required that deriv = 0,1,2
or 3.
Default: deriv = 0.
IMSL_RETURN_USER,
float value[]
(Output)
A user defined array of length nw to receive the
d-th derivative of  at the evaluation points in
w[]. When using
this option, the return value of the function is NULL.
at the evaluation points in
w[]. When using
this option, the return value of the function is NULL.
Description
The Hermite quintic spline interpolation is done over the
composite interval  , where breakpoints[i-1]
=
, where breakpoints[i-1]
= are given by
are given by 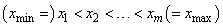 .
.
The Hermite quintic spline function is constructed using three primary functions, defined by
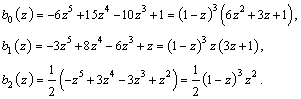
For each
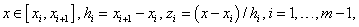
the spline is locally defined by

where
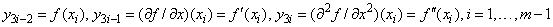
are the values of a given twice continuously differentiable
function 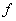 and its first two derivatives at
the breakpoints.
and its first two derivatives at
the breakpoints.
The approximating function  is twice continuously
differentiable on
is twice continuously
differentiable on  , whereas the third derivative is in
general only continuous within the interior of the intervals
, whereas the third derivative is in
general only continuous within the interior of the intervals 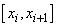 . From the local representation of
. From the local representation of
 it follows that
it follows that
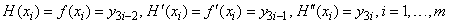 .
.
The spline coefficients 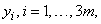 are stored as successive
triplets in array coef[].
For a given
are stored as successive
triplets in array coef[].
For a given 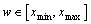 , function imsl_f_feynman_kac_evaluate
uses the information in coef[]
together with the values of
, function imsl_f_feynman_kac_evaluate
uses the information in coef[]
together with the values of 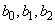 and its derivatives at
and its derivatives at
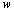 to compute
to compute 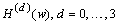 using the local representation
on the particular subinterval containing
using the local representation
on the particular subinterval containing 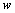 .
.
Example
Consider function 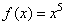 , a polynomial of degree 5, on the
interval
, a polynomial of degree 5, on the
interval 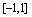 with breakpoints
with breakpoints 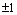 . Then, the end derivative values are
. Then, the end derivative values are
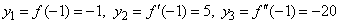
and
 .
.
Since the Hermite quintic interpolates all polynomials up
to degree 5 exactly, the spline interpolation on 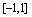 must agree with the exact
function value up to rounding errors.
must agree with the exact
function value up to rounding errors.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
/* Define function */
#define F(x) pow(x,5.0)
int main()
{
int i;
int nw = 7;
int m = 2;
float breakpoints[] = { -1.0, 1.0 };
float w[] = { -0.75, -0.5, -0.25, 0.0,
0.25, 0.5, 0.75 };
float coef[] = { -1.0, 5.0, -20.0,
1.0, 5.0, 20.0 };
float *result = NULL;
result = imsl_f_feynman_kac_evaluate(nw, m, breakpoints, w, coef, 0);
/* Print results */
printf(" x F(x) Interpolant Error\n\n");
for (i=0; i<=6; i++)
printf(" %6.3f %10.3f %10.3f %10.7f\n", w[i], F(w[i]),
result[i], fabs(F(w[i])-result[i]));
}
Output
x F(x) Interpolant Error
-0.750 -0.237 -0.237 0.0000000
-0.500 -0.031 -0.031 0.0000000
-0.250 -0.001 -0.001 0.0000000
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.0000000
0.250 0.001 0.001 0.0000000
0.500 0.031 0.031 0.0000000
0.750 0.237 0.237 0.0000000
