Computes the discrete Fourier sine transformation of an odd sequence.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_fft_sine (int n, float p[], …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_fft_sine.
Required Arguments
int n
(Input)
Length of the sequence to be transformed. It must be greater than
1.
float p[]
(Input)
Array of size n containing the
sequence to be transformed.
Return Value
A pointer to the transformed sequence. To release this space, use imsl_free. If no solution was computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float
*imsl_f_fft_sine (int
n,
float p[],
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float
q[],
IMSL_PARAMS, float
params[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float q[]
(Output)
Store the result in the user-provided space pointed to by q. Therefore, no
storage is allocated for the solution, and imsl_f_fft_sine
returns q. The
array must be of length at least n + 1.
IMSL_PARAMS, float params[]
(Input)
Pointer returned by a previous call to imsl_f_fft_sine_init. If imsl_f_fft_sine is
used repeatedly with the same value of n, then it is more
efficient to compute these parameters only once.
Default: Initializing
parameters computed each time imsl_f_fft_sine is
entered
Description
The function imsl_f_fft_sine computes the discrete Fourier sine transform of a real vector of size N. It uses the system’s high performance library for the computation, if available. Otherwise, the method used is a variant of the Cooley-Tukey algorithm, which is most efficient when N + 1 is a product of small prime factors. If N satisfies this condition, then the computational effort is proportional to N logN. Specifically, given an N-vector p, imsl_f_fft_sine returns in q
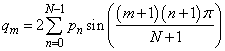
Finally, note that the Fourier sine transform is its own (unnormalized) inverse. The Cooley-Tukey algorithm is based on the sine FFT in FFTPACK, which was developed by Paul Swarztrauber at the National Center for Atmospheric Research.
Example
This example inputs a pure sine wave as a data vector and recovers its Fourier sine series, which is a vector with all components zero, except n at the appropriate frequency.
#include <imsl.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 7;
int i;
float p[7];
float *q;
float pi;
pi = imsl_f_constant("pi", 0);
/* fill p with a pure sine wave */
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
p[i] = sin((float)(i+1)*pi/(float)(n+1));
q = imsl_f_fft_sine (n, p, 0);
printf (" index\t p\t q\n");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
printf("\t%1d\t%5.2f\t%5.2f\n", i, p[i], q[i]);
}
Output
index p q
0 0.38 8.00
1 0.71 0.00
2 0.92 0.00
3 1.00 0.00
4 0.92 0.00
5 0.71 -0.00
6 0.38 0.00

