Integrates a function over an infinite or semi-infinite interval.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_int_fcn_inf (float fcn(), float bound, Imsl_quad interval, …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_int_fcn_inf.
Required Arguments
float fcn (float x)
(Input)
User-supplied function to be integrated.
float bound
(Input)
Finite limit of integration. This argument is ignored if interval has the value
IMSL_INF_INF.
Imsl_quad interval
(Input)
Flag indicating integration limits. The following settings are
allowed:
|
interval |
Integration Limits |
|
IMSL_INF_BOUND |
(−∞, bound) |
|
IMSL_BOUND_INF |
(bound, ∞) |
|
IMSL_INF_INF |
(−∞, ∞) |
Return Value
The value of
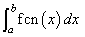
is returned where a and b are appropriate integration limits. If no value can be computed, NaN is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float imsl_f_int_fcn_inf (float fcn, float bound, Imsl_quad interval,
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float err_abs,
IMSL_ERR_REL, float err_rel,
IMSL_ERR_EST, float *err_est,
IMSL_MAX_SUBINTER, int max_subinter,
IMSL_N_SUBINTER, int *n_subinter,
IMSL_N_EVALS, int *n_evals,
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float fcn(), void *data,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_ERR_ABS, float err_abs
(Input)
Absolute accuracy desired.
Default: 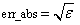 where ɛ is the machine
precision
where ɛ is the machine
precision
IMSL_ERR_REL, float err_rel
(Input)
Relative accuracy desired.
Default: 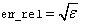 where ɛ is the machine
precision
where ɛ is the machine
precision
IMSL_ERR_EST, float *err_est
(Output)
Address to store an estimate of the absolute value of the error.
IMSL_MAX_SUBINTER, int max_subinter
(Input)
Number of subintervals allowed.
Default: max_subinter = 500.
IMSL_N_SUBINTER, int *n_subinter
(Output)
Address to store the number of subintervals generated.
IMSL_N_EVALS, int *n_evals
(Output)
Address to store the number of evaluations of fcn.
IMSL_FCN_W_DATA, float fcn (float x, void *data), void *data
(Input)
User supplied function to be integrated, which also accepts a pointer
to data that is supplied by the user. data is a pointer to
the data to be passed to the user-supplied function. See the
Introduction, Passing Data to User-Supplied Functions at the beginning of
this manual for more details.
Description
The function imsl_f_int_fcn_inf is a special-purpose integrator that uses a globally adaptive scheme to reduce the absolute error. It initially transforms an infinite or semi-infinite interval into the finite interval [0, 1]. It then uses the same strategy as the function imsl_f_int_fcn_sing.
On some platforms, imsl_f_int_fcn_inf can evaluate the user-supplied function fcn in parallel. This is done only if the function imsl_omp_options is called to flag user-defined functions as thread-safe. A function is thread-safe if there are no dependencies between calls. Such dependencies are usually the result of writing to global or static variables.
The function imsl_f_int_fcn_inf is based on the subroutine QAGI by Piessens et al. (1983).
Examples
Example 1
The value of
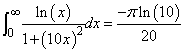
is computed.
#include <math.h>
#include <imsl.h>
float fcn(float x);
int main()
{
float q, exact, pi;
pi = imsl_f_constant("pi", 0);
imsl_omp_options(IMSL_SET_FUNCTIONS_THREAD_SAFE, 1, 0);
/* Evaluate the integral */
q = imsl_f_int_fcn_inf (fcn, 0.0,
IMSL_BOUND_INF,
0);
/* Print the result and the */
/* exact answer */
exact = -pi*log(10.)/20.;
printf("integral = %10.3f\nexact = %10.3f\n", q, exact);
}
float fcn(float x)
{
float z;
z = 10.*x;
return log(x)/(1+ z*z);
}
Output
integral =
-0.362
exact = -0.362
Example 2
The value of
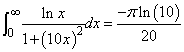
is again computed. The values of the actual and estimated error are printed as well. Note that these numbers are machine dependent. Furthermore, the error estimate is usually pessimistic. That is, the actual error is usually smaller than the error estimate, as in this example. The number of function evaluations also are printed.
#include <math.h>
#include <imsl.h>
float fcn(float x);
int main()
{
int n_evals;
float q, exact, err_est, exact_err, pi;
pi = imsl_f_constant("pi", 0);
imsl_omp_options(IMSL_SET_FUNCTIONS_THREAD_SAFE, 1, 0);
/* Evaluate the integral */
q = imsl_f_int_fcn_inf (fcn, 0.0,
IMSL_BOUND_INF,
IMSL_ERR_EST, &err_est,
IMSL_N_EVALS, &n_evals,
0);
/* Print the result and the */
/* exact answer */
exact = -pi*log(10.)/20.;
exact_err = fabs(exact - q);
printf("integral = %10.3f\nexact = %10.3f\n", q, exact);
printf("error estimate = %e\nexact error = %e\n", err_est,
exact_err);
printf("The number of function evaluations = %d\n", n_evals);
}
float fcn(float x)
{
float z;
z = 10.*x;
return log(x)/(1+ z*z);
}
Output
integral = -0.362
exact = -0.362
error estimate = 2.801418e-06
exact error = 2.980232e-08
The number of function evaluations = 285
Warning Errors
|
IMSL_ROUNDOFF_CONTAMINATION |
Roundoff error, preventing the requested tolerance from being achieved, has been detected. |
|
IMSL_PRECISION_DEGRADATION |
A degradation in precision has been detected. |
|
IMSL_EXTRAPOLATION_ROUNDOFF |
Roundoff error in the extrapolation table, preventing the requested tolerance from being achieved, has been detected. |
Fatal Errors
|
IMSL_DIVERGENT |
Integral is probably divergent or slowly convergent. |
|
IMSL_MAX_SUBINTERVALS |
The maximum number of subintervals allowed has been reached. |

