Computes the transpose of a matrix, a matrix-vector product, a matrix-matrix product, the bilinear form, or any triple product.
Synopsis
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_mat_mul_rect (char *string, …, 0)
The type double procedure is imsl_d_mat_mul_rect.
Required Arguments
char *string
(Input)
String indicating matrix multiplication to be performed.
Return Value
The result of the multiplication. This is always a pointer to a float, even if the result is a single number. To release this space, use imsl_free. If no answer was computed, then NULL is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsl.h>
float *imsl_f_mat_mul_rect (char *string,
IMSL_A_MATRIX, int nrowa, int ncola, float a[],
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim,
IMSL_B_MATRIX, int nrowb, int ncolb, float b[],
IMSL_B_COL_DIM, int b_col_dim,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, int nx, float *x,
IMSL_Y_VECTOR, int ny, float *y,
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float ans[],
IMSL_RETURN_COL_DIM, int return_col_dim,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSL_A_MATRIX, int nrowa, int ncola, float a[]
(Input)
The nrowa × ncola matrix A.
IMSL_A_COL_DIM, int a_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of A.
Default: a_col_dim = ncola
IMSL_B_MATRIX, int nrowb, int ncolb, float b[]
(Input)
The
nrowb × ncolb matrix
A.
IMSL_B_COL_DIM, int b_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of B.
Default: b_col_dim = ncolb
IMSL_X_VECTOR, int nx, float *x
(Input)
The vector x of size nx.
IMSL_Y_VECTOR, int ny, float *y
(Input)
The vector y of size ny.
IMSL_RETURN_USER, float ans[]
(Output)
A user-allocated array containing the result.
IMSL_RETURN_COL_DIM, int return_col_dim
(Input)
The column dimension of the answer.
Default: return_col_dim = the
number of columns in the answer
Description
This function computes a matrix-vector product, a matrix-matrix product, a bilinear form of a matrix, or a triple product according to the specification given by string. For example, if “A*x” is given, Ax is computed. In string, the matrices A and B and the vectors x and y can be used. Any of these four names can be used with trans, indicating transpose. The vectors x and y are treated as n × 1 matrices.
If string contains only one item, such as “x” or “trans(A)”, then a copy of the array, or its transpose, is returned. If string contains one multiplication, such as “A*x” or “B*A”, then the indicated product is returned. Some other legal values for string are “trans(y)*A”, “A*trans(B)”, “x*trans(y)”, or “trans(x)*y”.
The matrices and/or vectors referred to in string must be given as optional arguments. If string is “B*x”, then IMSL_B_MATRIX and IMSL_X_VECTOR must be given.
Example
Let
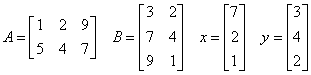
The arrays AT, Ax, xTAT, AB, BTAT, xTy, xyT, and xTAy are computed and printed.
#include <imsl.h>
int main()
{
float A[] = {1, 2, 9,
5, 4, 7};
float B[] = {3, 2,
7, 4,
9, 1};
float x[] = {7, 2, 1};
float y[] = {3, 4, 2};
float *ans;
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("trans(A)",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("trans(A)", 3, 2, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("A*x",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, 3, x,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("A*x", 1, 2, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("trans(x)*trans(A)",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
IMSL_X_VECTOR, 3, x,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("trans(x)*trans(A)", 1, 2, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("A*B",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
IMSL_B_MATRIX, 3, 2, B,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("A*B", 2, 2, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("trans(B)*trans(A)",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
IMSL_B_MATRIX, 3, 2, B,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("trans(B)*trans(A)", 2, 2, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("trans(x)*y",
IMSL_X_VECTOR, 3, x,
IMSL_Y_VECTOR, 3, y,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("trans(x)*y", 1, 1, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("x*trans(y)",
IMSL_X_VECTOR, 3, x,
IMSL_Y_VECTOR, 3, y,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("x*trans(y)", 3, 3, ans, 0);
ans = imsl_f_mat_mul_rect("trans(x)*A*y",
IMSL_A_MATRIX, 2, 3, A,
/* use only the first 2 components of x */
IMSL_X_VECTOR, 2, x,
IMSL_Y_VECTOR, 3, y,
0);
imsl_f_write_matrix("trans(x)*A*y", 1, 1, ans, 0);
}
Output
trans(A)
1 2
1 1 5
2 2 4
3 9 7
A*x
1 2
20 50
trans(x)*trans(A)
1 2
20 50
A*B
1 2
1 98 19
2 106 33
trans(B)*trans(A)
1 2
1 98 106
2 19 33
trans(x)*y
31
x*trans(y)
1 2 3
1 21 28 14
2 6 8 4
3 3 4 2
trans(x)*A*y
293
