Performs an Anderson-Darling test for normality.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float imsls_f_ad_normality_test (int nobs, float x[], … , 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_ad_normality_test.
Required Arguments
int nobs
(Input)
Number of observations. nobs must be greater
than or equal to 3.
float x[] (Input)
Vector
of length nobs
containing the observations.
Return Value
The p-value for the Anderson-Darling test of normality.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
imsls_f_ad_normality_test (int nobs,
float x[],
IMSLS_STAT,
float *adstat,
IMSLS_N_MISSING,
int *nmiss,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_STAT,
float *adstat,
(Output)
The Anderson-Darling
statistic.
IMSLS_N_MISSING,
int *nmiss,
(Output)
The number of missing observations.
Description
Given a data sample {Xi, i = 1 .. n}, where n = nobs and Xi = x[i-1], function imsls_f_ad_normality_test computes the Anderson-Darling (AD) normality statistic A = adstat and the corresponding Return Value (p-value) P = P == {probability that a normally distributed n element sample would have an AD statistic > A}. If P is sufficiently small (e.g. P < .05), then the AD test indicates that the null hypothesis that the data sample is normally-distributed should be rejected. A is calculated:
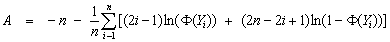
where 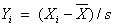 and
and 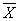 and s are the sample mean and
standard deviation respectively. P is calculated by first
transforming A to an “n-adjusted”
statistic A*:
and s are the sample mean and
standard deviation respectively. P is calculated by first
transforming A to an “n-adjusted”
statistic A*:
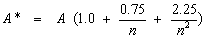
and then calculating P in terms of A* using a parabolic approximation taken from Table 4.9 in Stephens (1986).
Example
The following example is taken from Conover (1980, pages 364 and 195). The data consists of 50 two-digit numbers taken from a telephone book. The AD test fails to reject the null hypothesis of normality at the .05 level of significance.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int nobs = 50, nmiss;
float p_value, adstat;
float x[] = {
23.0, 36.0, 54.0, 61.0, 73.0, 23.0, 37.0, 54.0, 61.0, 73.0,
24.0, 40.0, 56.0, 62.0, 74.0, 27.0, 42.0, 57.0, 63.0, 75.0,
29.0, 43.0, 57.0, 64.0, 77.0, 31.0, 43.0, 58.0, 65.0, 81.0,
32.0, 44.0, 58.0, 66.0, 87.0, 33.0, 45.0, 58.0, 68.0, 89.0,
33.0, 48.0, 58.0, 68.0, 93.0, 35.0, 48.0, 59.0, 70.0, 97.0};
p_value = imsls_f_ad_normality_test (nobs, x,
IMSLS_STAT, &adstat,
IMSLS_N_MISSING, &nmiss,
0);
printf ("Anderson-Darling statistic = %11.4f \n", adstat);
printf ("p-value = %11.4f\n", p_value);
printf ("# missing values = %4d\n", nmiss);
}
Output
Anderson-Darling statistic = 0.3339
p-value = 0.5024
# missing values = 0
Informational Errors
|
IMSLS_PVAL_UNDERFLOW |
The p-value has fallen below the minimum value of # for which its calculation has any accuracy; ZERO is returned. |
Fatal Errors
|
IMSLS_TOO_MANY_MISSING |
After removing the missing observations only 2 observations remain. The test cannot proceed. |
