Performs a K-means (centroid) cluster analysis.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
int *imsls_f_cluster_k_means (int n_observations, int n_variables, float x[], int n_clusters, float cluster_seeds, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_cluster_k_means.
Required Arguments
int n_observations
(Input)
Number of observations.
int
n_variables (Input)
Number of variables to be used in
computing the metric.
float x[]
(Input)
Array of length n_observations × n_variables containing
the observations to be clustered.
int
n_clusters (Input)
Number of clusters.
float
cluster_seeds[] (Input)
Array of length n_clusters × n_variables containing
the cluster seeds, i.e., estimates for the cluster centers.
Return Value
The cluster membership for each observation is returned.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
int
*imsls_f_cluster_k_means (int
n_observations, int n_variables, float x[],
int
n_clusters,
float cluster_seeds,
IMSLS_WEIGHTS,
float
weights[],
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES,
float
frequencies[],
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS,
int
max_iterations,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS, float
**cluster_means,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS_USER, float
cluster_means[],
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ,
float
**cluster_ssq,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ_USER,
float
cluster_ssq[],
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM,
int
x_col_dim,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS_COL_DIM,
int cluster_means_col_dim,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SEEDS_COL_DIM,
int cluster_seeds_col_dim,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS,
int
**cluster_counts,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS_USER,
int
cluster_counts[],
IMSLS_CLUSTER_VARIABLE_COLUMNS,
int cluster_variables[],
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int
cluster_group[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_WEIGHTS, float weights[]
(Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the weight of each observation of matrix x.
Default: weights [ ] = 1.
IMSLS_FREQUENCIES, float
frequencies[] (Input)
Array of length n_observations
containing the frequency of each observation of matrix x.
Default: frequencies [ ] = 1.
IMSLS_MAX_ITERATIONS, int
max_iterations (Input)
Maximum number of
iterations.
Default: max_iterations = 30.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS, float
**cluster_means (Output)
The address of a pointer to an
internally allocated array of length n_clusters × n_variables containing
the cluster means.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS_USER, float
cluster_means[] (Output)
Storage for array cluster_means is
provided by the user. See IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ, float
**cluster_ssq (Output)
The address of a pointer to
internally allocated array of length n_clusters containing
the within sum-of-squares for each cluster.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ_USER, float
cluster_ssq[] (Output)
Storage for array cluster_ssq is
provided by the user. See IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ.
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, int x_col_dim
(Input)
Column dimension of x.
Default:
x_col_dim = n_variables.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS_COL_DIM, int cluster_means_col_dim
(Input)
Column dimension for the vector cluster_means.
Default:
cluster_means_col_dim = n_variables.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SEEDS_COL_DIM, int cluster_seeds_col_dim
(Input)
Column dimension for the vector cluster_seeds.
Default:
cluster_seeds_col_dim = n_variables.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS, int
**cluster_counts (Output)
The address of a pointer to an
internally allocated array of length n_clusters containing
the number of observations in each cluster.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS_USER, int
cluster_counts[] (Output)
Storage for array cluster_counts is
provided by the user. See IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS.
IMSLS_CLUSTER_VARIABLE_COLUMNS, int
cluster_variables[] (Input)
Vector of length n_variables containing
the columns of x
to be used in computing the metric. Columns are numbered 0, 1, 2, ..., n_variables
Default:
cluster_variables [ ] = 0, 1, 2, …, n_variables.
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, int
cluster_group[] (Output)
User-allocated array of length
n_observations
containing the cluster membership for each observation.
Description
Function imsls_f_cluster_k_means is an implementation of Algorithm AS 136 by Hartigan and Wong (1979). It computes K-means (centroid) Euclidean metric clusters for an input matrix starting with initial estimates of the K-cluster means. The function allows for missing values coded as NaN (Not a Number) and for weights and frequencies.
Let p = n_variables be the number of variables to be used in computing the Euclidean distance between observations. The idea in K-means cluster analysis is to find a clustering (or grouping) of the observations so as to minimize the total within-cluster sums-of-squares. In this case, the total sums-of-squares within each cluster is computed as the sum of the centered sum-of-squares over all nonmissing values of each variable. That is,
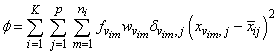
where νim denotes the row index of the m-th observation in the i-th cluster in the matrix X; ni is the number of rows of X assigned to group i; f denotes the frequency of the observation; w denotes its weight; δ is 0 if the j-th variable on observation νim is missing, otherwise δ is 1; and
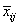
is the average of the nonmissing observations for variable j in group i. This method sequentially processes each observation and reassigns it to another cluster if doing so results in a decrease of the total within-cluster sums-of-squares. See Hartigan and Wong (1979) or Hartigan (1975) for details.
Example
This example performs K-means cluster analysis on Fisher’s Iris data, which is obtained by function imsls_f_data_sets (see Chapter 15, “Utilities”;). The initial cluster seed for each iris type is an observation known to be in the iris type.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <imsls.h>
int main()
{
#define N_OBSERVATIONS 150
#define N_VARIABLES 4
#define N_CLUSTERS 3
float x[N_OBSERVATIONS][5];
float cluster_seeds[N_CLUSTERS][N_VARIABLES];
float cluster_means[N_CLUSTERS][N_VARIABLES];
float cluster_ssq[N_CLUSTERS];
int cluster_variables[N_VARIABLES] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int cluster_counts[N_CLUSTERS];
int cluster_group[N_OBSERVATIONS];
int i;
/* Retrieve the data set */
imsls_f_data_sets(3, IMSLS_RETURN_USER, x, 0);
/* Assign initial cluster seeds */
for (i=0; i<N_VARIABLES; i++) {
cluster_seeds[0][i] = x[0][i+1];
cluster_seeds[1][i] = x[50][i+1];
cluster_seeds[2][i] = x[100][i+1];
}
/* Perform the analysis */
imsls_f_cluster_k_means(N_OBSERVATIONS, N_VARIABLES, (float*)x,
N_CLUSTERS, (float*)cluster_seeds,
IMSLS_X_COL_DIM, 5,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_VARIABLE_COLUMNS, cluster_variables,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_COUNTS_USER, cluster_counts,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_MEANS_USER, cluster_means,
IMSLS_CLUSTER_SSQ_USER, cluster_ssq,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, cluster_group,
0);
/* Print results */
imsls_i_write_matrix("Cluster Membership", 1, N_OBSERVATIONS,
cluster_group, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("Cluster Means", N_CLUSTERS, N_VARIABLES,
(float*)cluster_means, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("Cluster Sum of Squares", 1, N_CLUSTERS,
cluster_ssq, 0);
imsls_i_write_matrix("# Observations in Each Cluster", 1,
N_CLUSTERS, cluster_counts, 0);
}
Cluster Membership
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 2
81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115
2 3 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 2
116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131
3 3 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3
132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147
3 3 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 3 3 2 3 3 3 2
148 149 150
3 3 2
Cluster Means
1 2 3 4
1 5.006 3.428 1.462 0.246
2 5.902 2.748 4.394 1.434
3 6.850 3.074 5.742 2.071
Cluster Sum of Squares
1 2 3
15.15 39.82 23.88
# Observations in Each Cluster
1 2 3
50 62 38
Warning Errors
IMSLS_NO_CONVERGENCE Convergence did not occur.
