Computes a shuffled Faure sequence.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
Imsls_faure* imsls_faure_sequence_init (int ndim, …, 0)
float* imsls_f_faure_next_point (Imsls_faure *state, …, 0)
void imsls_faure_sequence_free (Imsls_faure *state)
The type double function is imsls_d_faure_next_point.
The functions imsls_faure_sequence_init
and imsls_faure_sequence_free
are precision independent.
Required Arguments for imsls_faure_sequence_init
int ndim
(Input)
The dimension of the hyper-rectangle.
Return Value for imsls_faure_sequence_init
Returns a structure that contains information about the sequence. The structure should be freed using imsls_faure_sequence_free after it is no longer needed.
Required Arguments for imsls_faure_next_point
Imsls_faure *state
(Input/Output)
Structure created by a call to imsls_faure_sequence_init.
Return Value for imsls_faure_next_point
Returns the next point in the shuffled Faure sequence. To release this space, use imsls_faure_sequence_free.
Required Arguments for imsls_faure_sequence_free
Imsls_faure *state
(Input/Output)
Structure created by a call to imsls_faure_sequence_init.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
Imsls_faure
*imsls_faure_sequence_init (int
ndim,
IMSLS_BASE,
int
base,
IMSLS_SKIP,
int
skip,
0)
float*
imsls_f_faure_next_point (Imsls_faure *state,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float
*user,
IMSLS_RETURN_SKIP,
int
*skip,
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_BASE, int base
(Input)
The base of the Faure sequence.
Default: The smallest prime
greater than or equal to ndim.
IMSLS_SKIP, int *skip
(Input)
The number of points to be skipped at the beginning of the Faure
sequence.
Default: 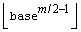 , where
, where 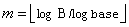 and B is the largest
representable integer.
and B is the largest
representable integer.
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float
*user (Output)
User-supplied array of length ndim containing the
current point in the sequence.
IMSLS_RETURN_SKIP, int *skip
(Output)
The current point in the sequence. The sequence can be restarted by
initializing a new sequence using this value for IMSLS_SKIP, and using
the same dimension for ndim.
Description
Discrepancy measures the deviation from uniformity of a point set.
The discrepancy of the point set 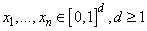 , is
, is
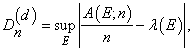
where the supremum is over all subsets of [0, 1]d of the form
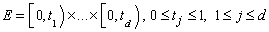 ,
,
λ is the Lebesque measure, and 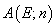 is the number of the xj
contained in E.
is the number of the xj
contained in E.
The sequence x1, x2, … of points [0,1]d is a low-discrepancy sequence if there exists a constant c(d), depending only on d, such that
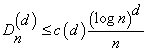
for all n>1.
Generalized Faure sequences can be defined for any prime base b≥d. The lowest bound for the discrepancy is obtained for the smallest prime b≥d, so the optional argument IMSLS_BASE defaults to the smallest prime greater than or equal to the dimension.
The generalized Faure sequence x1, x2, …, is computed as follows:
Write the positive integer n in its b-ary expansion,
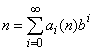
where ai(n) are integers, 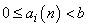 .
.
The j-th coordinate of xn is
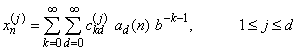
The generator matrix for the series, 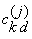 , is defined to be
, is defined to be
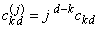
and 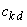 is an element of the
Pascal matrix,
is an element of the
Pascal matrix,
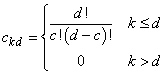
It is faster to compute a shuffled Faure sequence than to compute the Faure sequence itself. It can be shown that this shuffling preserves the low-discrepancy property.
The shuffling used is the b-ary Gray code. The function G(n) maps the positive integer n into the integer given by its b-ary expansion.
The sequence computed by this function is x(G(n)), where x is the generalized Faure sequence.
Example
In this example, five points in the Faure sequence are computed. The points are in the three-dimensional unit cube.
Note that imsls_faure_sequence_init is used to create a structure that holds the state of the sequence. Each call to imsls_f_faure_next_point returns the next point in the sequence and updates the Imsls_faure structure. The final call to imsls_faure_sequence_free frees data items, stored in the structure, that were allocated by imsls_faure_sequence_init.
#include "stdio.h"
#include "imsls.h"
int main()
{
Imsls_faure *state;
float *x;
int ndim = 3;
int k;
state = imsls_faure_sequence_init(ndim, 0);
for (k = 0; k < 5; k++) {
x = imsls_f_faure_next_point(state, 0);
printf("%10.3f %10.3f %10.3f\n", x[0], x[1],
x[2]);
free(x);
}
imsls_faure_sequence_free(state);
}
Output
0.334 0.493 0.064
0.667 0.826 0.397
0.778 0.270 0.175
0.111 0.604 0.509
0.445 0.937 0.842

