Generates pseudorandom numbers from a mixture of two exponential distributions.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_random_exponential_mix (int n_random, float theta1, float theta2, float p, ..., 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_random_exponential_mix.
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float theta1
(Input)
Mean of the exponential distribution which has the larger
mean.
float theta2
(Input)
Mean of the exponential distribution which has the smaller mean.
Parameter theta2
must be positive and less than or equal to theta1.
float p
(Input)
Mixing parameter. Parameter p must be non-negative
and less than or equal to theta1/(theta1 − theta2).
Return Value
An array of length n_random containing the random deviates of a mixture of two exponential distributions.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_random_exponential_mix (int n_random,
float theta1,
float theta2,
float
p,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float r[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float r[]
(Output)
User-supplied array of length n_random containing
the random deviates.
Description
Function imsls_f_random_exponential_mix generates pseudorandom numbers from a mixture of two exponential distributions. The probability density function is
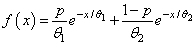
for x > 0, where p = p, θ1 = theta1, and θ2 = theta2.
In the case of a convex mixture, that is, the case 0 < p < 1, the mixing parameter p is interpretable as a probability; and imsls_f_random_exponential_mix with probability p generates an exponential deviate with mean θ1, and with probability 1 − p generates an exponential with mean θ2. When p is greater than 1, but less than θ1/(θ1 − θ2), then either an exponential deviate with mean θ1 or the sum of two exponentials with means θ1 and θ2 is generated. The probabilities are q = p − (p − 1) (θ1/θ2) and 1 − q, respectively, for the single exponential and the sum of the two exponentials.
Example
In this example, imsls_f_random_exponential_mix is used to generate five pseudorandom deviates from a mixture of exponentials with means 2 and 1, respecctively, and with mixing parameter 0.5.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n_random = 5;
float theta1 = 2.0;
float theta2 = 1.0;
float p = 0.5;
float *r;
imsls_random_seed_set(123457);
r = imsls_f_random_exponential_mix(n_random, theta1, theta2, p, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("Mixed exponential random deviates: ",
1, n_random, r, IMSLS_NO_COL_LABELS, 0);
}
Output
Mixed exponential random deviates:
0.070 1.302 0.630 1.976 0.372

