Generates pseudorandom numbers from a Weibull distribution.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
float *imsls_f_random_weibull (int n_random, float a, …, 0)
The type double function is imsls_d_random_weibull.
Required Arguments
int n_random
(Input)
Number of random numbers to generate.
float a
(Input)
Shape parameter of the Weibull distribution. This parameter must be
positive.
Return Value
An array of length n_random containing the random deviates of a Weibull distribution.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
float
*imsls_f_random_weibull (int n_random,
float
a,
IMSLS_B,
float
b,
IMSLS_RETURN_USER,
float r[],
0)
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_B, float b
(Input)
Scale parameter of the two parameter Weibull
distribution.
Default: b = 1.0
IMSLS_RETURN_USER, float r[]
(Output)
User-supplied array of length n_random containing
the random Weibull deviates.
Description
Function imsls_f_random_weibull generates pseudorandom numbers from a Weibull distribution with shape parameter a and scale parameter b. The probability density function is
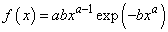
for x ≥ 0, a > 0, and b > 0. Function imsls_f_random_weibull uses an antithetic inverse CDF technique to generate a Weibull variate; that is, a uniform random deviate U is generated and the inverse of the Weibull cumulative distribution function is evaluated at 1.0 − U to yield the Weibull deviate.
Note that the Rayleigh distribution with probability density function
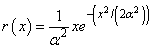
for x ≥ 0 is the same as a Weibull distribution with shape parameter a equal to 2 and scale parameter b equal to
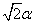
Example
In this example, imsls_f_random_weibull is used to generate five pseudorandom deviates from a two-parameter Weibull distribution with shape parameter equal to 2.0 and scale parameter equal to 6.0—a Rayleigh distribution with the following parameter:
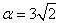
#include <stdio.h>
#include <imsls.h>
int main()
{
int n_random = 5;
float a = 3.0;
float *r;
imsls_random_seed_set(123457);
r = imsls_f_random_weibull(n_random, a, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("Weibull random deviates:",
1, n_random, r, IMSLS_NO_COL_LABELS, 0);
}
Output
Weibull random deviates:
0.325 1.104 0.643 0.826 0.552
Warning Errors
IMSLS_SMALL_A The shape parameter is so small that a relatively large proportion of the values of deviates from the Weibull cannot be represented.
