Converts ordinal data into proportions. Optionally, it can also reverse encoding, accepting proportions and converting them into ordinal values.
Synopsis
#include <imsls.h>
void
imsls_f_unsupervised_ordinal_filter (int
n_patterns,
int x[], float
z[]…,0)
The type double function is imsls_d_unsupervised_ordinal_filter.
Required Arguments
int
n_patterns (Input)
Number of observations.
int x[]
(Input/Output)
An array of length n_patterns containing
the classes for the ordinal data. Classes must be numbered 1 to IMSLS_N_CLASSES. This
is an output argument if IMSLS_DECODE is
specified, otherwise it is input.
float z[]
(Input/Output)
An array of length n_patterns containing
the encoded values for x represented as
cumulative proportions associated with each ordinal class (values between 0.0
and 1.0 inclusive). This is an input argument if IMSLS_DECODE is
specified, otherwise it is output.
Synopsis with Optional Arguments
#include <imsls.h>
void
imsls_f_unsupervised_ordinal_filter (int
n_patterns,
int x[],
float
z[],
IMSLS_ENCODE or
IMSLS_DECODE,
IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM,
or
IMSLS_SQUARE_ROOT,
or
IMSLS_ARC_SIN,
IMSLS_N_CLASSES, int
*
n_classes,
0)
The type double function is imsls_d_unsupervised_ordinal_filter.
Optional Arguments
IMSLS_ENCODE or
IMSLS_DECODE
(Input)
If IMSLS_ENCODE is specified, z is an output array
and x is an
input array that is filtered by converting each ordinal class value into a
cumulative proportion (a value between 0.0 and 1.0 inclusive). If IMSLS_DECODE is
specified, x is
an output array and z is an input array
that contains transformed cumulative proportions. In this case,
the transformed cumulative proportions are converted into ordinal class
values using the coding class=1, 2, … etc.
Default: IMSLS_ENCODE.
IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM or IMSLS_SQUARE_ROOT or
IMSLS_ARC_SIN
(Input)
IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM
indicates that the cumulative proportions used to encode the ordinal variable
are not transformed. If IMSLS_SQUARE_ROOT is
specified, cumulative proportions are transformed using the square root
transformation. If IMSLS_ARC_SIN is
specified, the cumulative proportions are transformed using the arcsin of
the square root of the cumulative proportions.
Default: IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM.
IMSLS_N_CLASSES,
int *n_classes
(Output)
The number of ordinal classes in x and the number of
unique proportions in z.
Description
The function imsls_f_unsupervised_ordinal_filter is designed to either encode or decode ordinal variables. Filtering consists of transforming the ordinal classes into proportions, with each proportion being equal to the proportion of the data at or below this class.
Ordinal Filtering: IMSLS_ENCODE
In this case, x is an input array that is filtered by converting each ordinal class value into a cumulative proportion.
For example, if x[]={2, 1, 3, 4, 2, 4, 1, 1, 3, 3} then n_patterns=10 and IMSLS_N_CLASSES=4. This function then fills z with cumulative proportions represented as proportions displayed in the table below. Cumulative proportions are equal to the proportion of the data in this class or a lower class.
|
Ordinal Class |
Frequency |
Cumulative Proportion |
|
1 |
3 |
30% |
|
2 |
2 |
50% |
|
3 |
3 |
80% |
|
4 |
2 |
100% |
If IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM is specified, then the equivalent proportions in z are
z[]={0.50, 0.30, 0.80, 1.00, 0.50, 1.00, 0.30, 0.30, 0.80, 0.80}.
If IMSLS_SQUARE_ROOT is specified, then the square root of these values is returned, i.e.,
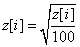
z[]={0.71, 0.55 , 0.89, 1.0, 0.71, 1.0, 0.55, 0.55, 0.89, 0.89};
If IMSLS_ARC_SIN is specified, then the arcsin square root of these values is returned using the following calculation:
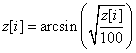
Ordinal UnFiltering: IMSLS_DECODE
Ordinal Unfiltering takes the transformed cumulative proportions in z and converts them into ordinal class values using the coding class=1, 2, … etc.
For example, if IMSLS_NO_TRANSFORM is specified and z[]={0.20, 1.00, 0.20, 0.40, 1.00, 1.00, 0.40, 0.10, 1.00, 1.00} then upon return, the output array would consist of the ordinal classes x[]={2, 4, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 1, 4, 4}.
If one of the transforms is specified, the same operation is performed since the transformations of the proportions are monotonically increasing. For example, if the original observations consisted of {2.8, 5.6, 5.6, 1.2, 4.5, 7.1}, then input x for encoding would be x[]={2, 4, 4, 1, 3, 5} and output IMSLS_N_CLASSES=5. The output array x after decoding would consist of the ordinal classes x[]={2, 4, 4, 1, 3, 5}.
Example 1
A taste test was conducted yielding the following data:
|
Individual |
Rating |
|
1 |
Poor |
|
2 |
Good |
|
3 |
Very Good |
|
4 |
Very Poor |
|
5 |
Very Good |
The data in the table above would have the coded values shown below. This assumes that the rating scale is: very poor, poor, good, and very good.
x={2, 3, 4, 1, 4}
The returned values are:
z={0.40, 0.60, 1.00, 0.20, 1.00}.
#include <imsls.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
#define N_PATTERNS 5
int x[N_PATTERNS] = {2,3,4,1,4};
int x2[N_PATTERNS], n_classes;
float z[N_PATTERNS];
/* Filtering. */
imsls_f_unsupervised_ordinal_filter(N_PATTERNS, x, z,
IMSLS_N_CLASSES, &n_classes,
0);
printf("n_classes = %d\n", n_classes);
imsls_i_write_matrix("x", N_PATTERNS, 1, x, 0);
imsls_f_write_matrix("z", N_PATTERNS, 1, z, 0);
/* Unfiltering. */
imsls_f_unsupervised_ordinal_filter(N_PATTERNS, x2, z,
IMSLS_DECODE,
IMSLS_N_CLASSES, &n_classes,
0);
printf("\nn_classes = %d\n", n_classes);
imsls_i_write_matrix("x-unfiltered", N_PATTERNS, 1, x2, 0);
}
Output
n_classes = 4
x
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
5 4
z
1 0.4
2 0.6
3 1.0
4 0.2
5 1.0
n_classes = 4
x-unfiltered
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 1
5 4
