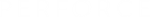ELRJ
This function evaluates Carlson’s incomplete elliptic integral of the third kind RJ(X, Y, Z, RHO)
Function Return Value
ELRJ — Function value. (Output)
Required Arguments
X — First variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. (Input)
It must be nonnegative.
Y — Second variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. (Input)
It must be nonnegative.
Z — Third variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. (Input)
It must be nonnegative.
RHO — Fourth variable of the incomplete elliptic integral. (Input)
It must be positive.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: ELRJ (X, Y, Z, RHO)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_ELRJ and D_ELRJ.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: ELRJ (X, Y, Z, RHO)
Double: The double precision name is DELRJ.
Description
The Carlson’s complete elliptic integral of the third kind is defined to be
The arguments must be nonnegative. In addition, x + y, x + z, y + z and ρ must be greater than or equal to and less than or equal to
, where s = AMACH(1) is the smallest representable floating-point number. Should any of these conditions fail, ELRJ is set to b = AMACH(2), the largest floating-point number.
The function ELRJ is based on the code by Carlson and Notis (1981) and the work of Carlson (1979).
Example
In this example, RJ(2, 3, 4, 5) is computed and printed.
USE ELRJ_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER NOUT
REAL RHO, VALUE, X, Y, Z
! Compute
X = 2.0
Y = 3.0
Z = 4.0
RHO = 5.0
VALUE = ELRJ(X, Y, Z, RHO)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) X, Y, Z, RHO, VALUE
99999 FORMAT (' ELRJ(', F6.3, ',', F6.3, ',', F6.3, ',', F6.3, &
') = ', F6.3)
END
Output
ELRJ( 2.000, 3.000, 4.000, 5.000) = 0.143