MATSE
Evaluates a sequence of odd, periodic, integer order, real Mathieu functions.
Required Arguments
X — Argument for which the sequence of Mathieu functions is to be evaluated. (Input)
Q — Parameter. (Input)
The parameter Q must be positive.
N — Number of elements in the sequence. (Input)
SE — Vector of length N containing the values of the function through the series. (Output)
SE(I) contains the value of the Mathieu function of order I at X for I = 1 to N.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL MATSE (X, Q, N, SE)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_MATSE and D_MATSE.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL MATSE (X, Q, N, SE)
Double: The double precision function name is DMATSE.
Description
The eigenvalues of Mathieu’s equation are computed using MATEE. The function values are then computed using a sum of Bessel functions, see Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (1965), equation 8.661.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of M2TSE/DM2TSE. The reference is
CALL M2TSE (X, Q, N, SE, NORDER, NEEDEV, EVAL0, EVAL1, COEF, WORK, BSJ)
The additional arguments are as follows:
NORDER — Order of the matrix used to compute the eigenvalues. (Input)
It must be greater than N. Routine MATSE computes NORDER by the following call to M3TEE:
CALL M3TEE (Q, N, NORDER)
NEEDEV — Logical variable, if .TRUE., the eigenvalues must be computed. (Input)
EVAL0 — Real work vector of length NORDER containing the eigenvalues computed by MATEE with ISYM = 1 and IPER = 0. (Input/Output)
If NEEDEV is .TRUE., then EVAL0 is computed by M2TSE; otherwise, it must be set as an input value.
EVAL1 — Real work vector of length NORDER containing the eigenvalues computed by MATEE with ISYM = 1 and IPER = 1. (Input/Output)
If NEEDEV is .TRUE., then EVAL1 is computed by M2TSE; otherwise, it must be set as an input value.
COEF — Real work vector of length NORDER + 4.
WORK — Real work vector of length NORDER + 4.
BSI — Real work vector of length 2 * NORDER + 1.
2. Informational error
|
Type |
Code |
Description |
|
4 |
1 |
The iteration for the eigenvalues did not converge. |
Example
In this example, sen(x = π/4, q = 10), n = 0, …, 9 is computed and printed.
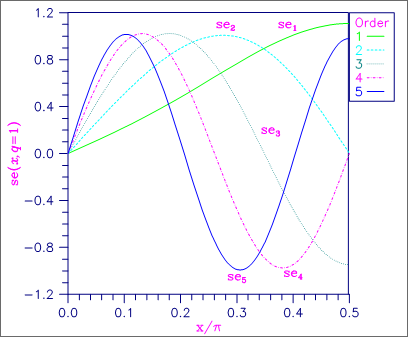
Figure 1, Plot of sen(x, q = 1)
USE CONST_INT
USE MATSE_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER N
PARAMETER (N=10)
!
INTEGER K, NOUT
REAL SE(N), Q, X
! Compute
Q = 10.0
X = CONST('PI')
X = 0.25* X
CALL MATSE (X, Q, N, SE)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
DO 10 K=1, N
WRITE (NOUT,99999) K-1, X, Q, SE(K)
10 CONTINUE
99999 FORMAT (' se sub', I2, ' (', F6.3, ',', F6.3, ') = ', F6.3)
END
Output
se sub 0 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.250
se sub 1 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.692
se sub 2 ( 0.785,10.000) = 1.082
se sub 3 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.960
se sub 4 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.230
se sub 5 ( 0.785,10.000) = -0.634
se sub 6 ( 0.785,10.000) = -0.981
se sub 7 ( 0.785,10.000) = -0.588
se sub 8 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.219
se sub 9 ( 0.785,10.000) = 0.871