Checks a user-supplied Jacobian of a system of equations with M functions in N unknowns.
Required Arguments
FCN — User-supplied subroutine to evaluate the function to be minimized. The usage is CALL FCN (M, N, X, F), where
M – Length of F. (Input)
N – Length of X. (Input)
X – The point at which
the function is evaluated. (Input)
X should not be
changed by FCN.
F – The computed function value at the point X. (Output)
FCN must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling program.
JAC —
User-supplied subroutine to evaluate the Jacobian at a
point X. The
usage is
CALL JAC
(M, N,
X, FJAC, LDFJAC), where
M – Length of F. (Input)
N – Length of X. (Input)
X – The point at which
the function is evaluated. (Input)
X should not be
changed by FCN.
FJAC – The computed M by N Jacobian at the point X. (Output)
LDFJAC – Leading dimension of FJAC. (Input)
JAC must be declared EXTERNAL in the calling program.
X — Vector of length N containing the point at which the Jacobian is to be checked. (Input)
INFO — Integer matrix of dimension M by N. (Output)
INFO(I, J) = 0 means the user-supplied Jacobian is a poor estimate for function I at the point X(J).
INFO(I, J) = 1 means the user-supplied Jacobian is a good estimate for function I at the point X(J).
INFO(I, J) = 2 means the user-supplied Jacobian disagrees with the numerical Jacobian for function I at the point X(J), but it might be impossible to calculate the numerical Jacobian.
INFO(I, J) = 3 means the user-supplied Jacobian for function I at the point X(J) and the numerical Jacobian are both zero. Therefore, the gradient should be rechecked at a different point.
Optional Arguments
M — The number of
functions in the system of equations. (Input)
Default: M = size
(INFO,1).
N — The number of
unknowns in the system of equations. (Input)
Default: N = size
(X,1).
LDINFO — Leading
dimension of INFO exactly as
specified in the dimension statement of the calling program.
(Input)
Default: LDINFO = size
(INFO,1).
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL CHJAC (FCN, JAC, X, INFO [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_CHJAC and D_CHJAC.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL CHJAC (FCN, JAC, M, N, X, INFO, LDINFO)
Double: The double precision name is DCHJAC.
Description
The routine CHJAC uses the following finite-difference formula to estimate the gradient of the i-th function of n variables at x:
gij(x) = (fi(x + hjej) - fi(x))/hj for j = 1, …, n
where hj = ɛ1/4 max{|xj|, 1/sj} sign(xj), ɛ is the machine epsilon, ej is the j-th unit vector, and sj is the scaling factor of the j-th variable.
Next, CHJAC checks the user-supplied Jacobian J(x) by comparing it with the finite difference gradient gi(x). If
|gij(x) - Jij(x)| < τ |Jij(x)|
where τ = ɛ1/4, then Jij(x) is declared correct; otherwise, CHJAC computes the bounds of calculation error and approximation error. When both bounds are too small to account for the difference, Jij(x) is reported as incorrect. In the case of a large error bound, CHJAC uses a nearly optimal stepsize to recompute gij(x) and reports that Jij(x) is correct if
|gij(x) - Jij(x)| < 2τ |Jij(x)|
Otherwise, Jij(x) is considered incorrect unless the error bound for the optimal step is greater than τ |Jij(x)|. In this case, the numeric gradient may be impossible to compute correctly. For more details, see Schnabel (1985).
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of C2JAC/DC2JAC. The reference is:
CALL C2JAC (FCN, JAC, N, X, INFO, LDINFO, FX, FJAC, GRAD, XSCALE, EPSFCN, INFT, NEWX)
The additional arguments are as follows:
FX — Vector of length M containing the value of each function in FCN at X.
FJAC — Real matrix of dimension M by N containing the Jacobian of FCN evaluated at X.
GRAD — Real work vector of length N used to store the gradient of each function in FCN.
XSCALE — Vector of length N used to store the diagonal scaling matrix for the variables.
EPSFCN — Estimate of the relative noise in the function.
INFT — Vector of length N. For I = 1 through N, INFT contains information about the Jacobian.
NEWX — Real work array of length N.
2. Informational errors
Type Code
4 1 The user-supplied Jacobian is a poor estimate of the numerical Jacobian.
Example
The user-supplied Jacobian of
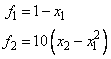
at (-1.2, 1.0) is checked.
USE
CHJAC_INT
USE WRIRN_INT
IMPLICIT
NONE
INTEGER LDINFO, N
PARAMETER (M=2,N=2,LDINFO=M)
!
INTEGER INFO(LDINFO,N)
REAL X(N)
EXTERNAL FCN, JAC
!
! Input value for X
! X = (-1.2, 1.0)
!
DATA X/-1.2, 1.0/
!
CALL CHJAC (FCN, JAC, X, INFO)
CALL WRIRN ('The information matrix', INFO)
!
END
!
SUBROUTINE FCN (M, N, X, F)
INTEGER M, N
REAL X(N), F(M)
!
F(1) = 1.0 - X(1)
F(2) = 10.0*(X(2)-X(1)*X(1))
RETURN
END
!
SUBROUTINE JAC (M, N, X, FJAC, LDFJAC)
INTEGER M, N, LDFJAC
REAL X(N), FJAC(LDFJAC,N)
!
FJAC(1,1) = -1.0
FJAC(1,2) = 0.0
FJAC(2,1) = -20.0*X(1)
FJAC(2,2) = 10.0
RETURN
END
Output
*** WARNING ERROR 2 from C2JAC. The numerical
value of the
Jacobian
*** evaluation
for function 1 at the point X(2) = 1.000000E+00
and
*** the
user-supplied value are both zero. The Jacobian for
this
*** function
should probably be re-checked at another value
for
*** this
point.
The information matrix
1
2
1 1 3
2 1 1
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |