This function returns the value of various mathematical and physical constants.
Function Return Value
CONST Value of
the constant. (Output)
See Comment 1.
Required Arguments
NAME Character
string containing the name of the desired constant. (Input)
See
Comment 3 for a list of valid constants.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CONST (NAME)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_CONST and D_CONST.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CONST (NAME)
Double: The double precision name is DCONST.
Description
Routine CONST returns the value of various mathematical and physical quantities. For all of the physical values, the Systeme International d'Unites (SI) are used.
The reference for constants are indicated by the code in [ ] Comment above.
[1] Cohen and Taylor (1986)
[2] Liepman (1964)
[3] Precomputed mathematical constants
The constants marked with an E before the [ ] are exact (to machine precision).
To change the units of the values returned by CONST, see CUNIT.
Comments
1. If the generic version of this function is used, the immediate result must be stored in a variable before use in an expression. For example:
X = CONST(PI')
Y =
COS(x)
must be used rather than
Y = COS(CONST(PI')).
If this is too much of a restriction on the programmer, then the specific name can be used without this restriction.
2. The case of the character string in NAME does not matter. The names PI, Pi, Pi, and pi are equivalent.
3. The units of the physical constants are in SI units (meter kilogram-second).
4. The names allowed are as follows:
|
Name |
Description |
Value |
Ref. |
|
AMU |
Atomic mass unit |
1.6605402E − 27 kg |
[1] |
|
ATM |
Standard atm pressure |
1.01325E + 5N/m2E |
[2] |
|
AU |
Astronomical unit |
1.496E + 11m |
[ ] |
|
Avogadro |
Avogadro's number |
6.0221367E + 231/mole |
[1] |
|
Boltzman |
Boltzman's constant |
1.380658E − 23J/K |
[1] |
|
C |
Speed of light |
2.997924580E + 8m/sE |
[1] |
|
Catalan |
Catalan's constant |
0.915965 E |
[3] |
|
E |
Base of natural logs |
2.718 E |
[3] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ElectronCharge |
Electron change |
1.60217733E −19C |
[1] |
|
ElectronMass |
Electron mass |
9.1093897E − 31 kg |
[1] |
|
ElectronVolt |
Electron volt |
1.60217733E − 19J |
[1] |
|
Euler |
Euler's constant gamma |
0.577 E |
[3] |
|
Faraday |
Faraday constant |
9.6485309E + 4C/mole |
[1] |
|
FineStructure |
fine structure |
7.29735308E − 3 |
[1] |
|
Gamma |
Euler's constant |
0.577 E |
[3] |
|
Gas |
Gas constant |
8.314510J/mole/k |
[1] |
|
Gravity |
Gravitational constant |
6.67259E − 11N * m2/kg2 |
[1] |
|
Hbar |
Planck constant / 2 pi |
1.05457266E − 34J * s |
[1] |
|
PerfectGasVolume |
Std vol ideal gas |
2.241383E − 2m3/mole |
[*] |
|
Pi |
Pi |
3.141 E |
[3] |
|
Planck |
Planck's constant h |
6.6260755E − 34J * s |
[1] |
|
ProtonMass |
Proton mass |
1.6726231E − 27 kg |
[1] |
|
Rydberg |
Rydberg's constant |
1.0973731534E + 7/m |
[1] |
|
SpeedLight |
Speed of light |
2.997924580E + 8m/s E |
[1] |
|
StandardGravity |
Standard g |
9.80665m/s2E |
[2] |
|
StandardPressure |
Standard atm pressure |
1.01325E + 5N/m2E |
[2] |
|
StefanBoltzmann |
Stefan-Boltzman |
5.67051E − 8W/K4/m2 |
[1] |
|
WaterTriple |
Triple point of water |
2.7316E + 2K E |
[2] |
Example
In this example, Euler's constant γ is obtained and printed. Euler's constant is defined to be
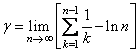
USE CONST_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER NOUT
REAL GAMA
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Get gamma
GAMA = CONST('GAMMA')
! Print gamma
WRITE (NOUT,*) 'GAMMA = ', GAMA
END
Output
GAMMA = 0.5772157
For another example, see CUNIT.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |