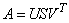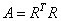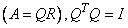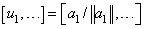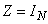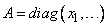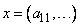For a detailed description of MPI Capability see “Dense Matrix Parallelism Using MPI.”
Several decompositions and functions required for numerical linear algebra follow. The convention of enclosing optional quantities in brackets, “[ ]” is used. The functions that use MPI for parallel execution of the box data type are marked in bold.
|
Defined Array Functions |
Matrix Operation |
|
S=SVD(A [,U=U, V=V]) |
|
|
E=EIG(A [[,B=B, D=D], V=V, W=W]) |
(AV = VE), AVD = BVE (AW = WE), AWD = BWE |
|
R=CHOL(A) |
|
|
Q=ORTH(A [,R=R]) |
|
|
U=UNIT(A) |
|
|
F=DET(A) |
Det(A) = determinant |
|
K=RANK(A) |
rank(A) = rank |
|
P=NORM(A[,[type=]i]) |
|
|
C=COND(A) |
|
|
Z=EYE(N) |
|
|
A=DIAG(X) |
|
|
X=DIAGONALS(A) |
|
|
Y=FFT (X,[WORK=W]); X=IFFT(Y,[WORK=W]) |
Discrete Fourier Transform, Inverse |
|
Y=FFT_BOX (X,[WORK=W]); X=IFFT_BOX(Y,[WORK=W]) |
Discrete Fourier Transform for Boxes, Inverse |
|
A=RAND(A) |
Random numbers, 0 < A < 1 |
|
L=isNaN(A) |
Test for NaN, if (l) then… |
In certain functions, the optional arguments are inputs while other optional arguments are outputs. To illustrate the example of the box SVD function, a code is given that computes the singular value decomposition and the reconstruction of the random matrix box, A, using the computed factors, R = USVT. Mathematically R = A, but this will be true, only approximately, due to rounding errors. The value units_of_error = ||A − R||/(||A||ɛ), shows the merit of this approximation.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |