Computes a least-squares approximation with user-supplied basis functions.
Required Arguments
F — User-supplied
function to evaluate basis functions. The form is F(K, X),
where
K – Number of the
basis function. (Input)
K may be equal to 1,
2, …, NBASIS.
X – Argument for
evaluation of the K-th basis function. (Input)
F – The function
value. (Output)
F must be declared
EXTERNAL in the
calling program. The data FDATA is approximated
by A(1) * F(1, X) + A(2) * F(2, X) +…+ A(NBASIS) * F(NBASIS, X) if INTCEP = 0 and is
approximated by A(1) + A(2) * F(1, X) +…+ A(NBASIS + 1) * F(NBASIS, X) if INTCEP = 1.
XDATA — Array of length NDATA containing the abscissas of the data points. (Input)
FDATA — Array of length NDATA containing the ordinates of the data points. (Input)
A — Array of
length INTCEP +
NBASIS
containing the coefficients of the approximation. (Output)
If
INTCEP = 1,
A(1) contains
the intercept. A(INTCEP + I) contains
the coefficient of the I-th basis
function.
SSE — Sum of squares of the errors. (Output)
Optional Arguments
INTCEP —
Intercept option. (Input)
Default: INTCEP = 0.
INTCEP Action
0 No intercept is automatically included in the model.
1 An intercept is automatically included in the model.
NBASIS — Number
of basis functions. (Input)
Default: NBASIS = size
(A,1)
NDATA — Number of
data points. (Input)
Default: NDATA = size (XDATA,1).
IWT — Weighting
option. (Input)
Default: IWT = 0.
IWT Action
0 Weights of one are assumed.
1 Weights are supplied in WEIGHT.
WEIGHT — Array of
length NDATA
containing the weights. (Input if IWT = 1)
If IWT = 0, WEIGHT is not
referenced and may be dimensioned of length one.
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL FNLSQ (F, XDATA, FDATA, A, SSE [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_FNLSQ and D_FNLSQ.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: CALL FNLSQ (F, INTCEP, NBASIS, NDATA, XDATA, FDATA, IWT, WEIGHT, A, SSE)
Double: The double precision name is DFNLSQ.
Description
The routine FNLSQ computes a best least-squares approximation to given univariate data of the form
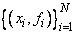
by M basis functions
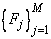
(where M = NBASIS). In particular, if INTCEP = 0, this routine returns the error sum of squares SSE and the coefficients a which minimize
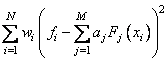
where w = WEIGHT, N = NDATA, x = XDATA, and, f = FDATA.
If INTCEP = 1, then an intercept is placed in the model; and the coefficients a, returned by FNLSQ, minimize the error sum of squares as indicated below.
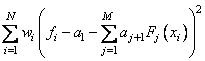
That is, the first element of the vector a is now the coefficient of the function that is identically 1 and the coefficients of the Fj's are now aj+1.
One additional parameter in the calling sequence for FNLSQ is IWT. If IWT is set to 0, then wi = 1 is assumed. If IWT is set to 1, then the user must supply the weights.
Comments
1. Workspace may be explicitly provided, if desired, by use of F2LSQ/DF2LSQ. The reference is:
CALL F2LSQ (F, INTCEP, NBASIS, NDATA, XDATA, FDATA, IWT, WEIGHT, A, SSE, WK)
The additional argument is
WK — Work vector of length (INTCEP + NBASIS)**2 + 4 * (INTCEP + NBASIS) + IWT + 1. On output, the first (INTCEP + NBASIS)**2 elements of WK contain the R matrix from a QR decomposition of the matrix containing a column of ones (if INTCEP = 1) and the evaluated basis functions in columns INTCEP + 1 through INTCEP + NBASIS.
2. Informational errors
Type Code
3 1 Linear dependence of the basis functions exists. One or more components of A are set to zero.
3 2 Linear dependence of the constant function and basis functions exists. One or more components of A are set to zero.
4 1 Negative weight encountered.
Example
In this example, we fit the following two functions (indexed by δ)
1 + sin x + 7 sin 3x + δɛ
where ɛ is random uniform deviate over the range [−1, 1], and δ is 0 for the first function and 1 for the second. These functions are evaluated at 90 equally spaced points on the interval [0, 6]. We use 4 basis functions, sin kx for k = 1, …, 4, with and without the intercept.
USE FNLSQ_INT
USE RNSET_INT
USE UMACH_INT
USE RNUNF_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER NBASIS, NDATA
PARAMETER (NBASIS=4, NDATA=90)
!
INTEGER I, INTCEP, NOUT
REAL A(NBASIS+1), F, FDATA(NDATA), FLOAT, G, RNOISE,&
SIN, SSE, X, XDATA(NDATA)
INTRINSIC FLOAT, SIN
EXTERNAL F
!
G(X) = 1.0 + SIN(X) + 7.0*SIN(3.0*X)
! Set random number seed
CALL RNSET (1234579)
! Set up data values
DO 10 I=1, NDATA
XDATA(I) = 6.0*(FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NDATA-1))
FDATA(I) = G(XDATA(I))
10 CONTINUE
! Compute least squares fit with no
! intercept
CALL FNLSQ (F, XDATA, FDATA, A, SSE, INTCEP=INTCEP, &
NBASIS=NBASIS)
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99996)
! Write output
WRITE (NOUT,99999) SSE, (A(I),I=1,NBASIS)
!
INTCEP = 1
! Compute least squares fit with
! intercept
CALL FNLSQ (F, XDATA, FDATA, A, SSE, INTCEP=INTCEP, &
NBASIS=NBASIS)
! Write output
WRITE (NOUT,99998) SSE, A(1), (A(I),I=2,NBASIS+1)
! Introduce noise
DO 20 I=1, NDATA
RNOISE = RNUNF()
RNOISE = 2.0*RNOISE - 1.0
FDATA(I) = FDATA(I) + RNOISE
20 CONTINUE
INTCEP = 0
! Compute least squares fit with no
! intercept
CALL FNLSQ (F, XDATA, FDATA, A, SSE, INTCEP=INTCEP, &
NBASIS=NBASIS)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99997)
! Write output
WRITE (NOUT,99999) SSE, (A(I),I=1,NBASIS)
!
INTCEP = 1
! Compute least squares fit with
! intercept
CALL FNLSQ (F, XDATA, FDATA, A, SSE, INTCEP=INTCEP, &
NBASIS=NBASIS)
! Write output
WRITE (NOUT,99998) SSE, A(1), (A(I),I=2,NBASIS+1)
!
99996 FORMAT (//, ' Without error introduced we have :', /,&
' SSE Intercept Coefficients ', /)
99997 FORMAT (//, ' With error introduced we have :', /, ' SSE '&
, ' Intercept Coefficients ', /)
99998 FORMAT (1X, F8.4, 5X, F9.4, 5X, 4F9.4, /)
99999 FORMAT (1X, F8.4, 14X, 5X, 4F9.4, /)
END
REAL FUNCTION F (K, X)
INTEGER K
REAL X
!
REAL SIN
INTRINSIC SIN
!
F = SIN(K*X)
RETURN
END
Output
Without error introduced we have
:
SSE
Intercept
Coefficients
89.8776
1.0101 0.0199 7.0291
0.0374
0.0000
1.0000 1.0000
0.0000 7.0000 0.0000
With error introduced
we have :
SSE
Intercept
Coefficients
112.4662
0.9963 -0.0675 6.9825
0.0133
30.9831
0.9522 0.9867
-0.0864 6.9548 -0.0223
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |