This function evaluates the derivative of a piecewise polynomial.
Function Return Value
PPDER — Value of the IDERIV-th derivative of the piecewise polynomial at X. (Output)
Required Arguments
X — Point at which the polynomial is to be evaluated. (Input)
BREAK — Array of
length NINTV + 1
containing the breakpoints of the piecewise polynomial
representation. (Input)
BREAK must be strictly
increasing.
PPCOEF — Array of
size KORDER
* NINTV containing the
local coefficients of the piecewise polynomial pieces. (Input)
PPCOEF is
treated internally as a matrix of size KORDER by NINTV.
Optional Arguments
IDERIV — Order of
the derivative to be evaluated. (Input)
In particular, IDERIV = 0 returns the
value of the polynomial.
Default: IDERIV = 1.
KORDER — Order of
the polynomial. (Input)
Default: KORDER = size (PPCOEF,1).
NINTV — Number of
polynomial pieces. (Input)
Default: NINTV = size
(PPCOEF,2).
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: PPDER (X, BREAK, PPCOEF [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_PPDER and D_PPDER.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: PPDER (IDERIV, X, KORDER, NINTV, BREAK, PPCOEF)
Double: The double precision function name is DPPDER.
Description
The routine PPDER evaluates the derivative of a piecewise polynomial function f at a given point. This routine is based on the subroutine PPVALU by de Boor (1978, page 89). In particular, if the breakpoint sequence is stored in ξ (a vector of length N = NINTV + 1), and if the coefficients of the piecewise polynomial representation are stored in c, then the value of the j-th derivative of f at x in[ξi, ξi + 1) is
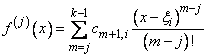
when j = 0 to k − 1 and zero otherwise. Notice that this representation forces the function to be right continuous. If x is less than ξ1, then i is set to 1 in the above formula; if x is greater than or equal to ξN , then i is set to N − 1. This has the effect of extending the piecewise polynomial representation to the real axis by extrapolation of the first and last pieces.
Example
In this example, a spline interpolant to a function f is computed using the IMSL routine BSINT. This routine represents the interpolant as a linear combination of B-splines. This representation is then converted to piecewise polynomial representation by calling the IMSL routine BSCPP. The piecewise polynomial's zero-th and first derivative are evaluated using PPDER. These values are compared to the corresponding values of f.
USE IMSL_LIBRARIES
IMPLICIT NONE
INTEGER KORDER, NCOEF, NDATA, NKNOT
PARAMETER (KORDER=4, NCOEF=20, NDATA=20, NKNOT=NDATA+KORDER)
!
INTEGER I, NOUT, NPPCF
REAL BREAK(NCOEF), BSCOEF(NCOEF), DF, DS, EXP, F,&
FDATA(NDATA), FLOAT, PPCOEF(KORDER,NCOEF), S,&
X, XDATA(NDATA), XKNOT(NKNOT)
INTRINSIC EXP, FLOAT
!
F(X) = X*EXP(X)
DF(X) = (X+1.)*EXP(X)
! Set up interpolation points
DO 10 I=1, NDATA
XDATA(I) = FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NDATA-1)
FDATA(I) = F(XDATA(I))
10 CONTINUE
! Generate knot sequence
CALL BSNAK (NDATA, XDATA, KORDER, XKNOT)
! Compute the B-spline interpolant
CALL BSINT (NCOEF, XDATA, FDATA, KORDER, XKNOT, BSCOEF)
! Convert to piecewise polynomial
CALL BSCPP (KORDER, XKNOT, NCOEF, BSCOEF, NPPCF, BREAK, PPCOEF)
! Get output unit number
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
! Write heading
WRITE (NOUT,99999)
! Print the interpolant on a uniform
! grid
DO 20 I=1, NDATA
X = FLOAT(I-1)/FLOAT(NDATA-1)
! Compute value of the piecewise
! polynomial
S = PPDER(X,BREAK,PPCOEF, IDERIV=0, NINTV=NPPCF)
! Compute derivative of the piecewise
! polynomial
DS = PPDER(X,BREAK,PPCOEF, IDERIV=1, NINTV=NPPCF)
WRITE (NOUT,'(2F12.3,F12.6,F12.3,F12.6)') X, S, F(X) - S, DS,&
DF(X), DS
20 CONTINUE
99999 FORMAT (11X, 'X', 8X, 'S(X)', 7X, 'Error', 7X, 'S''(X)', 7X,&
'Error')
END
Output
X
S(X)
Error
S'(X)
Error
0.000 0.000
0.000000 1.000
-0.000112
0.053 0.055
0.000000 1.109
0.000030
0.105 0.117
0.000000 1.228
-0.000008
0.158 0.185
0.000000 1.356
0.000002
0.211 0.260
0.000000 1.494
0.000000
0.263 0.342
0.000000 1.643
0.000000
0.316 0.433
0.000000 1.804
-0.000001
0.368 0.533
0.000000 1.978
0.000002
0.421 0.642
0.000000 2.165
0.000001
0.474 0.761
0.000000 2.367
0.000000
0.526 0.891
0.000000 2.584
-0.000001
0.579 1.033
0.000000 2.817
0.000001
0.632 1.188
0.000000 3.068
0.000001
0.684 1.356
0.000000 3.338
0.000001
0.737 1.540
0.000000 3.629
0.000001
0.789 1.739
0.000000 3.941
0.000000
0.842 1.955
0.000000 4.276
-0.000006
0.895 2.189
0.000000 4.636
0.000024
0.947 2.443
0.000000 5.022
-0.000090
1.000 2.718
0.000000 5.436
0.000341
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |