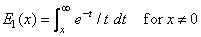This function evaluates the exponential integral for arguments greater than zero and the Cauchy principal value for arguments less than zero.
Function Return Value
Required Arguments
X — Argument for which the function value is desired. (Input)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Specific: The specific interface names are S_EI and D_EI.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Double: The double precision function name is DEI.
Description
The exponential integral, Ei(x), is defined to be
The argument x must be large enough to insure that the asymptotic formula ex/x does not underflow, and x must not be so large that ex overflows.
Comments
If principal values are used everywhere, then for all X, EI(X) = -E1(-X) and E1(X) = -EI(-X).
Example
In this example, Ei(1.15) is computed and printed.
99999 FORMAT (' EI(', F6.3, ') = ', F6.3)
Output
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |