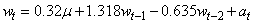Automatic selection and fitting of a univariate autoregressive time series model using Akaike's Final Prediction Error (FPE) criteria. Estimates of the autoregressive parameters for the model with minimum FPE are calculated using the methodology described in Akaike, H., et. al (1979).
Required Arguments
MAXLAG — Maximum lag of the sample autocovariances for the stationary time series, W. (Input)
ACV — Vector of length MAXLAG + 1 containing the sample autocovariances of W. The first element, ACV(0) must be the sample variance of the series and the remaining elements, ACV(1), …, ACV(MAXLAG), contain the autocovariances of the series for lags 1 through MAXLAG. (Input)
NOBS — Number of observations in the time series. (Input)
NPAR — Number of autoregressive parameters in the the selected model. (Output)
PAR — Vector of length MAXLAG containing estimates for the autoregressive parameters in the model with the minimum Final Prediction Error. The estimates are in the first NPAR values of this vector. The remaining values are set to 0. (Output)
Optional Arguments
IPRINT — Printing option. (Input)
FPE — Final Prediction Error for fitted model. (Output)
CHISQ — Chi-square statistic, with 1 degree of freedom, for the selected model. CHISQ is used to examine the significance of the fitted model. (Output)
AVAR — Estimate of noise varaince. (Output)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: CALL AUTO_FPE_UNI_AR (MAXLAG, ACV, NOBS, NPAR, PAR [,…])
Specific: The specific interface names are S_AUTO_FPE_UNI_AR and D_AUTO_FPE_UNI_AR.
Description
This routine is based upon the FPEAUT program published in the TIMSAC –71 Library described by Akaike, H. and Nakagawa, T (1972).
The Final Prediction Error for an autoregressive model with lag k is defined as:
where N =
NOBS
and 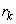 is the minimum of
is the minimum of
with respect to the autoregressive coefficients
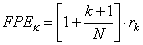 is estimated using the formula:
is estimated using the formula:
where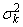 is calculated from the recursive relationship:
is calculated from the recursive relationship:
The model selected and parameter estimates vary depending
upon the value of MAXLAG.
Akaike and Nakagawa (1972) recommend that MAXLAG
start with values between 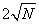 and
and 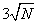 .
.
In every case, however, MAXLAG
must be strictly less than 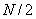 .
.
As MAXLAG is increased numerical accuracy decreases. It is even possible numerically for the estimated FPE to become negative. If this happens, use double precision.
Example
Consider the Wolfer Sunspot Data (Box and Jenkins 1976, page 530) consisting of the number of sunspots observed each year from 1770 through 1869. In this example, AUTO_FPE_UNI_AR, found the minimum FPE solution is an autoregressive model with 10 lags. This is slightly different from the optimum solution found by AUTO_UNI_AR, using minimum AIC instead of FPE.
The solution reported by AUTO_UNI_AR is an AR model with 2 lags.
we obtain the following reprensentation for this series.
! SPECIFICATIONS FOR PARAMETERS
integer, parameter :: maxlag=20, nobs=100
real(kind(1e0)) :: ac(maxlag+1), avar
real(kind(1e0)) :: acv(maxlag+1), par(maxlag)
write(*,*) 'Univariate FPE Automatic Order selection '
call acf (x(22:,2), maxlag, ac, acv=acv, nobs=nobs)
call auto_fpe_uni_ar(maxlag, acv, nobs, npar, par, &
fpe=fpe, chisq=chisq, avar=avar)
write(*,*) 'Minimum FPE = ', fpe
write(*,*) 'Chi-squared = ', chisq
call wrrrn('AR Coefficients', par, nra=npar, nca=1, lda=npar)
Output
Univariate FPE Automatic Order selection
Chi-squared = 39.056877
Avar =
289.03915
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |
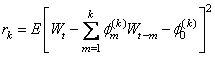
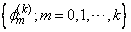 .
.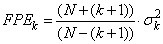 ,
,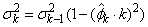 , where
, where 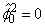 and
and 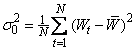 .
.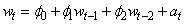
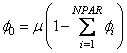 ,
,