C....... ELEMENTARY AND SPECIAL FUNCTIONS (search also class L5)
Generate orthogonal polynomials with respect to x values and specified weights.
Evaluate the chi-squared distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the chi-squared distribution function.
Evaluate the gamma distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the gamma distribution function.
Evaluate the beta probability distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the beta distribution function.
C8a.... Error functions, their inverses, integrals, including the normal distribution function
Evaluate the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function.
K....... APPROXIMATION (search also class L8)
K1..... Least squares (L2) approximation
K1a.... Linear least squares (search also classes D5, D6, D9)
Fit a multiple linear regression model given the variance-covariance matrix.
Fit a multivariate linear regression model via fast Givens transformations.
Fit a multivariate general linear model.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using least squares.
K1a1a. Univariate data (curve fitting)
Fit a polynomial curve using least squares.
Fit an orthogonal polynomial regression model.
Analyze a polynomial regression model.
Fit a multivariate linear regression model with linear equality restrictions HΒ = G imposed on the regression parameters given results from IMSL routine RGIVN after IDO = 1 and IDO = 2 and prior to IDO = 3.
K1b.... Nonlinear least squares
K1b1a1..... User provides no derivatives
Fit a nonlinear regression model.
K1b1a2..... User provides first derivatives
Fit a nonlinear regression model.
K2..... Minimax (L∞) approximation
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the minimax criterion.
K3..... Least absolute value (L1) approximation
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the Lp norm criterion.
K4..... Other analytic approximations (e.g., Taylor polynomial, Pade)
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the Lp norm criterion.
L....... STATISTICS, PROBABILITY
Produce a letter value summary.
Compute basic univariate statistics.
Compute basic univariate statistics.
Compute basic univariate statistics.
Compute tie statistics for a sample of observations.
Compute basic statistics from grouped data.
L1c.... Multi-dimensional data
Compute cell frequencies, cell means, and cell sums of squares for multivariate data.
L1c1b. Covariance, correlation
Compute the variance-covariance or correlation matrix.
Compute partial correlations or covariances from the covariance or correlation matrix.
Compute a robust estimate of a covariance matrix and mean vector.
L2a.... Transform (search also classes L10a, N6, and N8)
Perform a forward or an inverse Box-Cox (power) transformation.
Generate centered variables, squares, and crossproducts.
Generate orthogonal polynomials with respect to x values and specified weights.
Compute the ranks, normal scores, or exponential scores for a vector of observations.
Compute cell frequencies, cell means, and cell sums of squares for multivariate data.
Tally multivariate observations into a multi-way frequency table.
Tally observations into a one-way frequency table.
Tally observations into a two-way frequency table.
L2e.... Construct new variables (e.g., indicator variables)
Generate regressors for a general linear model.
L3...... Elementary statistical graphics (search also class Q)
L3a2.. Frequency, cumulative frequency, percentile plots
Print a sample cumulative distribution function (CDF), a theoretical CDF, and confidence band information.
L3a3.. EDA graphics (e.g., box plots)
Print boxplots for one or more samples.
L3b.... Two-dimensional data (search also class L3e)
L3b1.. Histograms (superimposed and bivariate)
Print a vertical histogram with every bar subdivided into two parts.
L3b2.. Frequency, cumulative frequency
Print a plot of two sample cumulative distribution functions.
L3e.... Multi-dimensional data
Print a plot of up to ten sets of points.
Print a scatterplot of several groups of data.
Print boxplots for one or more samples.
L4...... Elementary data analaysis
Print a sample cumulative distribution function (CDF), a theoretical CDF, and confidence band information.
L4a1a2e Exponential, extreme value
L4a1a21 Lambfa, logistic, lognormal
L4a1a2n Negative binomial, normal
L4a1a4..... Parameter estimates and tests
Estimate the parameter p of the binomial distribution.
Estimate the parameter of the Poisson distribution.
L4a1b1..... Estimates and test regarding location (e.g., median), dispersion and shape
Perform a sign test of the hypothesis that a given value is a specified quantile of a distribution.
Perform a Wilcoxon signed rank test.
L4a1b2..... Density function estimation
Perform nonparametric probability density function estimation by the kernel method.
Perform nonparametric probability density function estimation by the penalized likelihood method.
Estimate a probability density function at specified points using linear or cubic interpolation.
Compute Gaussian kernel estimates of a univariate density via the fast Fourier transform over a fixed interval.
Perform a chi-squared goodness-of-fit test.
Perform a Kolmogorov-Smirnov one-sample test for continuous distributions.
Perform Lilliefors test for an exponential or normal distribution.
Perform a Shapiro-Wilk W-test for normality.
L4ald.. Analysis of a sequnce of numbers (search also class L10a)
Perform the Noether test for cyclical trend.
Perform the Cox and Stuart sign test for trends in dispersion and location.
L4a3.. Grouped (and/or censored) data
Compute basic statistics from grouped data.
Compute maximum likelihood estimates of the mean and variance from grouped and/or censored normal data.
L4a4.. Data sampled from a finite population
SMPPR Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population proportion and total, given proportion data from a simple random sample.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population proportion and total, given proportion data from a stratified random sample.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total using single-stage cluster sampling with continuous data.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total, given data from a simple random sample.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total, given data from a stratified random sample.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total, given continuous data from a two-stage sample with equisized primary units.
L4b.... Two dimensional data (search also class L4c)
L4b1.. Pairwise independent data
L4b1a4..... Parameter estimates and hypothesis tests
Compute statistics for mean and variance inferences using samples from two normal populations.
L4b1b. Nonparametric analysis (e.g., tests based on ranks)
Calculate and test the significance of the Kendall coefficient of concordance.
Compute and test Kendall's rank correlation coefficient.
Perform the Wilcoxon rank sum test.
Perform a Kolmogorov-Smirnov two-sample test.
L4b4.. Pairwise dependent grouped data
Estimate the bivariate normal correlation coefficient using a contingency table.
Categorize bivariate data and compute the tetrachoric correlation coefficient.
L4b5.. Data sampled from a finite population
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total using ratio or regression estimation, or inferences regarding the population ratio, given a simple random sample.
Compute statistics for inferences regarding the population mean and total using ratio or regression estimation, given continuous data from a stratified random sample.
L4c.... Multi-dimensional data (search also classes L4b and L7a1)
Perform a Kruskal-Wallis test for identical population medians.
Perform a k-sample trends test against ordered alternatives.
Compute Mardia's multivariate measures of skewness and kurtosis and test for multivariate normality.
Perform a Cochran Q test for related observations.
L4e.... Multiple multi-dimensional data sets
Compute a test for the independence of k sets of multivariate normal variables.
L5...... Function evaluation (search also class C)
L5a1.. Cumulative distribution functions, probability density functions
Evaluate the beta probability distribution function.
Evaluate the binomial distribution function.
Evaluate the binomial probability function.
Evaluate the chi-squared distribution function.
Evaluate the noncentral chi-squared distribution function.
Evaluate the F distribution function.
L5a1g. Gamma, general, geometric
Evaluate the gamma distribution function.
Evaluate a general continuous cumulative distribution function given ordinates of the density.
L5a1h. Halfnormal, hyergeometric
Evaluate the hypergeometric distribution function.
Evaluate the hypergeometric probability function.
L5a1k. Kendall F statistic, Kolmogorsv-Smirnov
Evaluate the distribution function of the one-sided Kolmogorov-Smirnov goodness-of-fit D+ or D− test statistic based on continuous data for one sample.
Evaluate the distribution function of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov goodness-of-fit D test statistic based on continuous data for two samples.
Compute the frequency distribution of the total score in Kendall's rank correlation coefficient.
L5a1n. Negative binomial, normal
Evaluate the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function.
Evaluate the Poisson distribution function.
Evaluate the Poisson probability function.
Evaluate the Student's t distribution function.
Evaluate the noncentral Student's t distribution function.
L5a2.. Inverse cumulative distribution functions, sparsity functions
Evaluate the inverse of the beta distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the chi-squared distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the noncentral chi-squared function.
Evaluate the inverse of the F distribution function.
L5a2g. Gamma, general, geometric
Evaluate the inverse of the gamma distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of a general continuous cumulative distribution function given ordinates of the density.
Evaluate the inverse of a general continuous cumulative distribution function given in a subprogram.
Evaluate the inverse of the Student's t distribution function.
Evaluate the inverse of the noncentral Student's t distribution function.
L5b1.. Cumulative distribution functions, probability density functions
Evaluate the bivariate normal distribution function.
L6...... Random number generation
L6a2.. Beta, binomial, Boolean
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a beta distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a binomial distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a chi-squared distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a Cauchy distribution.
L6a5.. Exponential, extreme value
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a standard exponential distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a mixture of two exponential distributions.
L6a7.. Gamma, general (continuous, discrete), geometric
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a standard gamma distribution.
Set up table to generate pseudorandom numbers from a general continuous distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a general continuous distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution using an alias method.
Set up table to generate pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a general discrete distribution using a table lookup method.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a geometric distribution.
L6a8.. Halfnormal, hypergeometric
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a hypergeometric distribution.
L6a12. Lambda, logistic, lognormal
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a logarithmic distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a lognormal distribution.
L6a14. Negative binomial, normal, normal order statistics
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a negative binomial distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a standard normal distribution using an acceptance/rejection method.
Generate a pseudorandom number from a standard normal distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a standard normal distribution using an inverse CDF method.
Generate pseudorandom order statistics from a standard normal distribution.
L6a16. Pareto, Pascal, permutations, Poisson
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a nonhomogeneous Poisson process.
Generate a pseudorandom permutation.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a Poisson distribution.
L6a19. Samples, stable distribution
Generate a simple pseudorandom sample of indices.
Generate a simple pseudorandom sample from a finite population.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a stable distribution.
L6a20. t distribution, time series, triangular
Generate a time series from a specified ARMA model.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a nonhomogeneous Poisson process.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a Student's t distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a triangular distribution on the interval (0,1).
L6a21. Uniform (continuous, discrete), uniform order statistics
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a uniform (0,1) distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a discrete uniform distribution.
Generate a pseudorandom number from a uniform (0, 1) distribution.
Generate pseudorandom order statistics from a uniform (0, 1) distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a von Mises distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a Weibull distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a multivariate distribution determined from a given sample.
L6b3.. Contingency table, correlation matrix
Generate a pseudorandom orthogonal matrix or a correlation matrix.
Generate a pseudorandom two-way table.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a multinomial distribution.
Generate pseudorandom numbers from a multivariate normal distribution.
Generate a pseudorandom orthogonal matrix or a correlation matrix.
L6b21. Linear L-1 (least absolute value) approximation random numbers
FAURE_INIT Shuffles Faure sequence initialization.
FAURE_FREE Frees the structure containing information about the Faure sequence.
FAURE_NEXT Computes a shuffled Faure sequence.
Generate pseudorandom points on a unit circle or K-dimensional sphere.
L6c.... Service routines (e.g., seed)
RNGEF Retrieve the current value of the array used in the IMSL GFSR random number generator.
RNGES Retrieve the current value of the table in the IMSL random number generators that use shuffling.
RNGET Retrieve the current value of the seed used in the IMSL random number generators.
RNISD Determine a seed that yields a stream beginning 100,000 numbers beyond the beginning of the stream yielded by a given seed used in IMSL multiplicative congruential generators (with no shufflings).
RNOPG Retrieve the indicator of the type of uniform random number generator.
RNOPT Select the uniform (0, 1) multiplicative congruential pseudorandom number generator.
RNSEF Initialize the array used in the IMSL GFSR random number generator.
RNSES Initialize the table in the IMSL random number generators that use shuffling.
RNSET Initialize a random seed for use in the IMSL randomnumber generators.
L7...... Analysis of variance (including analysis of covariance)
Analyze a one-way classification model with covariates.
Analyze a one-way classification model.
Compute contrast estimates and sums of squares.
Compute simultaneous confidence intervals on all pairwise differences of means.
Perform Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test.
L7b.... Two-way (search also class L7d)
Analyze a randomized block design or a two-way balanced design.
Perform Friedman's test for a randomized complete block design.
Compute a median polish of a two-way table.
L7c.... Three-way (e.g., Latin squares) (search also class L7d)
Analyze a Latin square design.
L7d1.. Balanced complete data (e.g., factorial designs)
Analyze a balanced complete experimental design for a fixed, random, or mixed model.
Analyze a completely nested random model with possibly unequal numbers in the subgroups.
Analyze a balanced n-way classification model with fixed effects.
Compute a confidence interval on a variance component estimated as proportional to the difference in two mean squares in a balanced complete experimental design.
Reorder the responses from a balanced complete experimental design.
L7d2.. Balanced incomplete data (e.g., fractional factorial designs)
Analyze a balanced incomplete block design or a balanced lattice design.
L7d3.. General linear models (unbalanced data)
Analyze a completely nested random model with possibly unequal numbers in the subgroups.
Fit a multivariate general linear model.
Fit a multivariate general linear model.
L7f..... Generate experimental designs
Generate an orthogonal central composite design.
L8...... Regression (search also classes D5, D6, D9, G, K)
L8a.... Simple linear (e.g., y = β0 + β1x + ɛ)
Analyze a simple linear regression model.
Fit a line to a set of data points using least squares.
L8a1d. Inference (e.g., calibration) (search also class L8a1a)
Perform response control given a fitted simple linear regression model.
Perform inverse prediction given a fitted simple linear regression model.
L8a2.. Lp for p different from 2 (e.g., least absolute value, minimax)
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the least absolute values criterion.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the Lp norm criterion.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the minimax criterion.
L8b.... Polynomial (e.g., y = β0 + β1x + β2x2 + ɛ) (search also class L8c)
Fit an orthogonal polynomial regression model.
Analyze a polynomial regression model.
L8b1b2..... Using orthogonal polynomials
Fit a polynomial curve using least squares.
Fit an orthogonal polynomial regression model.
Analyze a polynomial regression model.
L8b1c. Analysis (search also class L8b1b)
Compute case statistics for a polynomial regression model given the fit based on orthogonal polynomials.
Analyze a polynomial regression model.
Compute summary statistics for a polynomial regression model given the fit based on orthogonal polynomials.
L8b1d. Inference (search also class L8b1b)
Compute case statistics for a polynomial regression model given the fit based on orthogonal polynomials.
Analyze a polynomial regression model.
Compute summary statistics for a polynomial regression model given the fit based on orthogonal polynomials.
L8c.... Multiple linear (e.g., y = β0 + β1x1 +…+ βkxk + ɛ)
L8c1a2..... Using correlation or covariance data
Perform a generalized sweep of a row of a nonnegative definite matrix.
Select the best multiple linear regression models.
Build multiple linear regression models using forward selection, backward selection, or stepwise selection.
L8c1b. Parameter estimation (search also class L8c1a)
Fit a multivariate linear regression model via fast Givens transformations.
Fit a multivariate general linear model.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using least squares.
L8c1b2..... Using correlation data
Fit a multiple linear regression model given the variance-covariance matrix.
L8c1c. Analysis (search also classes L8c1a and L8c1b)
Compute case
statistics and diagnostics given data points, coefficient estimates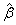 , and the R matrix for a fitted
general linear model.
, and the R matrix for a fitted
general linear model.
RCOVB Compute the estimated variance-covariance matrix of the estimated regression coefficients given the R matrix.
RLOFE Compute a lack-of-fit test based on exact replicates for a fitted regression model.
RLOFN Compute a lack-of-fit test based on near replicates for a fitted regression model.
ROTIN Compute diagnostics for detection of outliers and influential data points given residuals and the R matrix for a fitted general linear model.
Compute
statistics related to a regression fit given the coefficient estimates 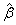 and the R matrix.
and the R matrix.
L8c1d. Inference (search also classes L8c1a and L8c1b)
CESTI Construct an equivalent completely testable multivariate general linear hypothesis HBU = G from a partially testable hypothesis HpBU = Gp.
Compute case
statistics and diagnostics given data points, coefficient estimates 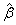 , and the R matrix for a fitted
general linear model.
, and the R matrix for a fitted
general linear model.
Compute the matrix of sums of squares and
crossproducts for the multivariate general linear hypothesis HBU =
G given the coefficient estimates 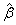 and the R matrix.
and the R matrix.
Perform tests for a multivariate general linear hypothesis HBU = G given the hypothesis sums of squares and crossproducts matrix SH and the error sums of squares and crossproducts matrix SE.
Compute
statistics related to a regression fit given the coefficient estimates 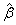 and the R matrix.
and the R matrix.
L8c3.. Lp for p different from 2
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the least absolute values criterion.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the Lp norm criterion.
Fit a multiple linear regression model using the minimax criterion.
L8d.... Polynomial in several variables
Generate an orthogonal central composite design.
Transform coefficients from a quadratic regression model generated from squares and crossproducts of centered variables to a model using uncentered variables.
L8e.... Nonlinear (i.e., y = f(X; θ) + ɛ)
Fit a nonlinear regression model.
L8f..... Simultaneous (i.e., Y = XB + ɛ)
Fit a multiple linear regression model given the variance-covariance matrix.
Fit a multivariate linear regression model via fast Givens transformations.
Fit a multivariate general linear model.
Compute the matrix of sums of squares and
crossproducts for the multivariate general linear hypothesis HBU =
G given the coefficient estimates 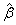 and the R matrix.
and the R matrix.
Perform tests for a multivariate general linear hypothesis HBU = G given the hypothesis sums of squares and crossproducts matrix SH and the error sums of squares and crossproducts matrix SE.
Fit a multivariate linear regression model with linear equality restrictions HΒ = G imposed on the regression parameters given results from IMSL routine RGIVN after IDO = 1 and IDO = 2 and prior to IDO = 3.
L8i..... Service routines (e.g., matrix manipulation for variable selection)
Get the unique values of each classification variable.
Generate centered variables, squares, and crossproducts.
Generate regressors for a general linear model.
Reorder rows and columns of a symmetric matrix.
Retrieve a symmetric submatrix from a symmetric matrix.
L9...... Categorical data analysis
Analyze categorical data using logistic, Probit, Poisson, and other generalized linear models.
Perform generalized Mantel-Haenszel tests in a stratified contingency table.
Perform a chi-squared analysis of a 2 by 2 contingency table.
L9b.... Two-way tables (search also class L9d)
Perform a chi-squared analysis of a two-way contingency table.
Compute Fisher's exact test probability and a hybrid approximation to the Fisher exact test probability for a contingency table using the network algorithm.
Compute exact probabilities in a two-way contingency table.
Estimate the bivariate normal correlation coefficient using a contingency table.
Perform a generalized linear least squares analysis of transformed probabilities in a two-dimensional contingency table.
Compute a median polish of a two-way table.
Tally observations into a two-way frequency table.
Compute partial association statistics for log-linear models in a multidimensional contingency table.
Compute model estimates and associated statistics for a hierarchical log-linear model.
Compute model estimates and covariances in a fitted log-linear model.
Build hierarchical log-linear models using forward selection, backward selection, or stepwise selection.
Perform iterative proportional fitting of a contingency table using a loglinear model.
L9d.... EDA (e.g., median polish)
Compute a median polish of a two-way table.
L10.... Time series analysis (search also class J)
L10a1b..... Stationarity (search also class L8a1)
Perform a forward or an inverse Box-Cox (power) transformation.
L10a1c1 Difference (nonseasonal and seasonal)
AUTO_FPE_
MUL_AR
Automatic selection and fitting of a multivariate
autoregressive time series model using Akaike's
Multivariate Final Prediction Error (MFPE) criteria.
AUTO_FPE_
UNI_AR
Automatic selection and fitting of a univariate
autoregressive time series model using Akaike's Final
Prediction Error (FPE) criteria.
AUTO_MUL_AR Automatic selection and fitting of a multivariate autoregressive time series model.
AUTO_UNI_AR Automatic selection and fitting of a univariate autoregressive time series model.
BAY_SEA Model allows for a decomposition of a time series into trend, seasonal, and an error component.
GARCH Computes estimates of the parameters of a GARCH(p,q) model.
MAX_ARMA Exact maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters in a univariate ARMA (auto-regressive, moving average) time series model.
L10a2a..... Summary statistics
L10a2a1 Autocovariances and autocorrelations
Compute the sample autocorrelation function of a stationary time series.
Perform lack-of-fit test for a univariate time series or transfer function given the appropriate correlation function.
L10a2a2 Partial autocorrelations
Compute the sample partial autocorrelation function of a stationary time series.
L10a2c..... Autoregressive models
Compute the Wiener forecast operator for a stationary stochastic process.
L10a2d..... ARMA and ARIMA models (including Box-Jenkins methods)
Compute method of moments estimates of the autoregressive parameters of an ARMA model.
Compute method of moments estimates of the moving average parameters of an ARMA model.
Compute least squares estimates of parameters for a nonseasonal ARMA model.
Compute preliminary estimates of the autoregressive and moving average parameters of an ARMA model.
Compute Box-Jenkins forecasts and their associated probability limits for a nonseasonal ARMA model.
L10a2e..... State-space analysis (e.g., Kalman filtering)
Perform Kalman filtering and evaluate the likelihood function for the state-space model.
L10a3. Frequency domain analysis (search also class J1)
ARMA_SPEC Calculates the rational power spectrum for an ARMA model.
Compute the periodogram of a stationary time series using a fast Fourier transform.
L10a3a3 Spectrum estimation using the periodogram
Estimate the nonnormalized spectral density of a stationary time series using a spectral window given the time series data.
Estimate the nonnormalized spectral density of a stationary time series using a spectral window given the periodogram.
Estimation of the nonnormalized spectral density of a stationary time series based on specified periodogram weights given the time series data.
Estimation of the nonnormalized spectral density of a stationary time series based on specified periodogram weights given the periodogram.
L10b.. Two time series (search also classes L10c and L10d)
L10b2a..... Summary statistics (e.g., cross-correlations)
Compute the sample cross-correlation function of two stationary time series.
L10b2b..... Transfer function models
Compute estimates of the impulse response weights and noise series of a univariate transfer function model.
Compute preliminary estimates of parameters for a univariate transfer function model.
L10b3. Frequency domain analysis (search also class J1)
L10b3a..... Cross-spectral analysis
L10b3a3 Cross-spectrum estimation using the cross-periodogram
Estimate the nonnormalized cross-spectral density of two stationary time series using a spectral window given the time series data.
Estimate the nonnormalized cross-spectral density of two stationary time series using a spectral window given the spectral densities and cross periodogram.
Estimate the nonnormalized cross-spectral density of two stationary time series using a weighted cross periodogram given the time series data.
Estimate the nonnormalized cross-spectral density of two stationary time series using a weighted cross periodogram given the spectral densities and cross periodogram.
L10c.. Multivariate time series (search also classes J1, L3e3 and L10b)
Perform Kalman filtering and evaluate the likelihood function for the state-space model.
OPT_DES Allows for multiple channels for both the controlled and manipulated variables
L10d.. Two multi-channel time series
Compute the multichannel cross-correlation function of two mutually stationary multichannel time series.
Compute least squares estimates of a linear regression model for a multichannel time series with a specified base channel.
Compute least squares estimates of the multichannel Wiener filter coefficients for two mutually stationary multichannel time series.
L11.... Correlation analysis (search also classes L4 and L13c)
Compute the biserial correlation coefficient for a dichotomous variable and a classification variable.
Compute the biserial and point-biserial correlation coefficients for a dichotomous variable and a numerically measurable classification variable.
Compute the variance-covariance or correlation matrix.
Compute a pooled variance-covariance matrix from the observations.
Estimate the bivariate normal correlation coefficient using a contingency table.
Compute the frequency distribution of the total score in Kendall's rank correlation coefficient.
Compute partial correlations or covariances from the covariance or correlation matrix.
Compute a robust estimate of a covariance matrix and mean vector.
Categorize bivariate data and compute the tetrachoric correlation coefficient.
Use Fisher's linear discriminant analysis method to reduce the number of variables.
Perform a linear or a quadratic discriminant function analysis among several known groups.
Perform a k nearest neighbor discrimination.
L13.... Covariance structures models
Extract initial factor-loading estimates in factor analysis.
Compute a matrix of factor score coefficients for input to the following IMSL routine (FSCOR).
Compute a direct oblimin rotation of a factor-loading matrix.
Compute direct oblique rotation according to a generalized fourth-degree polynomial criterion.
Compute an oblique rotation of an unrotated factor-loading matrix using the Harris-Kaiser method.
Compute the image transformation matrix.
Compute an orthogonal Procrustes rotation of a factor-loading matrix using a target matrix.
Compute an oblique Promax or Procrustes rotation of a factor-loading matrix using a target matrix, including pivot and power vector options.
Compute commonalities and the standardized factor residual correlation matrix.
Compute an orthogonal rotation of a factor-loading matrix using a generalized orthomax criterion, including quartimax, varimax, and equamax rotations.
Compute the factor structures and the variance explained by each factor.
Compute a set of factor scores given the factor score coefficient matrix.
L13b.. Principal components analysis
Maximum likelihood or least-squares estimates for principle components from one or more matrices.
Compute principal components from a variance-covariance matrix or a correlation matrix.
Perform canonical correlation analysis from a data matrix.
Perform canonical correlation analysis from a variance-covariance matrix or a correlation matrix.
L14a1a1 Joining (e.g., single link)
Perform a hierarchical cluster analysis given a distance matrix.
L14a1b..... Non-nested (e.g., K means)
KMEAN Perform a K-means (centroid) cluster analysis.
L14d.. Service routines (e.g., compute distance matrix)
Compute a matrix of dissimilarities (or similarities) between the columns (or rows) of a matrix.
Compute cluster membership for a hierarchical cluster tree.
L15.... Life testing, survival analysis
Produce population and cohort life tables.
Perform nonparametric hazard rate estimation using kernel functions. Easy-to-use version of the previous IMSL subroutine (HAZRD).
Perform nonparametric hazard rate estimation using kernel functions and quasi-likelihoods.
Perform hazard rate estimation over a grid of points using a kernel function.
Compute Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities in stratified samples.
Print Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities in stratified samples.
Compute maximum likelihood estimates of the mean and variance from grouped and/or censored normal data.
Analyze time event data via the proportional hazards model.
Estimate survival probabilities and hazard rates for various parametric models.
Analyze censored survival data using a generalized linear model.
Compute Turnbull's generalized Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities in samples with interval censoring.
L16.... Multidimensional scaling
Obtain normalized product-moment (double centered) matrices from dissimilarity matrices.
Compute distances in a multidimensional scaling model.
Perform individual-differences multidimensional scaling for metric data using alternating least squares.
Compute initial estimates in multidimensional scaling models.
Transform dissimilarity/similarity matrices and replace missing values by estimates to obtain standardized dissimilarity matrices.
Compute various stress criteria in multidimensional scaling.
Retrieve a commonly analyzed data set.
N....... DATA HANDLING (search also class L2)
Set or retrieve page width and length for printing.
Print an integer rectangular matrix with a given format and labels.
Print an integer rectangular matrix with integer row and column labels.
Set or retrieve an option for printing a matrix.
Print a real rectangular matrix with a given format and labels.
Print a real rectangular matrix with integer row and column labels.
N3..... Character manipulation
Return a character given its ASCII value.
Convert a character string containing an integer number into the corresponding integer form.
Return the integer ASCII value of a character argument.
Return the ASCII value of a character converted to uppercase.
Compare two character strings using the ASCII collating sequence without regard to case.
Determine the position in a string at which a given character sequence begins without regard to case.
Search a sorted integer vector for a given integer and return its index.
Search a sorted vector for a given scalar and return its index.
Search a character vector, sorted in ascending ASCII order, for a given string and return its index.
Determine the position in a string at which a given character sequence begins without regard to case.
Search a sorted integer vector for a given integer and return its index.
Search a sorted vector for a given scalar and return its index.
Search a character vector, sorted in ascending ASCII order, for a given string and return its index.
N6a1.. Passive (i.e., construct pointer array, rank)
Sort an integer array by algebraic value and return the permutations.
Compute the ranks, normal scores, or exponential scores for a vector of observations.
Sort columns of a real rectangular matrix using keys in rows.
Sort rows of a real rectangular matrix using keys in columns.
Sort a real array by algebraic value and return the permutations.
Sort an integer array by algebraic value.
Sort an integer array by algebraically increasing value and return the permutation that rearranges the array.
Sort columns of a real rectangular matrix using keys in rows.
Sort rows of a real rectangular matrix using keys in columns.
Sort a real array by algebraic value.
Sort a real array by algebraic value and return the permutations.
Move any rows of a matrix with the IMSL missing value code NaN (not a number) in the specified columns to the last rows of the matrix.
Permute the rows or columns of a matrix.
Rearrange the elements of an array as specified by a permutation.
Reorder rows and columns of a symmetric matrix.
Q....... GRAPHICS (search also classes L3)
Print boxplots for one or more samples.
Print a plot of two sample cumulative distribution functions.
Print a sample cumulative distribution function (CDF), a theoretical CDF, and confidence band information.
Print a plot of up to ten sets of points.
Print a scatterplot of several groups of data.
Print a vertical histogram with every bar subdivided into two parts.
Compute the day of the week for a given date.
Compute the number of days from January 1, 1900, to the given date.
Give the date corresponding to the number of days since January 1, 1900.
Obtain STAT/LIBRARY-related version, system and license numbers.
R1..... Machine-dependent constants
IFNAN Check if a floating-point number is NaN (not a number).
IMACH Retrieve integer machine constants.
UMACH Set or retrieve input or output device unit numbers.
R3b.... Set unit number for error messages
UMACH Set or retrieve input or output device unit numbers.
ERSET Set error handler default print and stop actions.
IERCD Retrieve the code for an informational error.
N1RTY Retrieve an error type for the most recently called IMSL routine.
S....... SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
CPSEC Return CPU time used in seconds.
|
Visual Numerics, Inc. PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |