The function extends FORTRAN's generic function COSH to evaluate the complex hyperbolic cosine.
Function Return Value
COSH — Complex function value. (Output)
Required Arguments
Z — Complex number representing the angle in radians for which the hyperbolic cosine is desired. (Input)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: COSH (Z)
Specific: The specific interface names are CCOSH and ZCOSH.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Complex: CCOSH (Z)
Double complex: The double complex function name is ZCOSH.
Description
Let ε = AMACH(4) be the machine precision. If |ℑz| is larger than
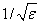
then the result will be less than half precision, and a recoverable error condition is reported. If |ℑz| is larger than 1/ε, the result has no precision and a fatal error is reported. Finally, if |ℜz| is too large, the result overflows and a fatal error results. Here, ℜz and ℑz represent the real and imaginary parts of z, respectively.
Example
In this example, cosh(−2 + 2i) is computed and printed.
USE COSH_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER NOUT
COMPLEX VALUE, Z
! Compute
Z = (-2.0, 2.0)
VALUE = COSH(Z)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) Z, VALUE
99999 FORMAT (' COSH((', F6.3, ',', F6.3, ')) = (',&
F6.3, ',', F6.3, ')')
END
Output
COSH((-2.000, 2.000)) = (-1.566,-3.298)
|
PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |