This function evaluates the complementary error function.
Function Return Value
ERFC — Function value. (Output)
Required Arguments
X — Argument for which the function value is desired. (Input)
FORTRAN 90 Interface
Generic: ERFC (X)
Specific: The specific interface names are S_ERFC and D_ERFC.
FORTRAN 77 Interface
Single: ERFC (X)
Double: The double precision function name is DERFC.
Description
The complementary error function, erfc(x), is defined to be
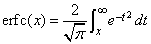
The argument x must not be so large that the result underflows. Approximately, x should be less than
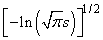
where s = AMACH(1) (see the Reference Material section of this manual) is the smallest representable positive floating-point number.
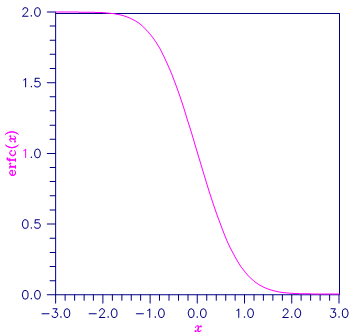
Figure 5- 2 Plot of erfc (x)
Comments
Informational error
Type Code
2 1 The function underflows because X is too large.
Example
In this example, erfc(1.0) is computed and printed.
USE ERFC_INT
USE UMACH_INT
IMPLICIT NONE
! Declare variables
INTEGER NOUT
REAL VALUE, X
! Compute
X = 1.0
VALUE = ERFC(X)
! Print the results
CALL UMACH (2, NOUT)
WRITE (NOUT,99999) X, VALUE
99999 FORMAT (' ERFC(', F6.3, ') = ', F6.3)
END
Output
ERFC( 1.000) = 0.157
|
PHONE: 713.784.3131 FAX:713.781.9260 |