Example 3
A spline interpolant  to a function
to a function 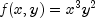 is constructed. Then, the values of the partial derivative
is constructed. Then, the values of the partial derivative 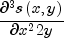 and the error are computed on a 4 x 4 grid.
and the error are computed on a 4 x 4 grid.
import java.text.*;
import com.imsl.math.*;
public class Spline2DInterpolateEx3 {
private static double F(double x, double y) {
return (x*x*x*y*y);
}
private static double F21(double x, double y) {
return(6.0 * x * 2.0 * y);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int nData = 11;
int outData = 2;
double[][] fData = new double[nData][nData];
double[] xData = new double[nData];
double[] yData = new double[nData];
double x, y, z;
// Set up grid
for (int i = 0; i < nData; i++) {
xData[i] = yData[i] = (double)i / ((double)(nData-1));
}
for (int i = 0; i < nData; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nData; j++) {
fData[i][j] = F(xData[i], yData[j]);
}
}
// Compute tensor-product interpolant
Spline2DInterpolate spline =
new Spline2DInterpolate(xData, yData, fData);
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(4);
nf.setMinimumFractionDigits(4);
// Print results
System.out.println(" x y F21(x, y) " +
"21InterpDeriv Error");
for (int i = 0; i < outData; i++) {
x = (double) (1+i) / (double) (outData+1);
for (int j = 0; j < outData; j++) {
y = (double) (1+j) / (double) (outData+1);
z = spline.derivative(x, y, 2, 1);
System.out.println(nf.format(x) + " " + nf.format(y) + " "
+ nf.format(F21(x, y)) + " " + nf.format(z) +
" " + nf.format(Math.abs(F21(x,y)-z)));
}
}
}
}
Output
x y F21(x, y) 21InterpDeriv Error
0.3333 0.3333 1.3333 1.3333 0.0000
0.3333 0.6667 2.6667 2.6667 0.0000
0.6667 0.3333 2.6667 2.6667 0.0000
0.6667 0.6667 5.3333 5.3333 0.0000
Link to Java source.