Programmer's Guide



| JMSL Chart Programmer's Guide | Introduction - Chart 3D |



|
Introduction - Chart 3D
Java3D
The JMSL 3D chart package is built on top of Java 3D, an open source Java package which renders accelerated 3D graphics using OpenGL or Direct3D.
Java 3D Parent project is at https://java3d.dev.java.net/.
Knowledge of Java3D is not required to use the 3D chart package, but Java 3D must be installed to run a chart 3D application.
Overview
The JMSL 3D chart package can be used to create customizable 3D using Java and Java3D. Knowledge of Java3D is not required.
The JMSL 3D chart package is similar to the JMSL 2D chart package. In both, a chart is created by assembling chart nodes into a tree. This chart tree is then rendered to the screen.
The following class is a simple example of the use of the 3D chart package. It plots the function z=2sin(x+y)-cos(2x-3y) over the square [-1,1] by [-1,1]. The chart is displayed in a Swing frame.
The class for this example extends the JFrameChart3d class which creates the
root Chart3D node. A tree of chart nodes is then created starting from the
Chart3D root node. After the tree is created, the render method is used to generate
a Java 3D scene graph from the chart node tree. The scene graph is used to generate
the image on the screen.
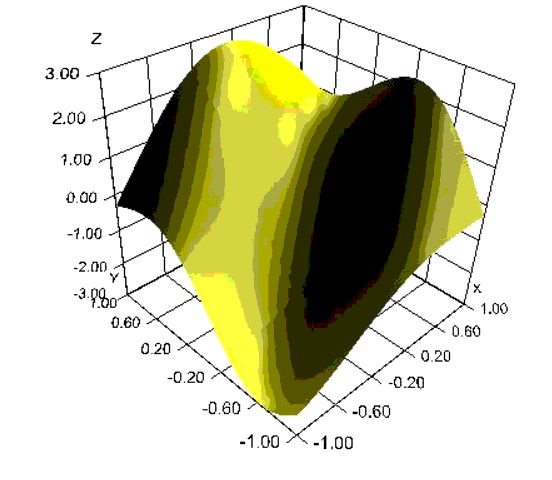
import com.imsl.chart3d.*;
public class SimpleSurface extends JFrameChart3D
implements Surface.ZFunction {
public SimpleSurface() {
Chart3D chart = getChart3D();
AxisXYZ axis = new AxisXYZ(chart);
Surface surface =
new Surface(axis, this, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0);
surface.setFillColor("yellow");
surface.setSurfaceType(Surface.SURFACE_TYPE_NICEST);
render();
}
public double f(double x, double y) {
return 2*Math.sin(x+y) - Math.cos(2*x-3*y);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
new SimpleSurface().setVisible(true);
}
}
The above example created and assembled three nodes into the following tree:
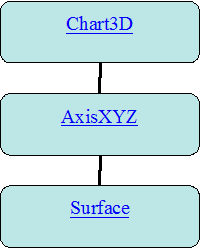
The general pattern of the AbstractChartNode class and derived classes have
constructors whose first argument is the parent AbstractChartNode of the
AbstractChartNode being created. The root node of the tree is always a
Chart3D object.
Chart nodes can contain attributes, such as FillColor and LineWidth.
Attributes are inherited via the chart tree. For example, when a Surface node is
being painted, its FillColor attribute determines the color of the surface. If this
attribute is set in the node being drawn, that is the value used. If it is not set, then
its parent node (an AxisXYZ node in the above example) is queried. If the attribute
is not set in the parent node, then its parent is queried. This continues until the root
node is reached, after which a default value is used. Note that this inheritance is not
the same as Java class inheritance.
Attributes are set using setter methods, such as setFillColor(Color) and
retrieved using getter methods, such as getFillColor().
| © Visual Numerics, Inc. All rights reserved. |



|