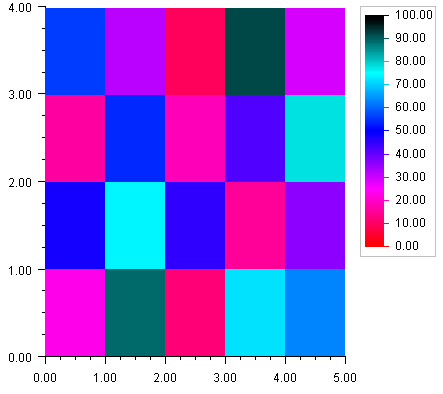
Heatmap
A
Heatmap divides a rectangle into subrectangles. The color of each subrectangle is determined by the value of a data array and a colormap.
If the data array is m by n then there are m divisions along the x-axis and n divisions along the y-axis.
A
Colormap is a mapping from [0,1] to color values. The blue-red colormap, used in the example below, maps 0 to red and 1 to dark blue and interpolates between these endpoints values. The heatmap maps the minimum data value to the color corresponding to 0 and the highest data value to the color corresponding to 1.
The Heatmap class has a special legend for Colormaps. It displays the color values as a gradient labeled with corresponding data values.
Example
In this example a two-dimensional array of data is plotted as a heatmap. The “red-blue” Colormap is used. The Heatmap Legend is enabled by settings its Paint attribute to true.
import com.imsl.chart.*;
public class SampleHeatmap extends JFrameChart {
public SampleHeatmap() {
Chart chart = getChart();
AxisXY axis = new AxisXY(chart);
double xmin = 0.0;
double xmax = 5.0;
double ymin = 0.0;
double ymax = 4.0;
double zmin = 0.0;
double zmax = 100.0;
double data[][] = {
{23, 48, 16, 56},
{89, 74, 54, 32},
{12, 45, 18, 9},
{72, 15, 42, 92},
{63, 36, 78, 29}
};
Heatmap heatmap = new Heatmap(axis, xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax,
zmin, zmax, data, Colormap.BLUE_RED);
heatmap.getHeatmapLegend().setPaint(true);
}
public static void main(String argv[]) {
new SampleHeatmap().setVisible(true);
}
}