Class Pdf
-
Nested Class Summary
Nested ClassesModifier and TypeClassDescriptionstatic classThe magnitude of alternating series sum is too small relative to the sum of positive terms to permit a reliable accuracy. -
Method Summary
Modifier and TypeMethodDescriptionstatic doublebeta(double x, double pin, double qin) Evaluates the beta probability density function.static doublebinomial(int k, int n, double p) Evaluates the binomial probability density function.static doublechi(double chsq, double df) Evaluates the chi-squared probability density functionstatic doublecontinuousUniform(double x, double a, double b) Evaluates the continuous uniform probability density function.static doublediscreteUniform(int x, int n) Evaluates the discrete uniform probability density function.static doubleexponential(double x, double scale) Evaluates the exponential probability density functionstatic doubleextremeValue(double x, double mu, double beta) Evaluates the extreme value probability density function.static doubleF(double x, double dfn, double dfd) Evaluates the F probability density function.static doublegamma(double x, double a, double b) Evaluates the gamma probability density function.static doublegeneralizedExtremeValue(double x, double mu, double sigma, double xi) Evaluates the generalized extreme value probability density function.static doublegeneralizedGaussian(double x, double mu, double alpha, double beta) Evaluates the generalized Gaussian (normal) probability density function.static doublegeneralizedPareto(double x, double mu, double sigma, double alpha) Evaluates the generalized Pareto probability density function.static doublegeometric(int x, double p) Evaluates the geometric probability density (or mass) function.static doublehypergeometric(int k, int sampleSize, int defectivesInLot, int lotSize) Evaluates the hypergeometric probability density function.static doubleinverseGaussian(double x, double mean, double lambda) Evaluates the inverse Gaussian probability density function.static doublelogistic(double x, double mu, double sigma) Evaluates the logistic probability density function.static doublelogLogistic(double x, double alpha, double beta) Evaluates the Log-logistic probability density function.static doublelogNormal(double x, double mu, double sigma) Evaluates the standard lognormal probability density function.static doublenegativeBinomial(int k, double r, double p) Evaluates the negative binomial probability density function.static doublenoncentralBeta(double x, double shape1, double shape2, double lambda) Evaluates the noncentral beta probability density function (PDF).static doublenoncentralChi(double chsq, double df, double alam) Evaluates the noncentral chi-squared probability density function (PDF).static doublenoncentralF(double f, double df1, double df2, double lambda) Evaluates the noncentral F probability density function (PDF).static doublenoncentralStudentsT(double t, double df, double delta) Evaluates the noncentral Student's t probability density function.static doublenormal(double x, double mean, double stdev) Evaluates the normal (Gaussian) probability density function.static doublePareto(double x, double xm, double k) Evaluates the Pareto probability density function.static doublepoisson(int k, double theta) Evaluates the Poisson probability density function.static doubleRayleigh(double x, double sigma) Evaluates the Rayleigh probability density function.static doubleWeibull(double x, double k, double lambda) Evaluates the Weibull probability density function.
-
Method Details
-
noncentralBeta
public static double noncentralBeta(double x, double shape1, double shape2, double lambda) Evaluates the noncentral beta probability density function (PDF).The noncentral beta distribution is a generalization of the beta distribution. If \(Z\) is a noncentral chi-square random variable with noncentrality parameter \(\lambda\) and \(2 \alpha_1\) degrees of freedom, and \(Y\) is a chi-square random variable with \(2 \alpha_2\) degrees of freedom which is statistically independent of \(Z\), then
$$X \;\; = \;\; \frac{Z}{Z \; + \; Y} \;\; = \;\; \frac{\alpha_1 F}{\alpha_1 F \; + \; \alpha_2}$$
is a noncentral beta-distributed random variable and
$$F \;\; = \;\; \frac{\alpha_2 Z}{\alpha_1 Y} \;\; = \;\; \frac{\alpha_2 X}{\alpha_1 (1 \; - \; X)}$$
is a noncentral F-distributed random variable. The PDF for noncentral beta variable X can thus be simply defined in terms of the noncentral F PDF:
$$PDF_{nc\beta}(x, \; \alpha_1, \; \alpha_2, \; \lambda) \;\; = \;\; PDF_{ncF}(f, \; 2 \alpha_1, \; 2 \alpha_2, \; \lambda) \; \frac{df}{dx}$$
where \(PDF_{nc\beta}(x, \; \alpha_1, \; \alpha_2, \; \lambda)\) is the noncentral beta PDF with \(x\) =
x, \(\alpha_1\) =shape1, \(\alpha_2\) =shape2, and noncentrality parameter \(\lambda\) =lambda; \(PDF_{ncF}(f, \; 2 \alpha_1, \; 2 \alpha_2, \; \lambda)\) is the noncentral F PDF with argument f, numerator and denominator degrees of freedom \(2 \alpha_1\) and \(2 \alpha_2\) respectively, and noncentrality parameter \(\lambda\); and $$\frac{df}{dx} \;\; = \;\; \frac{(\alpha_1 f \; + \; \alpha_2)^2}{\alpha_1 \alpha_2} \;\; = \;\; \frac{ \alpha_2}{\alpha_1 (1 \; - \; x)^2} $$ where $$f \;\; = \;\; \frac{\alpha_2 x}{\alpha_1 (1 \; - \; x)}$$ and $$x \;\; = \;\; \frac{\alpha_1 f}{\alpha_1 f \; + \; \alpha_2}$$(See documentation for class
CdfmethodnoncentralFfor a discussion of how the noncentral F PDF is defined and calculated.)With a noncentrality parameter of zero, the noncentral beta distribution is the same as the beta distribution.
- Parameters:
x- adoublescalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.xmust be nonnegative and less than or equal to 1.shape1- adoublescalar value representing the first shape parameter.shape1must be positive.shape2- adoublescalar value representing the second shape parameter.shape2must be positive.lambda- adoublescalar value representing the noncentrality parameter.lambdamust nonnegative.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value representing the probability density associated with a noncentral beta random variable with valuex.
-
binomial
public static double binomial(int k, int n, double p) Evaluates the binomial probability density function.Method
binomialevaluates the probability that a binomial random variable with parameters n and p takes on the value k. It does this by computing probabilities of the random variable taking on the values in its range less than (or the values greater than) k. These probabilities are computed by the recursive relationship$$\Pr \left( {X = j} \right) = \frac{{\left( {n + 1 - j} \right)p}}{{j\left( {1 - p} \right)}}\Pr \left( {X = j - 1} \right)$$
To avoid the possibility of underflow, the probabilities are computed forward from 0, if k is not greater than \(n \times p\), and are computed backward from n, otherwise. The smallest positive machine number, \(\varepsilon\), is used as the starting value for computing the probabilities, which are rescaled by \((1 - p)^n \varepsilon\) if forward computation is performed and by \(p^n\varepsilon\) if backward computation is done.
For the special case of p = 0,
binomialis set to 0 if k is greater than 0 and to 1 otherwise; and for the case p = 1,binomialis set to 0 if k is less than n and to 1 otherwise.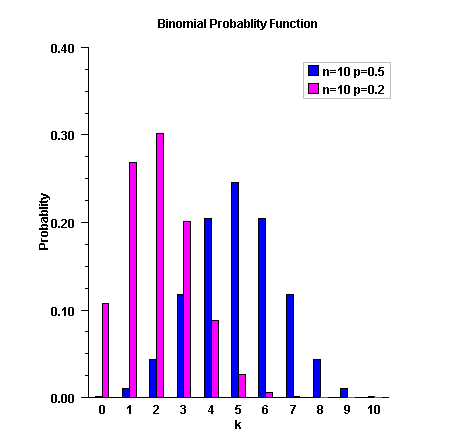
- Parameters:
k- theintargument for which the binomial distribution function is to be evaluated.n- theintnumber of Bernoulli trials.p- adoublescalar value representing the probability of success on each independent trial.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value representing the probability that a binomial random variable takes a value equal tok. - See Also:
-
poisson
public static double poisson(int k, double theta) Evaluates the Poisson probability density function.Method
poissonevaluates the probability density function of a Poisson random variable with parametertheta.theta, which is the mean of the Poisson random variable, must be positive. The probability function (with \(\theta = theta\)) is$$f(x) = e^{- \theta} \,\,\theta ^k /k!,\,\,\,\,\, for\,k = 0,\,\,1,\,\,2,\, \ldots$$
poissonevaluates this function directly, taking logarithms and using the log gamma function.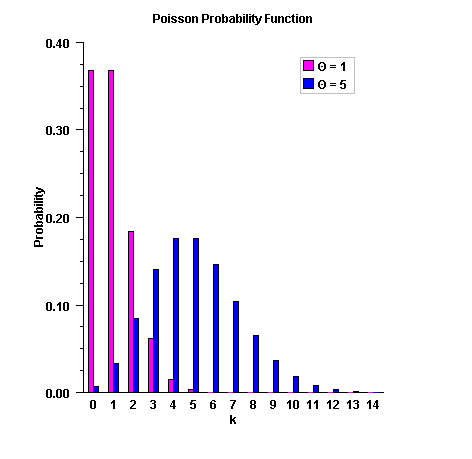
- Parameters:
k- theintargument for which the Poisson probability function is to be evaluated.theta- adoublescalar value representing the mean of the Poisson distribution.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value representing the probability that a Poisson random variable takes a value equal to k. - See Also:
-
beta
public static double beta(double x, double pin, double qin) Evaluates the beta probability density function.- Parameters:
x- adouble, the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.pin- adouble, the first beta distribution parameter.qin- adouble, the second beta distribution parameter.- Returns:
- a
double, the value of the probability density function atx.
-
F
public static double F(double x, double dfn, double dfd) Evaluates the F probability density function.The probability density function of the F distribution is $${\it f}(x, {\it dfn}, {\it dfd})= {\frac { {\Gamma}(\frac {v_1 + v_2}{2})({\frac {v_1}{v_2})}^{\frac{v_1}{2}} x^{\frac {v_1}{2}} } {{{\Gamma}(\frac {v_1}{2}) }{{\Gamma}(\frac {v_2}{2}) } {(1+\frac{v_1x}{v_2})}^{\frac{v_1+v_2}{2} } }}$$ where \(v_1\) and \(v_2\) are the shape parameters
dfnanddfdand \(\Gamma\) is the gamma function, $${\Gamma (a)} = {\int}_{0}^{\infty}{t^{a-1} e^{-t } \it dt}$$.- Parameters:
x- adouble, the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.dfn- adouble, the numerator degrees of freedom. It must be positive.dfd- adouble, the denominator degrees of freedom. It must be positive.- Returns:
- a
double, the value of the probability density function atx.
-
hypergeometric
public static double hypergeometric(int k, int sampleSize, int defectivesInLot, int lotSize) Evaluates the hypergeometric probability density function.Method
hypergeometricevaluates the probability density function of a hypergeometric random variable with parameters n, l, and m. The hypergeometric random variable X can be thought of as the number of items of a given type in a random sample of size n that is drawn without replacement from a population of size l containing m items of this type. The probability density function is:$${\rm{Pr}}\left( {X = k} \right) = \frac{{\left( {_k^m } \right)\left( {_{n - k}^{l - m} } \right)}}{{\left( {_n^l } \right)}}{\rm{for}} \,\,\, k = i,\;i + 1,\,i + 2\; \ldots ,\;\min \left( {n,m} \right)$$
where i = max(0, n - l + m).
hypergeometricevaluates the expression using log gamma functions.- Parameters:
k- anint, the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.sampleSize- anint, the sample size,n.defectivesInLot- anint, the number of defectives in the lot,m.lotSize- anint, the lot size,l.- Returns:
- a
double, the probability that a hypergeometric random variable takes on a value equal tok. - See Also:
-
gamma
public static double gamma(double x, double a, double b) Evaluates the gamma probability density function. The probability density function of the gamma distribution is$$ f(x; a, b) = x^{a - 1} \frac{1}{{b^{a} \Gamma (a)}} e^{ - {x}/{b}} $$
whereais the shape parameter andbis the scale parameter.- Parameters:
x- adoublescalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.a- adoublescalar value representing the shape parameter. This must be positive.b- adoublescalar value representing the scale parameter. This must be positive.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value, the probability density function atx.
-
generalizedExtremeValue
public static double generalizedExtremeValue(double x, double mu, double sigma, double xi) Evaluates the generalized extreme value probability density function.The probability density function of the generalized extreme value distribution is $$f(x|\mu,\sigma,\xi)=\frac{1}{\sigma}t(x)^{\xi+1}e^{-t(x)}$$ where $$t(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{lll} (1+\xi(\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}))^{-\frac{1}{\xi}}& \mbox{for} & \xi \ne 0 \\ e^{-\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}} & \mbox{for} & \xi = 0 \end{array}\right. $$ \( \mu\in \mathbb{R} \) is the location parameter, \(\sigma > 0 \) is the scale parameter, and \(\xi \in \mathbb{R} \) is the shape parameter. Furthermore, the support for the distribution is $$\left\{\begin{array}{lll} x \in \mathbb{R} & \mbox{for} & \xi = 0 \\ x \ge \mu - \frac{\sigma}{\xi} & \mbox{for} & \xi > 0 \\ x \le \mu - \frac{\sigma}{\xi} & \mbox{for} & \xi \lt 0 \end{array}\right. $$
References
1. Wikipedia contributors. "Generalized extreme value distribution." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfmu- adouble, the value of the location parametersigma- adouble, the value of the scale parameterxi- adouble, the value of the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the value of the pdf evaluated atxgiven the parameter values
-
generalizedGaussian
public static double generalizedGaussian(double x, double mu, double alpha, double beta) Evaluates the generalized Gaussian (normal) probability density function.The generalized Gaussian probability density function is given by
$$ f(x; \mu,\alpha, \beta) = \frac{\beta}{2\alpha\Gamma(\frac{1}{\beta})} e^{-(\frac{|x-\mu|}{\alpha})^\beta} $$
where \(\mu\) is the location parameter, \(\alpha >0 \) is the scale parameter, and \(\beta >0 \) is the shape parameter. Note that this follows the parameterization given in Wikipedia. There are alternative parameterizations, as in Roenko, et. al. 2014.References
1. Roenko, Alexey, Lukin, Vladimir, Djurovic, Igor, Simeunović, Marko. (2014). Estimation of parameters for generalized Gaussian distribution. ISCCSP 2014 - 2014 6th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing, Proceedings. 376-379.
2. Wikipedia contributors. "Generalized normal distribution." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the point at which the function is to be evaluatedmu- adouble, the location parameteralpha- adouble, the scale parameterbeta- adouble, the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density atxgiven the parameter values
-
generalizedPareto
public static double generalizedPareto(double x, double mu, double sigma, double alpha) Evaluates the generalized Pareto probability density function. The generalized Pareto probability density function is given by $$ f(x; \mu,\sigma, \alpha) = \frac{1}{\sigma}\left( 1 + \frac{\alpha (x-\mu)}{\sigma}\right)^{(-\frac{1}{\alpha} - 1)} $$ where \(\mu \in \mathbb{R} \) is the location parameter, \(\sigma \gt 0 \) is the scale parameter, and \(\alpha \in \mathbb{R} \) is the shape parameter. Note that for \(\alpha=0\), the pdf is the limiting form of the above. The support for \(\alpha \ge 0\) is \( x \ge \mu \), while for \( \alpha \lt 0 \), \(\mu \le x \le \mu - \frac{\sigma}{\alpha}\). Note that this follows the parameterization given in Wikipedia.References
1. Wikipedia contributors. "Generalized Pareto distribution." Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the point at which the function is to be evaluatedmu- adouble, the location parametersigma- adouble, the scale parameter. It must be positive.alpha- adouble, the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density atxgiven the parameter values
-
exponential
public static double exponential(double x, double scale) Evaluates the exponential probability density function- Parameters:
x- adoublescalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.scale- adoublescalar value representing the scale parameter.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value, the value of the probability density function atx.
-
normal
public static double normal(double x, double mean, double stdev) Evaluates the normal (Gaussian) probability density function.The probability density function for a normal distribution is given by $$\frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2\pi}} {e}^{ \frac{{-(x - \mu)}^2}{{2 {\sigma}^2}} } $$ where \(\mu\) and \(\sigma\) are the mean and standard deviation.
- Parameters:
x- adoublescalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.mean- adoublescalar value containing the mean.stdev- adoublescalar value containing the standard deviation.- Returns:
- a
doublecontaining the value of the probability density function atx
-
chi
public static double chi(double chsq, double df) Evaluates the chi-squared probability density function- Parameters:
chsq- adoublescalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.df- adoublescalar value representing the number of degrees of freedom.dfmust be positive.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value, the value of the probability density function atchsq.
-
noncentralChi
public static double noncentralChi(double chsq, double df, double alam) Evaluates the noncentral chi-squared probability density function (PDF).The noncentral chi-squared distribution is a generalization of the chi-squared distribution. If \(\{X_i\}\) are \(k\) independent, normally distributed random variables with means \(\mu_i\) and variances \(\sigma^2_i\), then the random variable
$$X \;\; = \;\; \sum_{i = 1}^k \left(\frac{X_i}{\sigma_i}\right)^2$$
is distributed according to the noncentral chi-squared distribution. The noncentral chi-squared distribution has two parameters, \(k\) which specifies the number of degrees of freedom (i.e. the number of \(X_i\)), and \(\lambda\) which is related to the mean of the random variables \(X_i\) by
$$\lambda \;\; = \;\; \sum_{i = 1}^k \left(\frac{\mu_i}{\sigma_i}\right)^2$$
The noncentral chi-squared distribution is equivalent to a (central) chi-squared distribution with \(k + 2i\) degrees of freedom, where \(i\) is the value of a Poisson distributed random variable with parameter \(\lambda/2\). Thus, the probability density function is given by:
$$F(x,k,\lambda) \;\; = \;\; \sum_{i = 0}^\infty {\frac{e^{-\lambda/2} (\lambda/2)^i}{i!}} f(x,k+2i)$$
where the (central) chi-squared PDF \(f(x, k)\) is given by:
$$f(x, k) \;\; = \;\; \frac{(x/2)^{k/2} \; e^{-x/2}}{x \; \Gamma(k/2)} \quad for \;\; x \; > \; 0, \;\; else \;\; 0$$
where \(\Gamma (\cdot)\) is the gamma function. The above representation of \(F(x,k,\lambda)\) can be shown to be equivalent to the representation:
$$F(x,k,\lambda) \;\; = \;\; \frac{e^{-(\lambda+x)/2} \; (x/2)^{k/2}}{x} \; \sum_{i = 0}^\infty {\phi_i}$$
$$\phi_i \;\; = \;\; \frac{(\lambda x / 4)^i}{i! \; \Gamma(k/2 \;\; + \;\; i)}$$
Method
noncentralChievaluates the probability density function, \(F(x,k,\lambda)\), of a noncentral chi-squared random variable withdfdegrees of freedom and noncentrality parameteralam, corresponding to k =df, \(\lambda\) =alam, and x =chsq.Method
noncentralChievaluates the cumulative distribution function incorporating the above probability density function.With a noncentrality parameter of zero, the noncentral chi-squared distribution is the same as the central chi-squared distribution.
- Parameters:
chsq- adoublescalar value at which the function is to be evaluated.chsqmust be nonnegative.df- adoublescalar value representing the number of degrees of freedom.dfmust be positive.alam- adoublescalar value representing the noncentrality parameter.alammust be nonnegative.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value representing the probability density associated with a noncentral chi-squared random variable with valuechsq.
-
noncentralStudentsT
public static double noncentralStudentsT(double t, double df, double delta) throws Pdf.AltSeriesAccuracyLossException Evaluates the noncentral Student's t probability density function.The noncentral Student's t-distribution is a generalization of the Student's t-distribution. If \(w\) is a normally distributed random variable with unit variance and mean \(\delta\) and \(u\) is a chi-square random variable with \(\nu\) degrees of freedom that is statistically independent of \(w\), then $$T \;\; = \;\; w/\sqrt{u/\nu}$$ is a noncentral t-distributed random variable with \(\nu\) degrees of freedom and noncentrality parameter \(\delta\), that is, with \(\nu\) =
df, and \(\delta\) =delta. The probability density function for the noncentral t-distribution is: $$f(t,\nu,\delta) \;\; = \;\; \frac{\nu^{\nu/2} \; e^{-\delta^2/2}}{\sqrt{\pi} \; \Gamma(\nu/2) \; ( \nu + t^2 ) ^ {(\nu + 1)/2}} \; \sum_{i = 0}^\infty {\Phi_i}$$ where $$\Phi_i \;\; = \;\; \frac{\Gamma((\nu + i + 1)/2)}{i!} \; [\delta t]^i \; \left(\frac{2}{\nu + t^2}\right)^{i/2}$$ and t =t.For noncentrality parameter \(\delta\) = 0, the PDF reduces to the (central) Student's t PDF: $$f(t,\nu,0) \;\; = \;\; \frac{\Gamma((\nu+1)/2) \; \left( 1 \; + \; (t^2/\nu) \right)^{-(\nu+1)/2}}{\sqrt{\nu \pi} \; \Gamma(\nu/2)}$$ and, for t = 0, the PDF becomes: $$f(0,\nu,\delta) \;\; = \;\; \frac{\Gamma((\nu+1)/2) \; e^{-\delta^2/2}}{\sqrt{\nu \pi} \; \Gamma(\nu/2)}$$ Method
noncentralStudentsTevaluates the cumulative distribution function incorporating the above probability density function.- Parameters:
t- adoublevalue representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.df- adoublevalue representing the number of degrees of freedom.dfmust be positive.delta- adoublevalue representing the noncentrality parameter.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue representing the probability density associated with a noncentral Student's t random variable with valuet. - Throws:
Pdf.AltSeriesAccuracyLossException- is thrown when the magnitude of alternating series sum is too small relative to the sum of positive terms to permit a reliable accuracy.
-
noncentralF
public static double noncentralF(double f, double df1, double df2, double lambda) Evaluates the noncentral F probability density function (PDF).The noncentral F distribution is a generalization of the F distribution. If \(x\) is a noncentral chi-square random variable with noncentrality parameter \(\lambda\) and \(\nu_1\) degrees of freedom, and \(y\) is a chi-square random variable with \(\nu_2\) degrees of freedom which is statistically independent of \(X\), then $$F \;\; = \;\; (x/\nu_1)/(y/\nu_2)$$ is a noncentral F-distributed random variable whose PDF is given by: $$PDF(f, \nu_1, \nu_2, \lambda) \;\; = \;\; \Psi \; \sum_{k = 0}^\infty {\Phi_k} $$ where $$\Psi \;\; = \;\; \frac{ e^{-\lambda/2}(\nu_1 f)^{\nu_1/2}(\nu_2)^{\nu_2/2} } { f \; (\nu_1 f \; + \; \nu_2)^{(\nu_1 + \nu_2)/2} \; \Gamma(\nu_2/2) }$$ $$\Phi_k \;\; = \;\; \frac{ R^k \; \Gamma(\frac{\nu_1 + \nu_2}{2} \; + \; k) } { k! \; \Gamma(\frac{\nu_1}{2} \; + \; k) } $$ $$R \;\; = \;\; \frac{ \lambda \nu_1 f }{ 2 (\nu_1 f \; + \; \nu_2)} $$ where \(\Gamma (\cdot)\) is the gamma function, \(\nu_1\) =
df1, \(\nu_2\) =df2, \(\lambda\) =lambda, and f =f.With a noncentrality parameter of zero, the noncentral F distribution is the same as the F distribution.
The efficiency of the calculation of the above series is enhanced by:
- calculating each term \(\Phi_k\) in the series recursively in terms of either the term \(\Phi_{k-1}\) preceding it or the term \(\Phi_{k+1}\) following it, and
- initializing the sum with the largest series term and adding the subsequent terms in order of decreasing magnitude.
Special cases:
For \(R \;\; = \;\; \lambda f \;\; = \;\; 0\):
$$PDF(f, \nu_1, \nu_2, \lambda) \;\; = \;\; \Psi \; \Phi_0 \;\; = \;\; \Psi \; \frac{ \Gamma([\nu_1 + \nu_2]/2) }{ \Gamma(\nu_1/2) } $$For \(\lambda \;\; = \;\; 0\):
$$PDF(f, \nu_1, \nu_2, \lambda) \;\; = \;\; \frac{ (\nu_1 f)^{\nu_1/2} \; (\nu_2)^{\nu_2/2} \; \Gamma([\nu_1 + \nu_2]/2) } { f \; (\nu_1 f \; + \; \nu_2)^{(\nu_1 + \nu_2)/2} \; \Gamma(\nu_1/2) \; \Gamma(\nu_2/2) } $$For \(f \;\; = \;\; 0\):
$$PDF(f, \nu_1, \nu_2, \lambda) \;\; = \;\; \frac{{e^{ - \lambda /2} \;f^{\nu _1 /2\;\; - \;\;1} \;(\nu _1 /\nu _2 )^{\nu _1 /2} \;\Gamma ([\nu _1 \; + \;\nu _2 ]/2)}} {{\;\Gamma (\nu _1 /2)\;\Gamma (\nu _2 /2)}}$$ $$PDF(f, \nu_1, \nu_2, \lambda) \;\; = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 0 \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \mbox{if} \;\; \nu_1 \;\; > \;\; 2; \\ e^{-\lambda/2} \;\; \mbox{if} \;\; \nu_1 \;\; = \;\; 2; \\ \infty \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \mbox{if} \;\; \nu_1 \;\; \lt \;\; 2 \ \end{array} \right. $$- Parameters:
f- adoublevalue representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluated.fmust be nonnegative.df1- adoublevalue representing the number of numerator degrees of freedom.df1must be positive.df2- adoublevalue representing the number of denominator degrees of freedom.df2must be positive.lambda- adoublevalue representing the noncentrality parameter.lambdamust be nonnegative.- Returns:
- a
doublevalue representing the probability density associated with a noncentral F random variable with valuef.
-
Weibull
public static double Weibull(double x, double k, double lambda) Evaluates the Weibull probability density function. The probability density function of the Weibull distribution is $$f\left(x;\lambda,k\right)=\left\{\begin{array} {ll}\frac{k}{\lambda}\left(\frac{x}{\lambda}\right)^{k-1}e^{-\left(x/ \lambda\right)^k} & x\ge 0\\[5pt] 0 & x\lt 0\end{array}\right.$$ where \(k > 0\) is the shape parameter and \(\lambda >0\) is the scale parameter.- Parameters:
x- adouble, the argument at which the function is to be evaluatedk- adouble, the shape parameterlambda- adouble, the scale parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density function atxgiven the parameter values
-
logNormal
public static double logNormal(double x, double mu, double sigma) Evaluates the standard lognormal probability density function. $$f\left( x \right) = \frac{1}{x\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}} {e^{-\frac{ {(\ln{x}-\mu)}^2 }{2{\sigma}^2}} }$$- Parameters:
x- adouble,the value at which the function is to be evaluatedmu- adouble, the location parametersigma- adouble, the shape parameter.sigmamust be a positive.- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density function atx
-
extremeValue
public static double extremeValue(double x, double mu, double beta) Evaluates the extreme value probability density function.The extreme value distribution, also known as the Gumbel minimum distribution, is the limiting distribution of the minimum of a large number of continuous, identically distributed random variables. The probability density function of the extreme value distribution is $$f(x;\mu,\beta)=\frac{1}{\beta}e^{\frac{x-\mu}{\beta}}\exp\left(-e^{\frac{x-\mu}{\beta}}\right)$$ where \(\mu \in\mathbb{R}\) is the location parameter and \(\beta>0\) is the scale parameter.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the value at which the function is to be evaluated.mu- adouble, the location parameterbeta- adouble, the scale parameter. It must be positive.- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density function atx - See Also:
-
Rayleigh
public static double Rayleigh(double x, double sigma) Evaluates the Rayleigh probability density function.The Rayleigh probability density function with scale parameter \(\sigma >0\) is given by $$ f(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{x}{\sigma^2}\exp\left(-\frac{x^2}{2\sigma^2}\right) & x\ge0 \\ 0 & x=0 \end{array} \right. $$
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfsigma- adouble, the scale parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density function atxgiven the parameter value
-
continuousUniform
public static double continuousUniform(double x, double a, double b) Evaluates the continuous uniform probability density function.The probability density function of the continuous uniform distribution is $$f(x|a,b)=\left\{\begin{array}{lll}\frac{1}{b-a} & \mbox{for} & a\le x\le b \\ 0 & \mbox{for} & x \lt a \; \mbox{or} \; x\gt b \end{array}\right. $$ where (\( -\infty \lt a \lt b \lt \infty \)).
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfa- adouble, the lower parameter \(a\)b- adouble, the upper parameter \(b\)- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density atxgiven the parameter values
-
discreteUniform
public static double discreteUniform(int x, int n) Evaluates the discrete uniform probability density function.- Parameters:
x- anint, the value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdf.xshould be a value between the lower limit 0 and upper limitn.n- anint, the upper limit of the discrete uniform distribution- Returns:
- a
double, the probability that a discrete uniform random variable takes a value equal tox - See Also:
-
geometric
public static double geometric(int x, double p) Evaluates the geometric probability density (or mass) function.Given the probability of success \(p\) for a sequence of independent and identical trials, the probability of \(X = k \in {0,1,2,\ldots }\) failures until the first success is given by \(Pr[X=k]=(1-p)^k p \). The discrete random variable \(X\) is a geometric random variable with parameter \(p\).
- Parameters:
x- anint, the value at which to evaluate the probabilityp- adouble, the probability of success- Returns:
- a
double, the probability that a geometric random variable equalsx
-
logistic
public static double logistic(double x, double mu, double sigma) Evaluates the logistic probability density function.The probability density function of the logistic distribution is
$$f(x,\mu,\sigma)=\frac{e^{-(x-\mu)/\sigma}} {\sigma\left (1+e^{-(x-\mu)/\sigma} \right )^{2}}$$
where \(\mu\) is the location parameter and \(\sigma \gt 0\) is the scale parameter.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfmu- adouble, the value of the location parametersigma- adouble, the value of the scale parameter- Returns:
- a
double,the value of the probability density function atxgiven the parameters
-
Pareto
public static double Pareto(double x, double xm, double k) Evaluates the Pareto probability density function.The probability density function of the Pareto distribution is
$$f(x,x_m,k)=1-\frac{kx_m^{k}}{x^{k+1}}$$
where the scale parameter \(x_m>0\) and the shape parameter \(k>0\). The function is only defined for \(x \geq x_m\).
- Parameters:
x- adoublethe value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfxm- adouble, the scale parameterk- adouble, the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the probability density function atxgiven the parameters
-
logLogistic
public static double logLogistic(double x, double alpha, double beta) Evaluates the Log-logistic probability density function.The probability density function of the Log-logistic distribution is
$$f(x,\alpha,\beta)=\frac{\beta}{\alpha} \frac{\left( x/\alpha \right )^{\beta - 1}}{\left( 1 + \left( x/\alpha \right)^{\beta} \right)^2}$$
where \(\alpha \gt 0\) is the scale parameter and \(\beta \gt 0\) is the shape parameter.
- Parameters:
x- adouble, the strictly positive value (quantile) at which to evaluate the pdfalpha- adouble, the value of the scale parameterbeta- adouble, the value of the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
double, the value of the probability density function atxgiven the parameters
-
inverseGaussian
public static double inverseGaussian(double x, double mean, double lambda) Evaluates the inverse Gaussian probability density function. The probability density function for an inverse Gaussian distribution is given by $$f(x; \mu,\lambda) = \sqrt{\frac{\lambda}{2 \pi x^3}} \exp^{ -\frac{\lambda (x - \mu)^2}{2 \mu^2 x}} $$ where \(\mu > 0\) and \(\lambda > 0\) are the mean and shape of the random variable.- Parameters:
x- adoublestrictly positive scalar value representing the argument at which the function is to be evaluatedmean- adoublescalar value containing the meanlambda- adoublescalar value containing the shape parameter- Returns:
- a
doublecontaining the value of the probability density function atx
-
negativeBinomial
public static double negativeBinomial(int k, double r, double p) Evaluates the negative binomial probability density function. The negative binomial probability density function of a discrete random variable taking values$$k = 0, 1, 2,\ldots$$
is defined as$$\Pr \left( {X = k} \right) = \frac{\Gamma(k+r)}{k! \Gamma(r)} p^r (1-p)^k$$
where \(r > 0\), \(p \in [0,1]\), and \(\Gamma(a)\) is the complete Gamma function,$$\Gamma(a) = \int_0^\infty e^{-t}t^{a-1}dt$$
If \(r\) is an integer, an equivalent expression is$$\Pr \left( {X = k} \right) = {k+r-1 \choose r - 1} p^r (1-p)^k, \quad r =1, 2, \ldots $$
and in this case \(X\) can be interpreted as the number of failures before obtaining \(r\) successes in binomial trials with probability of success \(p\).- Parameters:
k- anint, the value of the discrete random variable. Ifris an integer, the number of failures beforersuccesses.r- adouble, the negative binomial parameter of the distribution. Ifris an integer, the number of successes.p- adoublescalar value representing the probability of success on each independent trial.- Returns:
- a
doublescalar value representing the probability that a negative binomial random variable takes a value equal tok.
-