Example 3: Integral of the entire real line
The integral 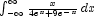 is computed and compared to its expected value. This integral is evaluated in Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (equation 3.417.1).
is computed and compared to its expected value. This integral is evaluated in Gradshteyn and Ryzhik (equation 3.417.1).
using System;
using Imsl.Math;
public class QuadratureEx3 : Quadrature.IFunction
{
public double F(double x)
{
return x / (4.0 * Math.Exp(x) + 9.0 * Math.Exp(-x));
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Quadrature q = new Quadrature();
Quadrature.IFunction fcn = new QuadratureEx3();
double result = q.Eval(fcn, Double.NegativeInfinity,
Double.PositiveInfinity);
double expect = System.Math.PI * System.Math.Log(1.5) / 12.0;
Console.Out.WriteLine("result = " + result);
Console.Out.WriteLine("expect = " + expect);
}
}
Output
result = 0.106150517076628
expect = 0.106150517076633
Link to C# source.
Reference
Gradshteyn, I. S. and I. M. Ryzhik (1965), Table of Integrals, Series, and Products
, Academic Press, New York.