Sparse Cholesky factorization of a matrix of type SparseMatrix.
For a list of all members of this type, see SparseCholesky Members.
System.Object
Imsl.Math.SparseCholesky
Thread Safety
Public static (Shared in Visual Basic) members of this type are safe for multithreaded operations. Instance members are not guaranteed to be thread-safe.
Remarks
Class SparseCholesky computes the Cholesky factorization of a sparse symmetric positive definite matrix A. This factorization can then be used to compute the solution of the linear system ![]() .
.
Typically, the solution of a large sparse positive definite system ![]() is done in 4 steps:
is done in 4 steps:
- In step one, an ordering algorithm is used to preserve sparsity in the Cholesky factor L of matrix A during the numerical factorization process. The new order can be described by a permutation matrix P.
- Step two consists of setting up the data structure for the Cholesky factor L, where
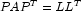 . This step is called the symbolic factorization phase of the computation. During symbolic factorization, only the sparsity pattern of sparse matrix A, i.e., the locations of the nonzero entries of matrix A are needed but not any of the elements themselves.
. This step is called the symbolic factorization phase of the computation. During symbolic factorization, only the sparsity pattern of sparse matrix A, i.e., the locations of the nonzero entries of matrix A are needed but not any of the elements themselves. - In step 3, the numerical factorization phase, the Cholesky factorization is done numerically.
- Step 4 is the solution phase. Here, the numerical solution, x, to the original system is obtained by solving the two triangular systems
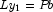 ,
, 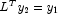 and the permutation
and the permutation 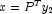 .
.
Class SparseCholesky realizes all four steps by algorithms described in George and Liu (1981). Especially, step one, is a realization of a minimum degree ordering algorithm. The numerical factorization in its standard form is based on a sparse compressed storage scheme. Alternatively, a multifrontal method can be used. The multifrontal method requires more storage but will be faster than the standard method in certain cases. The multifrontal method is based on the routines in Liu (1987). For a detailed description of this method, see Liu (1990), also Duff and Reid(1983, 1984), Ashcraft (1987) et al. (1987), and Liu (1986, 1989, 1992).The numerical factorization method can be specified by using the NumericFactorizationMethod property.
The Solve method will compute the symbolic and numeric factorizations if they have not already been computed or supplied by the user through
FactorSymbolically,
FactorNumerically,
SetNumericFactor, or
SetSymbolicFactor. These factorizations are retained for later use by the Solve method when different right-hand sides are to be solved.
There is a special situation where computations can be simplified. If an application generates different sparse symmetric positive definite coefficient matrices that all have the same sparsity pattern, then by using SetSymbolicFactor the symbolic factorization need only be computed once.
Requirements
Namespace: Imsl.Math
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll)
See Also
SparseCholesky Members | Imsl.Math Namespace | Example