Generate a pseudorandom number from a negative Binomial distribution.
Parameters
- rk
- A
doublewhich specifies the negative binomial parameter,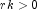 .
. - p
- A
doublewhich specifies the probability of success on each trial. It must be greater than machine precision and less than one.
Return Value
A int which specifies the pseudorandom number from a negative binomial distribution. If rk is an integer, the deviate can be thought of as the number of failures in a sequence of Bernoulli trials before rk successes occur.
Remarks
Method NextNegativeBinomial generates pseudorandom numbers from a negative Binomial distribution with parameters ![]() and
and ![]() .
. ![]() and
and ![]() must be positive and p must be less than 1. The probability function with (
must be positive and p must be less than 1. The probability function with (![]() and
and ![]() ) is
) is
for ![]() .
.
If r is an integer, the distribution is often called the Pascal distribution and can be thought of as modeling the length of a sequence of Bernoulli trials until r successes are obtained, where p is the probability of getting a success on any trial. In this form, the random variable takes values r, r + 1, ![]() and can be obtained from the negative binomial random variable defined above by adding r to the negative binomial variable. This latter form is also equivalent to the sum of r geometric random variables defined as taking values
and can be obtained from the negative binomial random variable defined above by adding r to the negative binomial variable. This latter form is also equivalent to the sum of r geometric random variables defined as taking values ![]() .
.
If rp/(1 - p) is less than 100 and ![]() is greater than the machine epsilon,
is greater than the machine epsilon, NextNegativeBinomial uses the inverse CDF technique; otherwise, for each negative binomial deviate, NextNegativeBinomial generates a gamma (r, p/(1 - p)) deviate y and then generates a Poisson deviate with parameter y.
See Also
Random Class | Imsl.Stat Namespace | Example