Performs a sign test.
For a list of all members of this type, see SignTest Members.
System.Object
Imsl.Stat.SignTest
Thread Safety
Public static (Shared in Visual Basic) members of this type are safe for multithreaded operations. Instance members are not guaranteed to be thread-safe.
Remarks
Class SignTest tests hypotheses about the proportion p of a population that lies below a value q, where p and q corresponds to the Percentage and Percentile properties, respectively. In continuous distributions, this can be a test that q is the 100 p-th percentile of the population from which x was obtained. To carry out testing, SignTest tallies the number of values above q in the number of positive differences ![]() for
for ![]() . The binomial probability of the number of values above q in the number of positive differences
. The binomial probability of the number of values above q in the number of positive differences ![]() for
for ![]() or more values above q is then computed using the proportion p and the sample size in
or more values above q is then computed using the proportion p and the sample size in x (adjusted for the missing observations and ties).
Hypothesis testing is performed as follows for the usual null and alternative hypotheses:
-
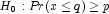 (the p-th quantile is at least q)
(the p-th quantile is at least q) 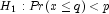
Reject
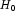 if probability is less than or equal to the significance level.
if probability is less than or equal to the significance level. -
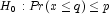 (the p-th quantile is at least q)
(the p-th quantile is at least q) 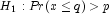
Reject
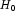 if probability is greater than or equal to 1 minus the significance level.
if probability is greater than or equal to 1 minus the significance level. -
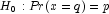 (the p-th quantile is q)
(the p-th quantile is q) 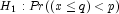 or
or 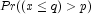
Reject
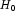 if probability is less than or equal to half the significance level or greater than or equal to 1 minus half the significance level.
if probability is less than or equal to half the significance level or greater than or equal to 1 minus half the significance level.
The assumptions are as follows:
- They are independent and identically distributed.
- Measurement scale is at least ordinal; i.e., an ordering less than, greater than, and equal to exists in the observations.
Many uses for the sign test are possible with various values of p and q. For example, to perform a matched sample test that the difference of the medians of y and z is 0.0, let p = 0.5, q = 0.0, and ![]() in matched observations y and z. To test that the median difference is c, let q = c.
in matched observations y and z. To test that the median difference is c, let q = c.
Requirements
Namespace: Imsl.Stat
Assembly: ImslCS (in ImslCS.dll)
See Also
SignTest Members | Imsl.Stat Namespace | Example 1 | Example 2