The LU Factorization of the sparse complex ![]() matrix
matrix
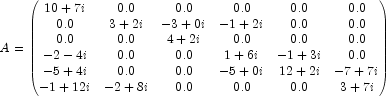
| row | column | value |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 10+7i |
| 1 | 1 | 3+2i |
| 1 | 2 | -3+0i |
| 1 | 3 | -1+2i |
| 2 | 2 | 4+2i |
| 3 | 0 | -2-4i |
| 3 | 3 | 1+6i |
| 3 | 4 | -1+3i |
| 4 | 0 | -5+4i |
| 4 | 3 | -5+0i |
| 4 | 4 | 12+2i |
| 4 | 5 | -7+7i |
| 5 | 0 | -1+12i |
| 5 | 1 | -2+8i |
| 5 | 5 | 3+7i |
Let
The LU factorization of ![]() is used to solve the complex sparse linear systems
is used to solve the complex sparse linear systems ![]() and
and ![]() with iterative refinement. The reciprocal pivot growth factor and the reciprocal condition number are also computed.
with iterative refinement. The reciprocal pivot growth factor and the reciprocal condition number are also computed.
using System;
using Imsl.Math;
public class ComplexSuperLUEx1
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int m;
ComplexSuperLU cslu;
double conditionNumber, recip_pivot_growth;
Complex[] sol = null;
double Ferr, Berr;
Complex[] b1 = { new Complex(3.0, 17.0), new Complex(-19.0, 5.0),
new Complex(6.0, 18.0), new Complex(-38.0, 32.0),
new Complex(-63.0, 49.0), new Complex(-57.0, 83.0)
};
Complex[] b2 = { new Complex(54.0, -112.0), new Complex(46.0, -58.0),
new Complex(12.0, 0.0), new Complex(5.0, -51.0),
new Complex(78.0, 34.0), new Complex(60.0, -94.0)
};
// Initialize input matrix A.
m = 6;
ComplexSparseMatrix a = new ComplexSparseMatrix(m, m);
a.Set(0, 0, new Complex(10.0, 7.0));
a.Set(1, 1, new Complex(3.0, 2.0));
a.Set(1, 2, new Complex(-3.0, 0.0));
a.Set(1, 3, new Complex(-1.0, 2.0));
a.Set(2, 2, new Complex(4.0, 2.0));
a.Set(3, 0, new Complex(- 2.0, -4.0));
a.Set(3, 3, new Complex(1.0, 6.0));
a.Set(3, 4, new Complex(-1.0, 3.0));
a.Set(4, 0, new Complex(-5.0, 4.0));
a.Set(4, 3, new Complex(-5.0, 0.0));
a.Set(4, 4, new Complex(12.0, 2.0));
a.Set(4, 5, new Complex(-7.0, 7.0));
a.Set(5, 0, new Complex(-1.0, 12.0));
a.Set(5, 1, new Complex(-2.0, 8.0));
a.Set(5, 5, new Complex(3.0, 7.0));
// Compute the sparse LU factorization of a
cslu = new ComplexSuperLU(a);
cslu.Equilibrate = false;
cslu.ColumnOrderingMethod =
ComplexSuperLU.ColumnOrdering.Natural;
cslu.PivotGrowth =true;
// Set option of iterative refinement
cslu.IterativeRefinement=true;
// Solve sparse system A*x = b1
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Solve sparse System A*x=b1");
Console.Out.WriteLine("==========================");
Console.Out.WriteLine();
sol = cslu.Solve(b1);
new PrintMatrix("Solution").Print(sol);
// Determine error bounds
Ferr = cslu.ForwardErrorBound;
Berr = cslu.RelativeBackwardError;
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Forward error bound: " + Ferr);
Console.Out.WriteLine("Relative backward error: " + Berr);
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine();
// Solve sparse system (A^H)*x = b2
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Solve sparse System (A^H)*x=b2");
Console.Out.WriteLine("==============================");
Console.Out.WriteLine();
sol = cslu.SolveConjugateTranspose(b2);
new PrintMatrix("Solution").Print(sol);
// Determine error bounds
Ferr = cslu.ForwardErrorBound;
Berr = cslu.RelativeBackwardError;
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Forward error bound: " + Ferr);
Console.Out.WriteLine("Relative backward error: " + Berr);
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine();
// Compute reciprocal pivot growth factor and condition number
recip_pivot_growth = cslu.ReciprocalPivotGrowthFactor;
conditionNumber = cslu.ConditionNumber;
Console.Out.WriteLine("Pivot growth factor and condition number");
Console.Out.WriteLine("========================================");
Console.Out.WriteLine();
Console.Out.WriteLine("Reciprocal pivot growth factor: " + recip_pivot_growth);
Console.Out.WriteLine("Reciprocal condition number: " + conditionNumber);
Console.Out.WriteLine();
}
}
Solve sparse System A*x=b1
==========================
Solution
0
0 1+1i
1 2+2i
2 3+3i
3 4+4i
4 5+5i
5 6+6i
Forward error bound: 2.83933305928053E-15
Relative backward error: 1.70803542250024E-16
Solve sparse System (A^H)*x=b2
==============================
Solution
0
0 1+1i
1 2+2.00000000000001i
2 3+3i
3 4+4i
4 5+5i
5 6+6i
Forward error bound: 8.54834098797111E-15
Relative backward error: 1.02977208081174E-16
Pivot growth factor and condition number
========================================
Reciprocal pivot growth factor: 0.799382716049383
Reciprocal condition number: 0.0700654479096751
Link to C# source.