splineInterp¶
Compute a spline interpolant.
Synopsis¶
splineInterp (xdata, fdata)
Required Arguments¶
- float
xdata[](Input) - Array with
ndatacomponents containing the abscissas of the interpolation problem. - float
fdata[](Input) - Array with
ndatacomponents containing the ordinates of the interpolation problem.
Return Value¶
The structure that represents the spline interpolant. If an interpolant
cannot be computed, then None is returned.
Optional Arguments¶
order, int (Input)The order of the spline subspace for which the knots are desired. This option is used to communicate the order of the spline subspace.
Default:
order= 4, i.e., cubic splinesknots, float (Input)This option requires the user to provide the knots.
Default: knots are selected by the function
splineKnotsusing its defaults.
Description¶
Given the data points x = xdata, f = fdata, and the number n =
ndata of elements in xdata and fdata, the default action of
splineInterp computes a cubic (\(k = 4\)) spline interpolant s to the
data using the default knot sequence generated by
splineKnots.
The optional argument order allows the user to choose the order of the
spline interpolant. The optional argument knots allows user
specification of knots.
The function splineInterp is based on the routine SPLINT by de Boor
(1978, p. 204).
First, splineInterp sorts the xdata vector and stores the result in
x. The elements of the fdata vector are permuted appropriately and
stored in f, yielding the equivalent data \((x_i, f_i)\) for
\(i = 0\) to \(n − 1\).
The following preliminary checks are performed on the data. We verify that
The first test checks to see that the abscissas are distinct. The second and third inequalities verify that a valid knot sequence has been specified.
In order for the interpolation matrix to be nonsingular, we also check \(t_{k-1} \leq x_i \leq t_n\) for \(i = 0\) to \(n − 1\). This first inequality in the last check is necessary since the method used to generate the entries of the interpolation matrix requires that the k possibly nonzero B-splines at \(x_i\),
be well-defined (that is, \(j − k + 1 \geq 0\)).
General conditions are not known for the exact behavior of the error in spline interpolation; however, if t and x are selected properly and the data points arise from the values of a smooth (say \(C^k\)) function f, i.e. \(f_j = f(x_j)\), then the error will behave in a predictable fashion. The maximum absolute error satisfies
where
For more information on this problem, see de Boor (1978, Chapter 13) and his reference.
The return value for this function is the structure Imsl_d_spline. This structure contains all the information to determine the spline (stored as a linear combination of B-splines) that is computed by this function. For example, the following code sequence evaluates this spline at x and returns the value in y.
y = cubSplineValue (x, sp, 0)
Three spline interpolants of order 2, 3, and 5 are plotted. These splines use the default knots.
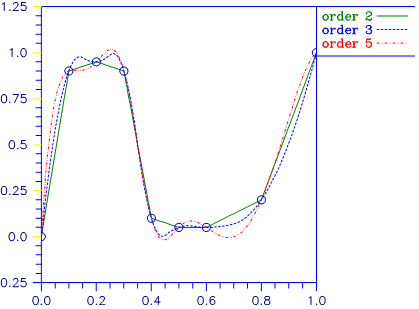
Figure 3.4 — Three Spline Interpolants
Examples¶
Example 1¶
In this example, a cubic spline interpolant to a function f is computed. The values of this spline are then compared with the exact function values. Since the default settings are used, the interpolant is determined by the “not-a-knot” condition (see de Boor 1978).
from __future__ import print_function
from numpy import *
from pyimsl.math.splineInterp import splineInterp
from pyimsl.math.splineValue import splineValue
# Define function
def F(x):
return sin(15.0 * x)
# Set up a grid
ndata = 11
xdata = empty(ndata)
fdata = empty(ndata)
for i in range(0, ndata):
xdata[i] = float(i) / (ndata - 1)
fdata[i] = F(xdata[i])
# Compute cubic spline interpolant
sp = splineInterp(xdata, fdata)
# Print results
print(" x F(x) Interpolant Error")
for i in range(0, 2 * ndata - 1):
x = float(i) / (2 * ndata - 2)
y = splineValue(x, sp)
print('%6.3f %10.3f %10.3f %10.4f' % (x, F(x), y, abs(F(x) - y)))
Output¶
x F(x) Interpolant Error
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.0000
0.050 0.682 0.809 0.1270
0.100 0.997 0.997 0.0000
0.150 0.778 0.723 0.0552
0.200 0.141 0.141 0.0000
0.250 -0.572 -0.549 0.0228
0.300 -0.978 -0.978 0.0000
0.350 -0.859 -0.843 0.0162
0.400 -0.279 -0.279 0.0000
0.450 0.450 0.441 0.0093
0.500 0.938 0.938 0.0000
0.550 0.923 0.903 0.0199
0.600 0.412 0.412 0.0000
0.650 -0.320 -0.315 0.0049
0.700 -0.880 -0.880 0.0000
0.750 -0.968 -0.938 0.0295
0.800 -0.537 -0.537 0.0000
0.850 0.183 0.148 0.0347
0.900 0.804 0.804 0.0000
0.950 0.994 1.086 0.0926
1.000 0.650 0.650 0.0000
Example 2¶
Recall that in the first example, a cubic spline interpolant to a function f is computed. The values of this spline are then compared with the exact function values. This example chooses to use a quadratic (\(k = 3\)) and a quintic \(k = 6\) spline interpolant to the data instead of the default values.
from __future__ import print_function
from numpy import *
from pyimsl.math.splineInterp import splineInterp
from pyimsl.math.splineValue import splineValue
# Define function
def F(x):
return sin(15.0 * x)
# Set up a grid
ndata = 11
xdata = empty(ndata)
fdata = empty(ndata)
for i in range(0, ndata):
xdata[i] = float(i) / (ndata - 1)
fdata[i] = F(xdata[i])
for order in range(3, 7, 3):
# Compute cubic spline interpolant
sp = splineInterp(xdata, fdata, order=order)
# Print results
print("\nThe order of the spline is: ", order)
print(" x F(x) Interpolant Error")
for i in range(int(ndata / 2), int(3 * ndata / 2)):
x = float(i) / (2 * ndata - 2)
y = splineValue(x, sp)
print('%6.3f %10.3f %10.3f %10.4f' % (x, F(x), y, abs(F(x) - y)))
Output¶
The order of the spline is: 3
x F(x) Interpolant Error
0.250 -0.572 -0.542 0.0299
0.300 -0.978 -0.978 0.0000
0.350 -0.859 -0.819 0.0397
0.400 -0.279 -0.279 0.0000
0.450 0.450 0.429 0.0210
0.500 0.938 0.938 0.0000
0.550 0.923 0.879 0.0433
0.600 0.412 0.412 0.0000
0.650 -0.320 -0.305 0.0149
0.700 -0.880 -0.880 0.0000
0.750 -0.968 -0.922 0.0459
The order of the spline is: 6
x F(x) Interpolant Error
0.250 -0.572 -0.573 0.0016
0.300 -0.978 -0.978 0.0000
0.350 -0.859 -0.856 0.0031
0.400 -0.279 -0.279 0.0000
0.450 0.450 0.448 0.0020
0.500 0.938 0.938 0.0000
0.550 0.923 0.922 0.0003
0.600 0.412 0.412 0.0000
0.650 -0.320 -0.322 0.0025
0.700 -0.880 -0.880 0.0000
0.750 -0.968 -0.959 0.0090
Warning Errors¶
IMSL_ILL_COND_INTERP_PROB |
The interpolation matrix is ill-conditioned. The solution might not be accurate. |
Fatal Errors¶
IMSL_DUPLICATE_XDATA_VALUES |
The xdata values must be distinct. |
IMSL_KNOT_MULTIPLICITY |
Multiplicity of the knots cannot exceed the order of the spline. |
IMSL_KNOT_NOT_INCREASING |
The knots must be nondecreasing. |
IMSL_KNOT_XDATA_INTERLACING |
The i-th smallest element of xdata (\(x_j\)) must satisfy \(t_j \leq x_j < t_{j+order}\) where t is the knot sequence. |
IMSL_XDATA_TOO_LARGE |
The array xdata must satisfy \(xdata_j \leq t_{ndata}\), for i = 1, …, ndata. |
IMSL_XDATA_TOO_SMALL |
The array xdata must satisfy \(xdata_j \geq t_{order-1}\), for i = 1, …, ndata. |