normalCdf¶
Evaluates the standard normal (Gaussian) distribution function.
Synopsis¶
normalCdf (x)
Required Arguments¶
- float
x(Input) - Point at which the normal distribution function is to be evaluated.
Return Value¶
The probability that a normal random variable takes a value less than or equal to x.
Description¶
The function normalCdf evaluates the distribution function, Φ, of a
standard normal (Gaussian) random variable; that is,
The value of the distribution function at the point x is the probability that the random variable takes a value less than or equal to x.
The standard normal distribution (for which normalCdf is the distribution
function) has mean of 0 and variance of 1. The probability that a normal
random variable with mean μ and variance \(\sigma^2\) is less than
y is given by normalCdf evaluated at \((y-\mu)/\sigma\).
\(\Phi(x)\) is evaluated by use of the complementary error function,
erfc. The relationship is:
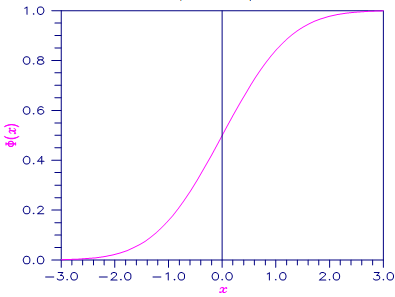
Figure 9.20 — Plot of Φ(x)
Example¶
Suppose X is a normal random variable with mean 100 and variance 225. This example finds the probability that X is less than 90 and the probability that X is between 105 and 110.
from __future__ import print_function
from numpy import *
from pyimsl.math.normalCdf import normalCdf
x1 = (90.0 - 100.0) / 15.0
p = normalCdf(x1)
print("The probability that X is less than 90 is %6.4f" % (p))
x1 = (105.0 - 100.0) / 15.0
x2 = (110.0 - 100.0) / 15.0
p = normalCdf(x2) - normalCdf(x1)
print("The probability that X is between 105 and 110 is %6.4f" % (p))
Output¶
The probability that X is less than 90 is 0.2525
The probability that X is between 105 and 110 is 0.1169